Abstract
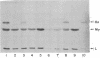
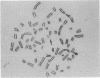
We have studied somatic cell hybrids between P3x63Ag8 mouse myeloma cells deficient in hypoxanthine phosphoribosyltransferase (EC 2.4.2.8) and either human peripheral lymphocytes or human lymphoblastoid or myeloma cells for the production of human immunoglobulin chains and for the expression of enzyme markers assigned to each of the different human chromosomes. Human chromosome 14 was the only human chromosome present in all independent hybrids producing mu, gamma, and alpha human heavy chains. In two of the independent hybrids that produced human heavy chains, human chromosome 14 was the only human chromosome present in the hybrid cells. Loss of human chromosome 14 from these hybrids resulted in the concomitant loss of their ability to produce human immunoglobulin heavy chains. In view of these results, we conclude that the genes for human immunoglobulin heavy chains are located on human chromosome 14 in immunoglobulin-producing human cells.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bobrow M., Cross J. Differential staining of human and mouse chromosomes in interspecific cell hybrids. Nature. 1974 Sep 6;251(5470):77–79. doi: 10.1038/251077a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner W. M., Laskey R. A. A film detection method for tritium-labelled proteins and nucleic acids in polyacrylamide gels. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jul 1;46(1):83–88. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03599.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chern C. J., Croce C. M. Assignment of the structural gene for human beta glucuronidase to chromosome 7 and tetrameric association of subunits in the enzyme molecule. Am J Hum Genet. 1976 Jul;28(4):350–356. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coffino P., Knowles B., Nathenson S. G., Scharff M. D. Suppression of immunoglobulin synthesis by cellular hybridization. Nat New Biol. 1971 May 19;231(20):87–90. doi: 10.1038/newbio231087a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Croce C. M. Assignment of the integration site for simian virus 40 to chromosome 17 in GM54VA, a human cell line transformed by simian virus 40. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jan;74(1):315–318. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.1.315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Croce C. M., Girardi A. J., Koprowski H. Assignment of the T-antigen gene of simian virus 40 to human chromosome C-7. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Dec;70(12):3617–3620. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.12.3617. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Croce C. M., Kieba I., Koprowski H. Unidirectional loss of human chromosomes in rat-human hybrids. Exp Cell Res. 1973 Jun;79(2):461–463. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(73)90470-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Croce C. M., Litwack G., Koprowski H. Human regulatory gene for inducible tyrosine aminotransferase in rat-human hybrids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Apr;70(4):1268–1272. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.4.1268. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cullen S. E., Schwartz B. D. An improved method for isolation of H-2 and Ia alloantigens with immunoprecipitation induced by protein A-bearing staphylococci. J Immunol. 1976 Jul;117(1):136–142. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koprowski H., Gerhard W., Croce C. M. Production of antibodies against influenza virus by somatic cell hybrids between mouse myeloma and primed spleen cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jul;74(7):2985–2988. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.7.2985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Köhler G., Milstein C. Continuous cultures of fused cells secreting antibody of predefined specificity. Nature. 1975 Aug 7;256(5517):495–497. doi: 10.1038/256495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LITTLEFIELD J. W. SELECTION OF HYBRIDS FROM MATINGS OF FIBROBLASTS IN VITRO AND THEIR PRESUMED RECOMBINANTS. Science. 1964 Aug 14;145(3633):709–710. doi: 10.1126/science.145.3633.709. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margulies D. H., Kuehl W. M., Scharff M. D. Somatic cell hybridization of mouse myeloma cells. Cell. 1976 Jul;8(3):405–415. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90153-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McBreen P., Engel E., Croce C. M. Assignment of the gene for glyoxalase I to region p21 leads to pter of human chromosome 6. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1977;19(4):208–214. doi: 10.1159/000130810. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien D., Linnenbach A., Croce C. M. Assignment of the gene for lactic dehydrogenase A to mouse chromosome 7 using mouse-human hybrids. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1978;21(1-2):72–76. doi: 10.1159/000130879. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pontecorvo G. Production of mammalian somatic cell hybrids by means of polyethylene glycol treatment. Somatic Cell Genet. 1975 Oct;1(4):397–400. doi: 10.1007/BF01538671. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruddle F. H. Linkage analysis using somatic cell hybrids. Adv Hum Genet. 1972;30:173–235. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4757-4429-3_4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seabright M. A rapid banding technique for human chromosomes. Lancet. 1971 Oct 30;2(7731):971–972. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)90287-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seidman J. G., Leder P. The arrangement and rearrangement of antibody genes. Nature. 1978 Dec 21;276(5690):790–795. doi: 10.1038/276790a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith M., Hirschhorn K. Location of the genes for human heavy chain immunoglobulin to chromosome 6. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jul;75(7):3367–3371. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.7.3367. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]