Abstract
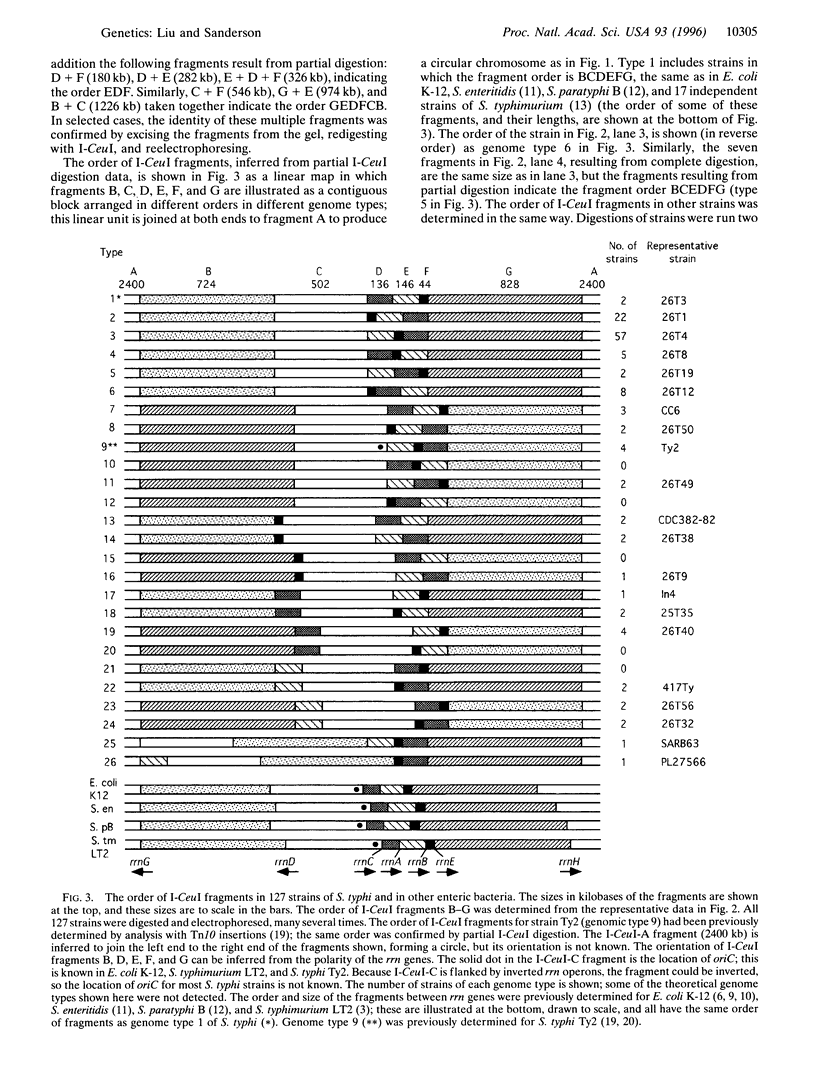
Gene order in the chromosomes of Escherichia coli K-12 and Salmonella typhimurium LT2, and in many other species of Salmonella, is strongly conserved, even though the genera diverged about 160 million years ago. However, partial digestion of chromosomal DNA of Salmonella typhi, the causal organism of typhoid fever, with the endonuclease I-CeuI followed by separation of the DNA fragments by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis showed that the chromosomes of independent wild-type isolates of S. typhi are rearranged due to homologous recombination between the seven rrn genes that code for ribosomal RNA. The order of genes within the I-CeuI fragments is largely conserved, but the order of the fragments on the chromosome is rearranged. Twenty-one different orders of the I-CeuI fragments were detected among the 127 wild-type strains we examined. Duplications and deletions were not found, but transpositions and inversions were common. Transpositions of I-CeuI fragments into sites that do not change their distance from the origin of replication (oriC) are frequently detected among the wild-type strains, but transpositions that move the fragments much further from oriC were rare. This supports the gene dosage hypothesis that genes at different distances from oriC have different gene dosages and, hence, different gene expression, and that during evolution genes become adapted to their specific location; thus, cells with changes in gene location due to transpositions may be less fit. Therefore, gene dosage may be one of the forces that conserves gene order, although its effects seem less strong in S. typhi than in other enteric bacteria. However, both the gene dosage and the genomic balance hypotheses, the latter of which states that the origin (oriC) and terminus (TER) of replication must be separated by 180 degrees C, need further investigation.
Full text
PDF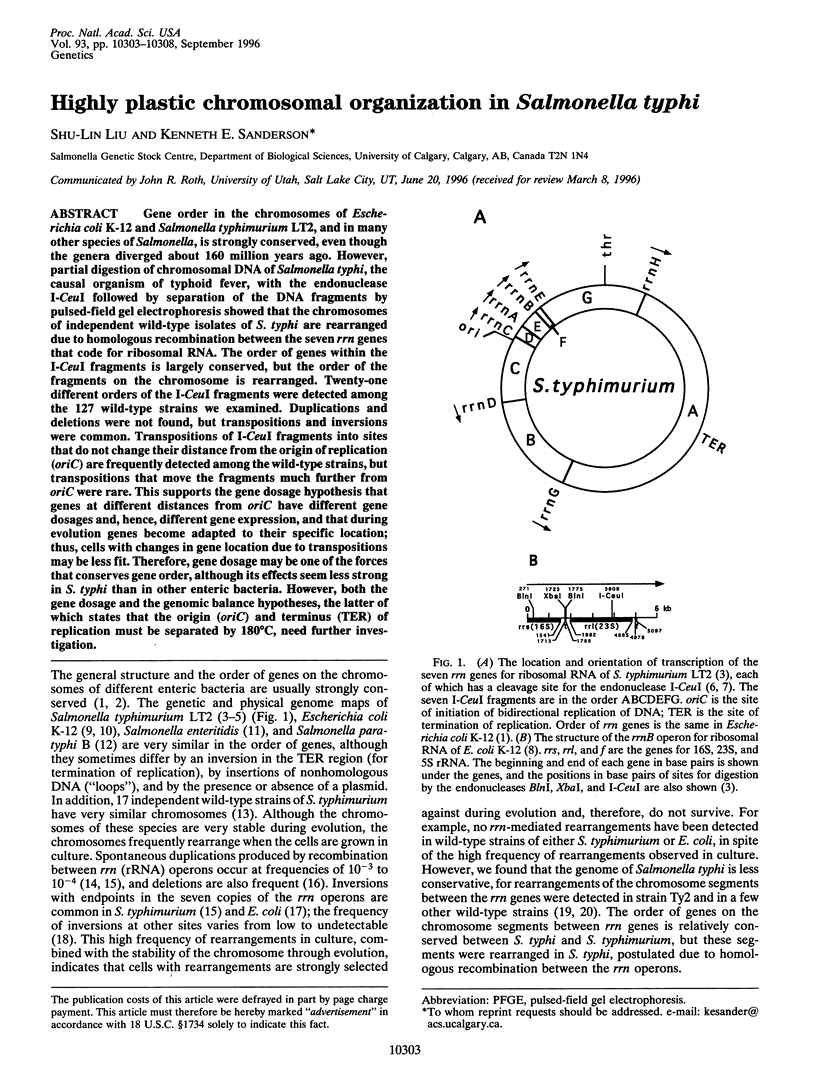




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson R. P., Roth J. R. Gene duplication in bacteria: alteration of gene dosage by sister-chromosome exchanges. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1979;43(Pt 2):1083–1087. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1979.043.01.120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bachmann B. J. Linkage map of Escherichia coli K-12, edition 8. Microbiol Rev. 1990 Jun;54(2):130–197. doi: 10.1128/mr.54.2.130-197.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beltran P., Plock S. A., Smith N. H., Whittam T. S., Old D. C., Selander R. K. Reference collection of strains of the Salmonella typhimurium complex from natural populations. J Gen Microbiol. 1991 Mar;137(3):601–606. doi: 10.1099/00221287-137-3-601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brosius J., Dull T. J., Sleeter D. D., Noller H. F. Gene organization and primary structure of a ribosomal RNA operon from Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1981 May 15;148(2):107–127. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90508-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crosa J. H., Brenner D. J., Ewing W. H., Falkow S. Molecular relationships among the Salmonelleae. J Bacteriol. 1973 Jul;115(1):307–315. doi: 10.1128/jb.115.1.307-315.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelman R., Levine M. M. Summary of an international workshop on typhoid fever. Rev Infect Dis. 1986 May-Jun;8(3):329–349. doi: 10.1093/clinids/8.3.329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fonstein M., Haselkorn R. Physical mapping of bacterial genomes. J Bacteriol. 1995 Jun;177(12):3361–3369. doi: 10.1128/jb.177.12.3361-3369.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill C. W., Combriato G. Genetic duplications induced at very high frequency by ultraviolet irradiation in Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1973 Dec 31;127(3):197–214. doi: 10.1007/BF00333760. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill C. W., Gray J. A. Effects of chromosomal inversion on cell fitness in Escherichia coli K-12. Genetics. 1988 Aug;119(4):771–778. doi: 10.1093/genetics/119.4.771. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill C. W., Harnish B. W. Inversions between ribosomal RNA genes of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Nov;78(11):7069–7072. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.11.7069. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill C. W., Harnish B. W. Transposition of a chromosomal segment bounded by redundant rRNA genes into other rRNA genes in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1982 Feb;149(2):449–457. doi: 10.1128/jb.149.2.449-457.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krawiec S., Riley M. Organization of the bacterial chromosome. Microbiol Rev. 1990 Dec;54(4):502–539. doi: 10.1128/mr.54.4.502-539.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Minor L. Typing of Salmonella species. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 1988 Apr;7(2):214–218. doi: 10.1007/BF01963091. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu S. L., Hessel A., Cheng H. Y., Sanderson K. E. The XbaI-BlnI-CeuI genomic cleavage map of Salmonella paratyphi B. J Bacteriol. 1994 Feb;176(4):1014–1024. doi: 10.1128/jb.176.4.1014-1024.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu S. L., Hessel A., Sanderson K. E. Genomic mapping with I-Ceu I, an intron-encoded endonuclease specific for genes for ribosomal RNA, in Salmonella spp., Escherichia coli, and other bacteria. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jul 15;90(14):6874–6878. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.14.6874. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu S. L., Hessel A., Sanderson K. E. The XbaI-BlnI-CeuI genomic cleavage map of Salmonella enteritidis shows an inversion relative to Salmonella typhimurium LT2. Mol Microbiol. 1993 Nov;10(3):655–664. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1993.tb00937.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu S. L., Hessel A., Sanderson K. E. The XbaI-BlnI-CeuI genomic cleavage map of Salmonella typhimurium LT2 determined by double digestion, end labelling, and pulsed-field gel electrophoresis. J Bacteriol. 1993 Jul;175(13):4104–4120. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.13.4104-4120.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu S. L., Sanderson K. E. A physical map of the Salmonella typhimurium LT2 genome made by using XbaI analysis. J Bacteriol. 1992 Mar;174(5):1662–1672. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.5.1662-1672.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu S. L., Sanderson K. E. Genomic cleavage map of Salmonella typhi Ty2. J Bacteriol. 1995 Sep;177(17):5099–5107. doi: 10.1128/jb.177.17.5099-5107.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu S. L., Sanderson K. E. I-CeuI reveals conservation of the genome of independent strains of Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1995 Jun;177(11):3355–3357. doi: 10.1128/jb.177.11.3355-3357.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu S. L., Sanderson K. E. Rearrangements in the genome of the bacterium Salmonella typhi. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Feb 14;92(4):1018–1022. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.4.1018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu S. L., Sanderson K. E. The chromosome of Salmonella paratyphi A is inverted by recombination between rrnH and rrnG. J Bacteriol. 1995 Nov;177(22):6585–6592. doi: 10.1128/jb.177.22.6585-6592.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maher K. O., Morris J. G., Jr, Gotuzzo E., Ferreccio C., Ward L. R., Benavente L., Black R. E., Rowe B., Levine M. M. Molecular techniques in the study of Salmonella typhi in epidemiologic studies in endemic areas: comparison with Vi phage typing. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1986 Jul;35(4):831–835. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1986.35.831. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall P., Davis T. B., Lemieux C. The I-CeuI endonuclease: purification and potential role in the evolution of Chlamydomonas group I introns. Eur J Biochem. 1994 Mar 15;220(3):855–859. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1994.tb18688.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moshitch S., Doll L., Rubinfeld B. Z., Stocker B. A., Schoolnik G. K., Gafni Y., Frankel G. Mono- and bi-phasic Salmonella typhi: genetic homogeneity and distinguishing characteristics. Mol Microbiol. 1992 Sep;6(18):2589–2597. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb01436.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Popoff M. Y., Bockemühl J., McWhorter-Murlin A. Supplement 1992 (no. 36) to the Kauffmann-White scheme. Res Microbiol. 1993 Jul-Aug;144(6):495–498. doi: 10.1016/0923-2508(93)90058-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeves M. W., Evins G. M., Heiba A. A., Plikaytis B. D., Farmer J. J., 3rd Clonal nature of Salmonella typhi and its genetic relatedness to other salmonellae as shown by multilocus enzyme electrophoresis, and proposal of Salmonella bongori comb. nov. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Feb;27(2):313–320. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.2.313-320.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanderson K. E. Genetic relatedness in the family Enterobacteriaceae. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1976;30:327–349. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.30.100176.001551. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanderson K. E., Hessel A., Rudd K. E. Genetic map of Salmonella typhimurium, edition VIII. Microbiol Rev. 1995 Jun;59(2):241–303. doi: 10.1128/mr.59.2.241-303.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanderson K. E., Stocker B. A. Gene rfaH, which affects lipopolysaccharide core structure in Salmonella typhimurium, is required also for expression of F-factor functions. J Bacteriol. 1981 May;146(2):535–541. doi: 10.1128/jb.146.2.535-541.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmid M. B., Roth J. R. Gene location affects expression level in Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1987 Jun;169(6):2872–2875. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.6.2872-2875.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selander R. K., Beltran P., Smith N. H., Helmuth R., Rubin F. A., Kopecko D. J., Ferris K., Tall B. D., Cravioto A., Musser J. M. Evolutionary genetic relationships of clones of Salmonella serovars that cause human typhoid and other enteric fevers. Infect Immun. 1990 Jul;58(7):2262–2275. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.7.2262-2275.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zawadzki P., Cohan F. M. The size and continuity of DNA segments integrated in Bacillus transformation. Genetics. 1995 Dec;141(4):1231–1243. doi: 10.1093/genetics/141.4.1231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



