Abstract
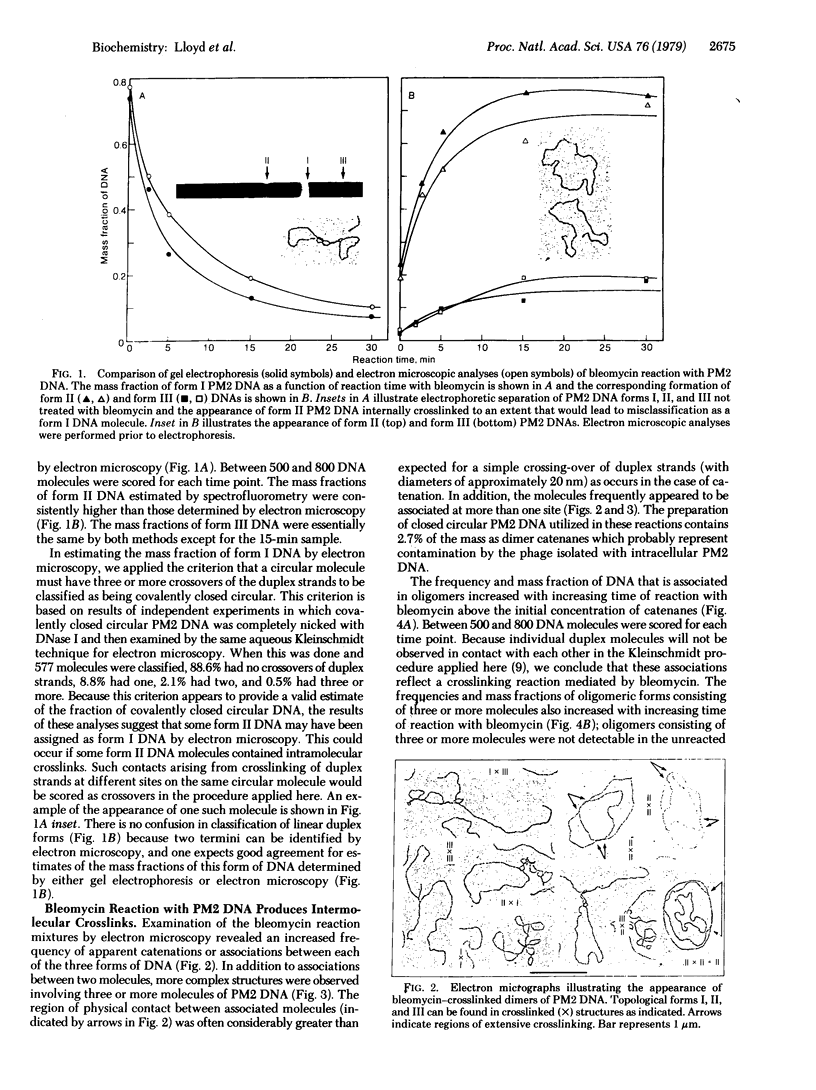
Reaction of covalently closed circular PM2 bacteriophage DNA with the anticancer drug bleomycin produces nicked circular (form II) and linear duplex (form III) DNA [Lloyd, R.S., Haidle, C.W. & Robberson, D.L. (1978) Biochemistry 17, 1890-1896]. As the reaction proceeds, the frequencies of both form II and form III DNA increase and, concomitantly, an increasing fraction of the DNA mass is found to be in crosslinked structures. Approximately 16% of the PM2 DNA mass is found to be crosslinked after 30 min of reaction with bleomycin at 0.5 microgram/ml. The proportion of each form found in any given crosslinked structure is directly related to the concentration of uncrosslinked (monomeric) forms. Multiple sites of crosslinking occur, and these frequently extend over a region of approximately 500 nucleotide pairs. The intermolecular crosslinked bonds are dissociated by extensive dialysis or by the addition of salt at high concentration (0.8 M NaCl), as would be expected if the bonds were noncovalent. Because intramolecular covalent crosslinks between complementary strands are not detected, it is suggested that intermolecular crosslinks are formed by noncovalent association of bleomycin molecules bound to each of the forms of DNA.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cole R. S. Light-induced cross-linking of DNA in the presence of a furocoumarin (psoralen). Studies with phage lambda, Escherichia coli, and mouse leukemia cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Sep 17;217(1):30–39. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(70)90119-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Andrea A. D., Haseltine W. A. Sequence specific cleavage of DNA by the antitumor antibiotics neocarzinostatin and bleomycin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Aug;75(8):3608–3612. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.8.3608. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis R. W., Davidson N. Electron-microscopic visualization of deletion mutations. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 May;60(1):243–250. doi: 10.1073/pnas.60.1.243. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GEIDUSCHEK E. P. "Reversible" DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1961 Jul 15;47:950–955. doi: 10.1073/pnas.47.7.950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haidle C. W. Fragmentation of deoxyribonucleic acid by bleomycin. Mol Pharmacol. 1971 Nov;7(6):645–652. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haidle C. W., Weiss K. K., Kuo M. T. Release of free bases from deoxyribonucleic acid after reaction with bleomycin. Mol Pharmacol. 1972 Sep;8(5):531–537. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- IYER V. N., SZYBALSKI W. A MOLECULAR MECHANISM OF MITOMYCIN ACTION: LINKING OF COMPLEMENTARY DNA STRANDS. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1963 Aug;50:355–362. doi: 10.1073/pnas.50.2.355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lloyd R. S., Haidle C. W., Hewitt R. R. Bleomycin-induced alkaline-labile damage and direct strand breakage of PM2 DNA. Cancer Res. 1978 Oct;38(10):3191–3196. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lloyd R. S., Haidle C. W., Robberson D. L. Bleomycin-specific fragmentation of double-stranded DNA. Biochemistry. 1978 May 16;17(10):1890–1896. doi: 10.1021/bi00603a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller W. E., Yamazaki Z., Breter H. J., Zahn R. K. Action of bleomycin on DNA and RNA. Eur J Biochem. 1972 Dec 18;31(3):518–525. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1972.tb02560.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Povirk L. F., Wübter W., Köhnlein W., Hutchinson F. DNA double-strand breaks and alkali-labile bonds produced by bleomycin. Nucleic Acids Res. 1977 Oct;4(10):3573–3580. doi: 10.1093/nar/4.10.3573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salditt M., Braunstein S. N., Camerini-Otero R. D., Franklin R. M. Structure and synthesis of a lipid-containing bacteriophage. X. Improved techniques for the purification of bacteriophage PM2. Virology. 1972 Apr;48(1):259–262. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(72)90133-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stüber D., Bujard H. Electron microscopy of DNA: determination of absolute molecular weights and linear density. Mol Gen Genet. 1977 Sep 9;154(3):299–303. doi: 10.1007/BF00571286. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]