Abstract
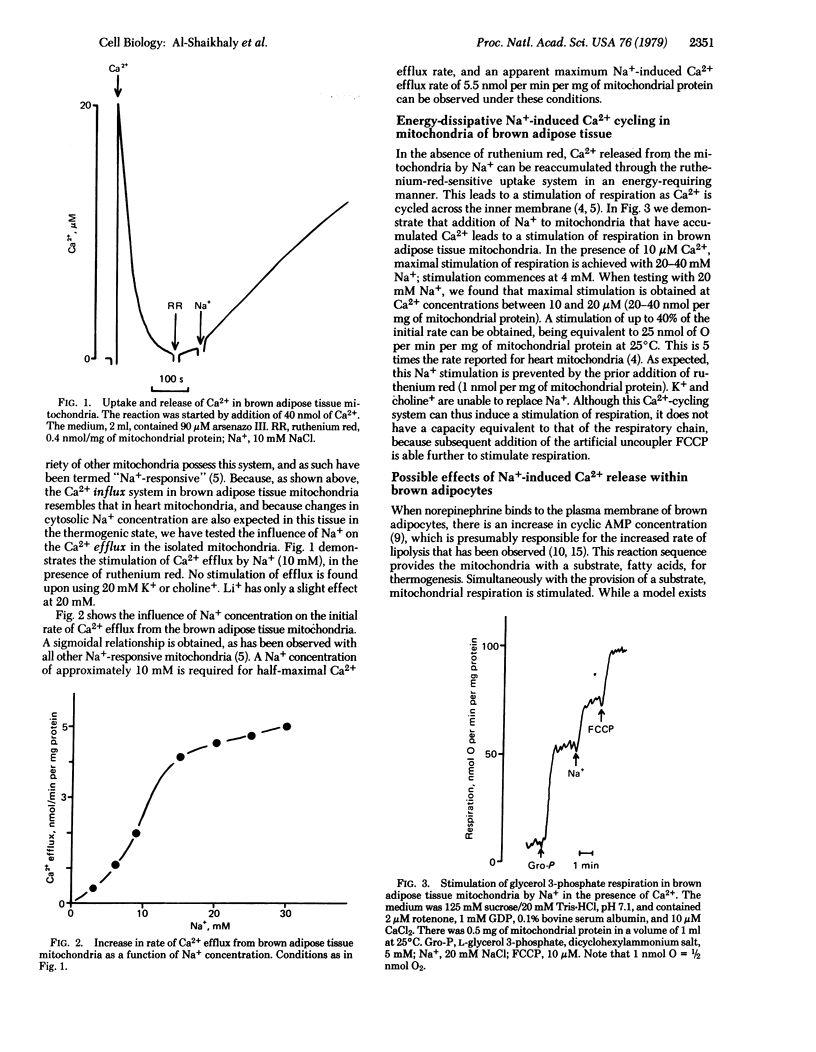
Coupled mitochondria of brown adipose tissue can accumulate Ca2+ if a substrate is present. The Ca2+ is released by addition of 20 mM Na+, but not by addition of K+ or choline +. Energy-dissipating Na+-induced Ca2+ cycling occurs maximally with 20 mM Na+ and 10 microM Ca2+. In brown adipocytes, the Ca2+ ionophore A23187 and the Na+ ionophore monensin increase respiration if substrate is added, and incubation in a low-Na+ buffer decreases norepinephrine-induced respiration. Thus Na+-induced Ca2+ release takes place in brown adipose tissue; released Ca2+ could have a regulatory or thermogenic role or both.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bieber L. L., Pettersson B., Lindberg O. Studies on norepinephrine-induced efflux of free fatty acid from hamster brown-adipose-tissue cells. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Oct 15;58(2):375–381. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb02384.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cannon B., Sundin U., Romert L. Palmitoyl coenzyme A: a possible physiological regulator of nucleotide binding to brown adipose tissue mitochondria. FEBS Lett. 1977 Feb 15;74(1):43–46. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)80748-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cannon B., Vogel G. The mitochondrial ATPase of brown adipose tissue. Purification and comparison with the mitochondrial ATPase from beef heart. FEBS Lett. 1977 Apr 15;76(2):284–289. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)80169-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carafoli E., Tiozzo R., Lugli G., Crovetti F., Kratzing C. The release of calcium from heart mitochondria by sodium. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 1974 Aug;6(4):361–371. doi: 10.1016/0022-2828(74)90077-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christiansen E. N. Calcium uptake and its effect on respiration and phosphorylation in mitochondria from brown adipose tissue. Eur J Biochem. 1971 Mar 11;19(2):276–282. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1971.tb01315.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crompton M., Moser R., Lüdi H., Carafoli E. The interrelations between the transport of sodium and calcium in mitochondria of various mammalian tissues. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Jan 2;82(1):25–31. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb11993.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GORNALL A. G., BARDAWILL C. J., DAVID M. M. Determination of serum proteins by means of the biuret reaction. J Biol Chem. 1949 Feb;177(2):751–766. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Girardier L., Seydoux J., Clausen T. Membrane potential of brown adipose tissue. A suggested mechanism for the regulation of thermogenesis. J Gen Physiol. 1968 Dec;52(6):925–940. doi: 10.1085/jgp.52.6.925. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris E. J. The uptake and release of calcium by heart mitochondria. Biochem J. 1977 Dec 15;168(3):447–456. doi: 10.1042/bj1680447. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heaton G. M., Wagenvoord R. J., Kemp A., Jr, Nicholls D. G. Brown-adipose-tissue mitochondria: photoaffinity labelling of the regulatory site of energy dissipation. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Jan 16;82(2):515–521. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12045.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herd P. A., Hammond R. P., Hamolsky M. W. Sodium pump activity during norepinephrine-stimulated respiration in brown adipocytes. Am J Physiol. 1973 Jun;224(6):1300–1304. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1973.224.6.1300. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herd P. A., Horwitz B. A., Smith R. E. Norepinephrine-sensitive Na+-K+ ATPase activity in brown adipose tissue. Experientia. 1970 Aug 15;26(8):825–826. doi: 10.1007/BF02114197. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hittelman K. J., Lindberg O., Cannon B. Oxidative phosphorylation and compartmentation of fatty acid metabolism in brown fat mitochondria. Eur J Biochem. 1969 Nov;11(1):183–192. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1969.tb00759.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horowitz J. M., Horwitz B. A., Smith R. E. Effect in vivo of norepinephrine on the membrane resistance of brown fat cells. Experientia. 1971 Dec 15;27(12):1419–1421. doi: 10.1007/BF02154265. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz B. A. Ouabain-sensitive component of brown fat thermogenesis. Am J Physiol. 1973 Feb;224(2):352–355. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1973.224.2.352. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobus W. E., Tiozzo R., Lugli G., Lehninger A. L., Carafoli E. Aspects of energy-linked calcium accumulation by rat heart mitochondria. J Biol Chem. 1975 Oct 10;250(19):7863–7870. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholls D. G. The bioenergetics of brown adipose tissue mitochondria. FEBS Lett. 1976 Jan 15;61(2):103–110. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(76)81014-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson N. O., Belfrage P. Effects of acetate, acetaldehyde, and ethanol on lipolysis in isolated rat adipocytes. J Lipid Res. 1978 Aug;19(6):737–411. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pettersson B., Vallin I. Norepinephrine-induced shift in levels of adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate and ATP parallel to increased respiratory rate and lipolysis in isolated hamster brown-fat cells. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Feb 16;62(2):383–390. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10170.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vasington F. D., Gazzotti P., Tiozzo R., Carafoli E. The effect of ruthenium red on Ca 2+ transport and respiration in rat liver mitochondria. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Jan 21;256(1):43–54. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(72)90161-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


