Abstract
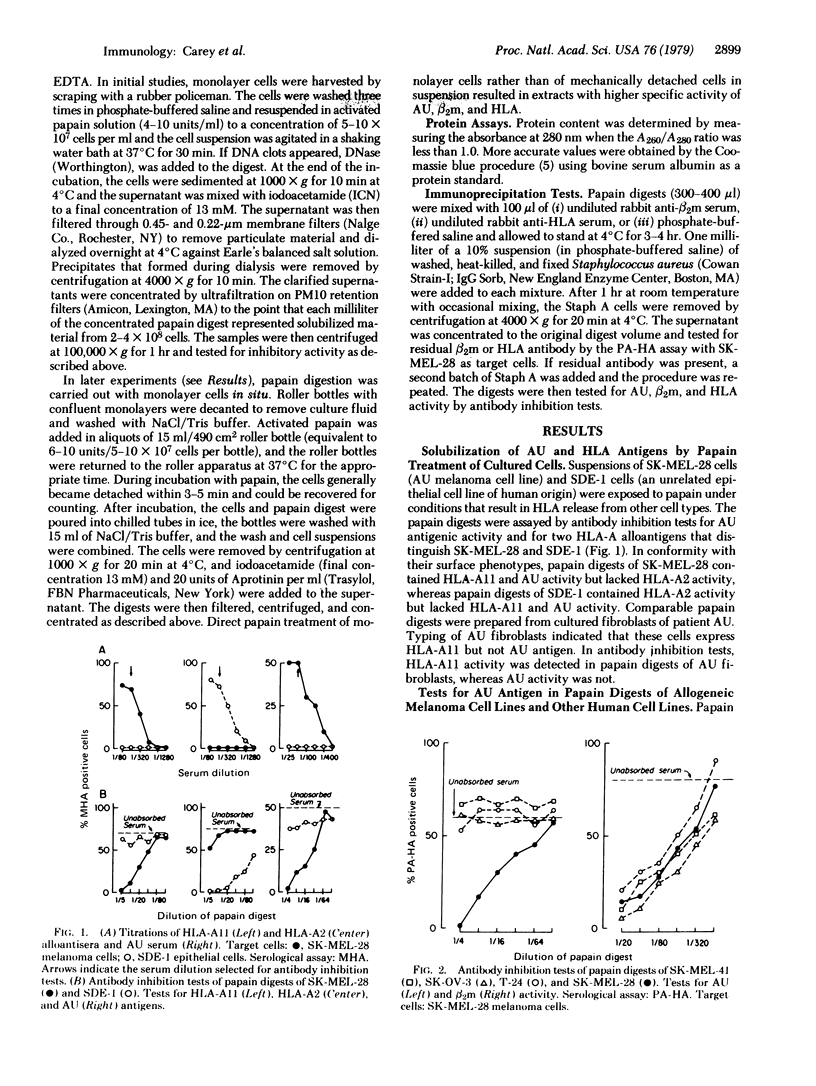
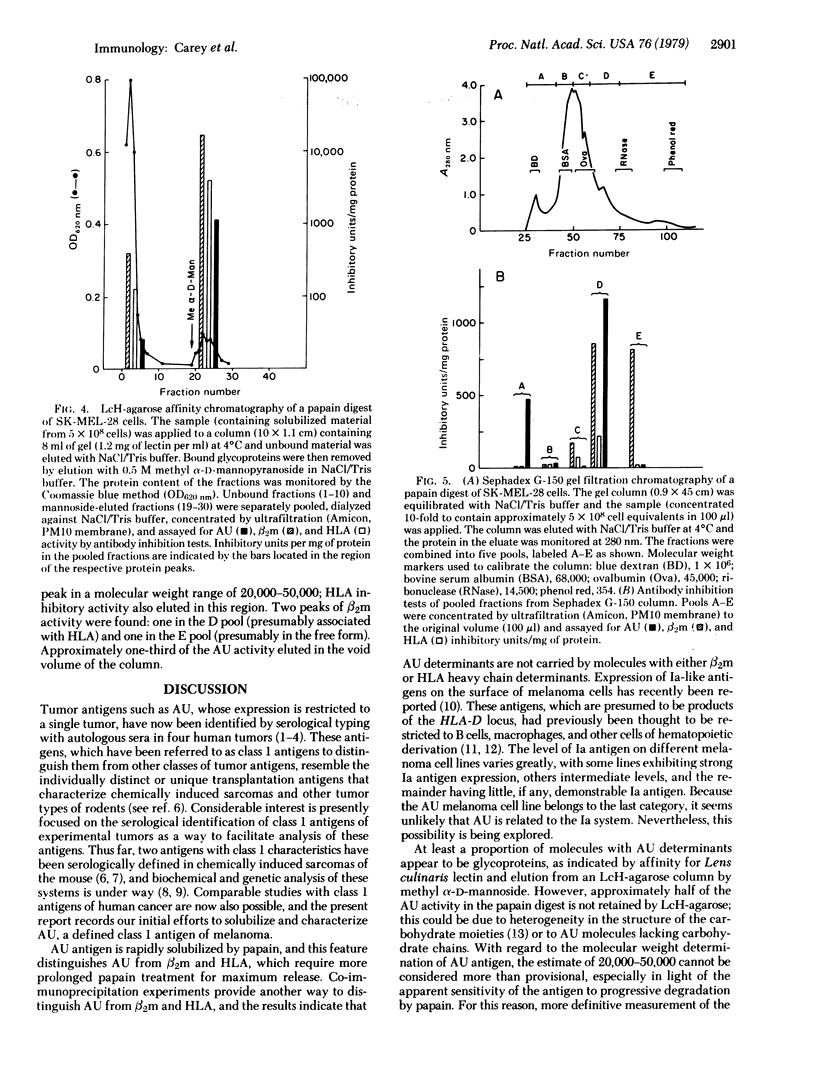
AU antigen is defined by reactions of sera from patient AU with cell-surface antigens of cultured autologous melanoma cells (SK-MEL-28). Past studies established that no available cell type other than AU melanoma expressed AU antigen. By use of antibody inhibition tests for antigen detection, limited papain digestion of AU melanoma cells was found to result in the solubilization of AU antigen along with beta2-microglobulin (beta 2m) and HLA allogeneic and xenogeneic specificities. Comparable papain treatment of other melanoma and non-melanoma cell lines solubilized beta 2m and HLA, but did not result in the release of antigen with AU reactivity. Maximum yield of AU antigen from AU melanoma cells was obtained after very short (5-15 min) digestion times in contrast to the more prolonged proteolysis required for maximum HLA and beta 2m release. AU antigen was not immunoprecipitated by rabbit antiserum against beta 2m or HLA under conditions leading to partial or complete removal of beta 2m and HLA. At least a proportion of the molecules with AU determinants appear to be glycoproteins, as indicated by specific affinity for Lens culinaris hemagglutinin (LcH). After affinity chromatography on LcH-agarose, the specific activity of AU antigen was increased 50-fold. As determined by gel filtration chromatography, AU antigen has a molecular weight in the range of 20,000-50,000.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Carey T. E., Takahashi T., Resnick L. A., Oettgen H. F., Old L. J. Cell surface antigens of human malignant melanoma: mixed hemadsorption assays for humoral immunity to cultured autologous melanoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Sep;73(9):3278–3282. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.9.3278. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLeo A. B., Jay G., Appella E., Dubois G. C., Law L. W., Old L. J. Detection of a transformation-related antigen in chemically induced sarcomas and other transformed cells of the mouse. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 May;76(5):2420–2424. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.5.2420. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLeo A. B., Shiku H., Takahashi T., John M., Old L. J. Cell surface antigens of chemically induced sarcomas of the mouse. I. Murine leukemia virus-related antigens and alloantigens on cultured fibroblasts and sarcoma cells: description of a unique antigen on BALB/c Meth A sarcoma. J Exp Med. 1977 Sep 1;146(3):720–734. doi: 10.1084/jem.146.3.720. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lloyd K. O. The preparation of two insoluble forms of the phytohemagglutinin, concanavalin A, and their interactions with polysaccharides and glycoproteins. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1970 Apr;137(2):460–468. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(70)90463-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Natori T., Law L. W., Appella E. Biological and biochemical properties of Nonidet P40-solubilized and partially purified tumor-specific antigens of the transplantation type from plasma membranes of a methylcholanthrene-induced sarcoma. Cancer Res. 1977 Sep;37(9):3406–3413. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfreundschuh M., Shiku H., Takahashi T., Ueda R., Ransohoff J., Oettgen H. F., Old L. J. Serological analysis of cell surface antigens of malignant human brain tumors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Oct;75(10):5122–5126. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.10.5122. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sedmak J. J., Grossberg S. E. A rapid, sensitive, and versatile assay for protein using Coomassie brilliant blue G250. Anal Biochem. 1977 May 1;79(1-2):544–552. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90428-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiku H., Takahashi T., Oettgen H. F. Cell surface antigens of human malignant melanoma. II. Serological typing with immune adherence assays and definition of two new surface antigens. J Exp Med. 1976 Oct 1;144(4):873–881. doi: 10.1084/jem.144.4.873. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiku H., Takahashi T., Resnick L. A., Oettgen H. F., Old L. J. Cell surface antigens of human malignant melanoma. III. Recognition of autoantibodies with unusual characteristics. J Exp Med. 1977 Mar 1;145(3):784–789. doi: 10.1084/jem.145.3.784. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winchester R. J., Ross G. D., Jarowski C. I., Wang C. Y., Halper J., Broxmeyer H. E. Expression of Ia-like antigen molecules on human granulocytes during early phases of differentiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Sep;74(9):4012–4016. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.9.4012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winchester R. J., Wang C. Y., Gibofsky A., Kunkel H. G., Lloyd K. O., Old L. J. Expression of Ia-like antigens on cultured human malignant melanoma cell lines. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Dec;75(12):6235–6239. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.12.6235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winchester R. J., Wang C. Y., Halper J., Hoffman T. Studies with B-cell allo- and hetero-antisera: parallel reactivity and special properties. Scand J Immunol. 1976;5(6-7):745–757. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1976.tb03024.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


