Abstract
The side chain cation of Arg235 provides a 5.6 and 2.6 kcal/mol stabilization of the transition states for orotidine 5'-monophosphate decarboxylase from Saccharomyces cerevisiae (OMPDC) catalyzed reactions of OMP and 5-fluoroorotidine 5'-monophosphate (FOMP), respectively, a 7.2 kcal/mol stabilization of the vinyl carbanion-like transition state for enzyme-catalyzed exchange of the C-6 proton of 5-fluorouridine 5'-monophosphate (FUMP), but no stabilization of the transition states for enzyme-catalyzed decarboxylation of truncated substrates 1-(β-d-erythrofuranosyl)orotic acid and 1-(β-d-erythrofuranosyl) 5-fluorouracil. These observations show that the transition state stabilization results from formation of a protein cation-phosphodianion pair, and that there is no detectable stabilization from an interaction between the side chain and the pyrimidine ring of substrate. The 5.6 kcal/mol side chain interaction with the transition state for the decarboxylation reaction is 50% of the total 11.2 kcal/mol transition state stabilization by interactions with the phosphodianion of OMP, while the 7.2 kcal/mol side-chain interaction with the transition state for the deuterium exchange reaction is a larger 78% of the total 9.2 kcal/mol transition state stabilization by interactions with the phosphodianion of FUMP. The effect of the R235A mutation on the enzyme-catalyzed deuterium exchange is expressed predominantly as a change in the turnover number kex while the effect on the enzyme-catalyzed decarboxylation of OMP is expressed predominantly as a change in the Michaelis constant Km. These results are rationalized by a mechanism in which the binding of OMP, compared with FUMP, provides a larger driving force for conversion of OMPDC from an inactive open conformation to a productive, active, closed conformation.
INTRODUCTION
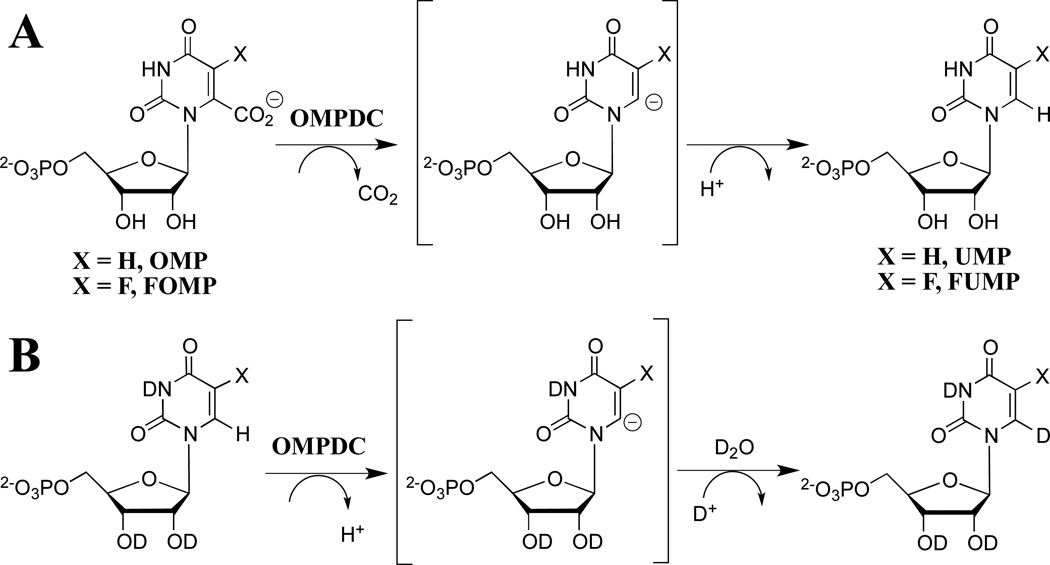
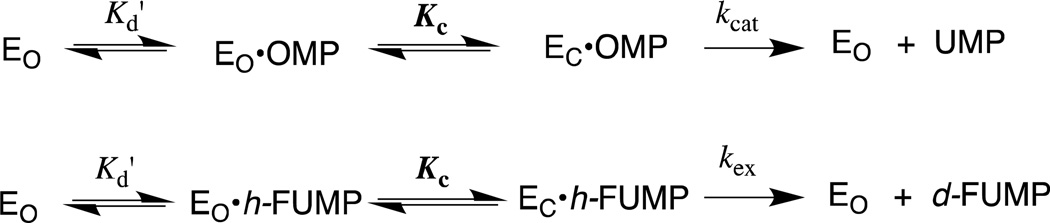
The mechanism of action of orotidine 5'-monophosphate decarboxylase (OMPDC) has attracted the interest of enzymologists and other chemists interested in catalysis, because of the difficulty in rationalizing the enormous 1017-fold enzymatic rate acceleration of chemically difficult nonenzymatic decarboxylation of orotidine 5'-monophosphate (OMP, Scheme 1A, X = H) to give uridine 5'-monophosphate (UMP).1,2 The well-known large barrier to nonenzymatic decarboxylation of OMP, which arises from the great instability of the putative vinyl carbanion reaction intermediate,1,3–5 prompted proposals of reaction mechanisms that avoid formation of this intermediate,6–12 but surprisingly little experimental data in support of any mechanism, until it was shown that OMPDC catalyzes both the decarboxylation of OMP and 5-fluoroorotidine 5'- monophosphate (FOMP, Scheme 1A, X = F) and exchange of the C-6 proton of UMP and of 5-fluorouridine 5'-monophosphate (FUMP) for deuterium from solvent D2O (Scheme 1B).13–15 These results provide compelling evidence that OMPDC-catalyzed reactions are through a vinyl carbanion reaction intermediate that is strongly stabilized by interactions with the protein catalyst. The unusual failure of OMPDC to discriminate between the reaction of hydrogen and deuterium, from a mixed solvent of 50/50 H2O/D2O, in protonation of the vinyl carbanion is consistent with a short lifetime for the reaction intermediate.16,17
Scheme 1.
OMPDC provides a large ~31 kcal/mol stabilization of the transition state for the decarboxylation of OMP, and a smaller ~8 kcal/mol stabilization of the Michaelis complex.1 These observations show that it is necessary both to determine the network of stabilizing protein-transition state interactions and the mechanism by which these interactions develop on moving from the Michaelis complex to the reaction transition state. The interactions between OMPDC and the substrate phosphodianion provide an 11.2 kcal/mol stabilization of the transition state for decarboxylation, which is 40% of the total transition state stabilization.18,19 Interactions between OMPDC and the phosphodianion of 5-fluorouridine 5'-monophosphate (FUMP) provide a smaller 9.2 kcal/mol stabilization of the transition state for the enzyme-catalyzed deuterium exchange reaction.20 This intrinsic phosphodianion binding energy is similar to that determined for the proton and hydride-ion transfer reactions, catalyzed by triosephosphate isomerase and α-glycerol phosphate dehydrogenase, respectively.21–24
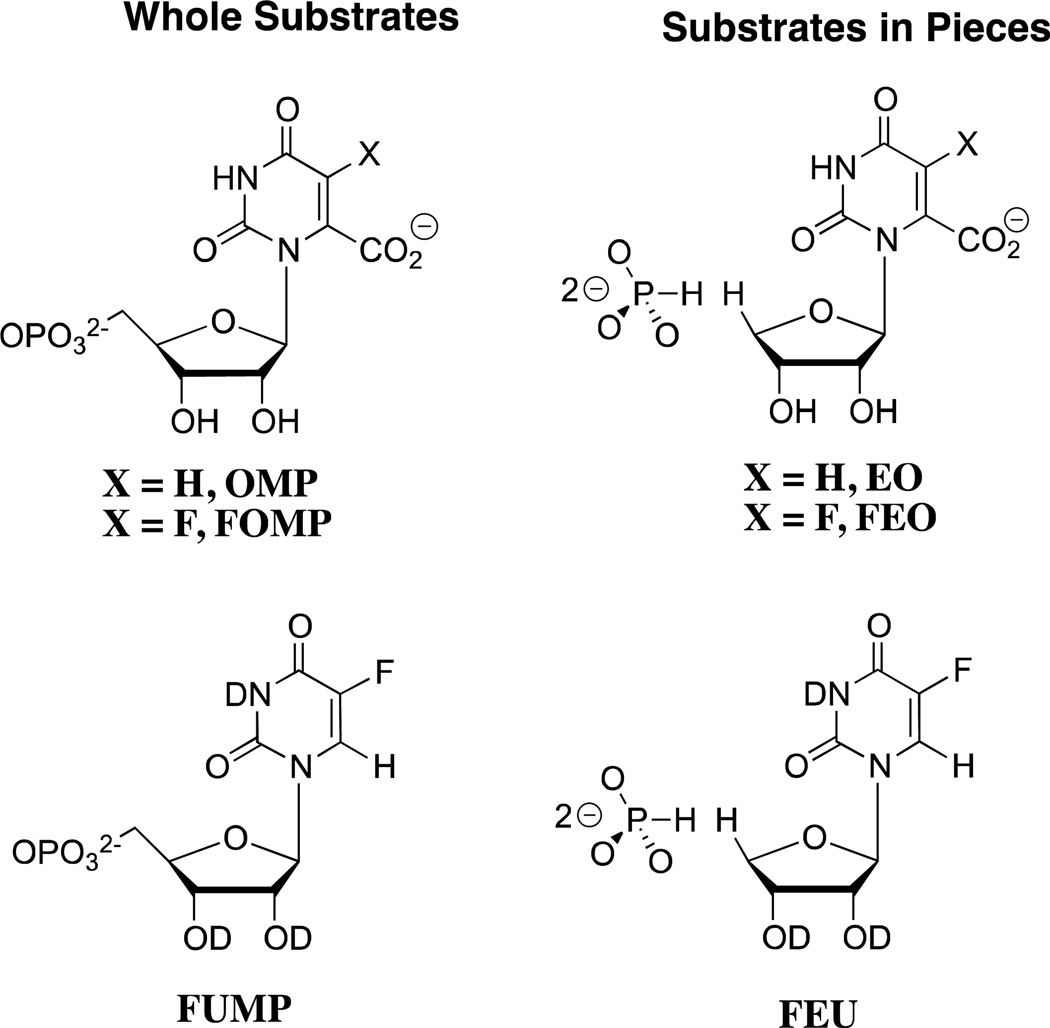
The 9 – 11 kcal/mol phosphodianion binding energy might be utilized to anchor the substrate to OMPDC (Km, effect) or to activate the enzyme for catalysis of the decarboxylation and deuterium exchange reactions, in which case the binding interactions will be expressed specifically at the transition state for the enzyme-catalyzed reaction (kcat effect).25 We have distinguished between anchoring and activating interactions of OMPDC with the phosphodianion of OMP or FUMP by cutting the covalent connection that anchors the phosphodianion to the whole substrates and examining the OMPDC-catalyzed reactions of substrate pieces (Scheme 2). The binding of phosphite dianion (HPO32−) to OMPDC results in a large increase in the observed second-order rate constant kcat/Km for enzyme-catalyzed decarboxylation of 1-(β-d-erythrofuranosyl)orotic acid (EO) and the deuterium exchange reaction of 1-(β-d-erythrofuranosyl) 5-fluorouracil (FEU, Scheme 2).18,20 This is the result of utilization of protein-dianion binding interactions to activate OMPDC for catalysis of reactions at the distant pyrimidine ring.
Scheme 2.
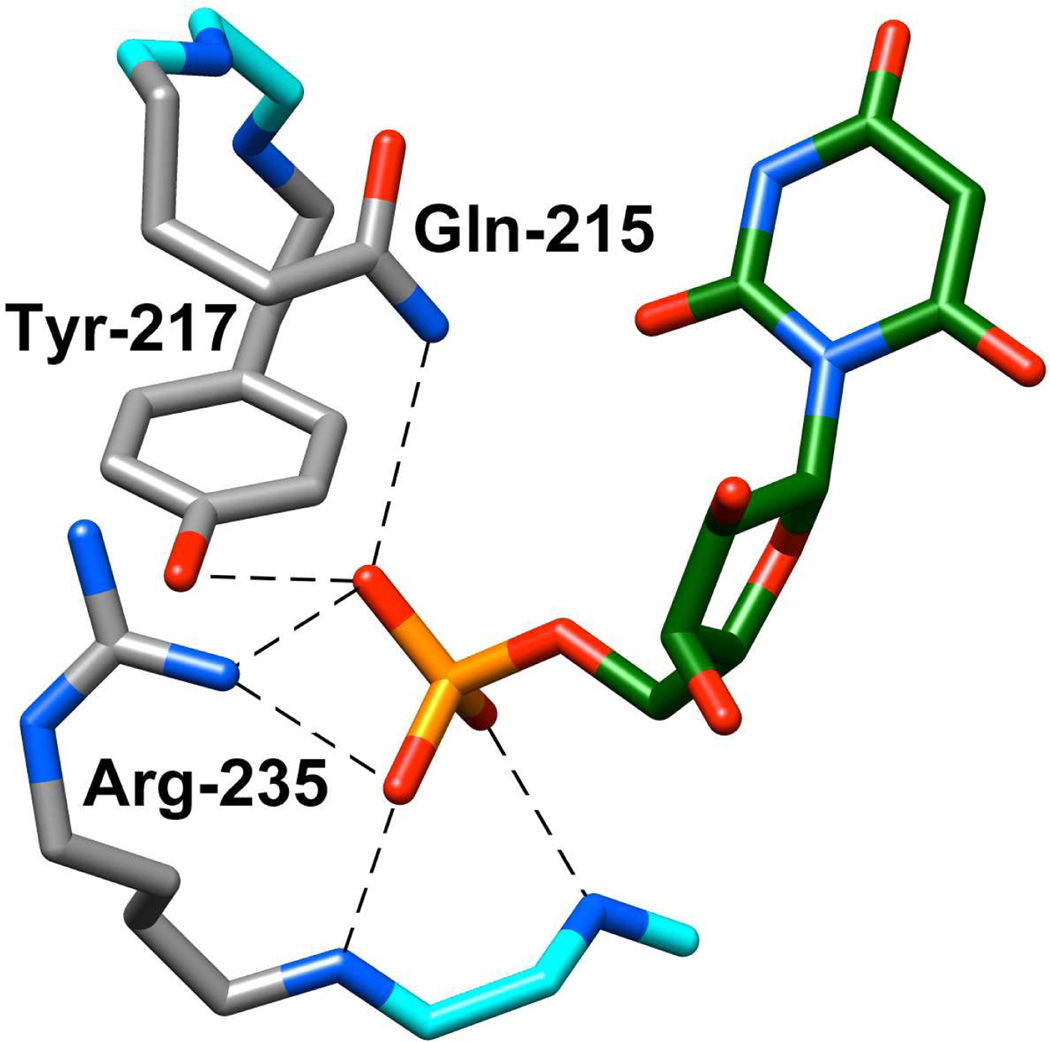
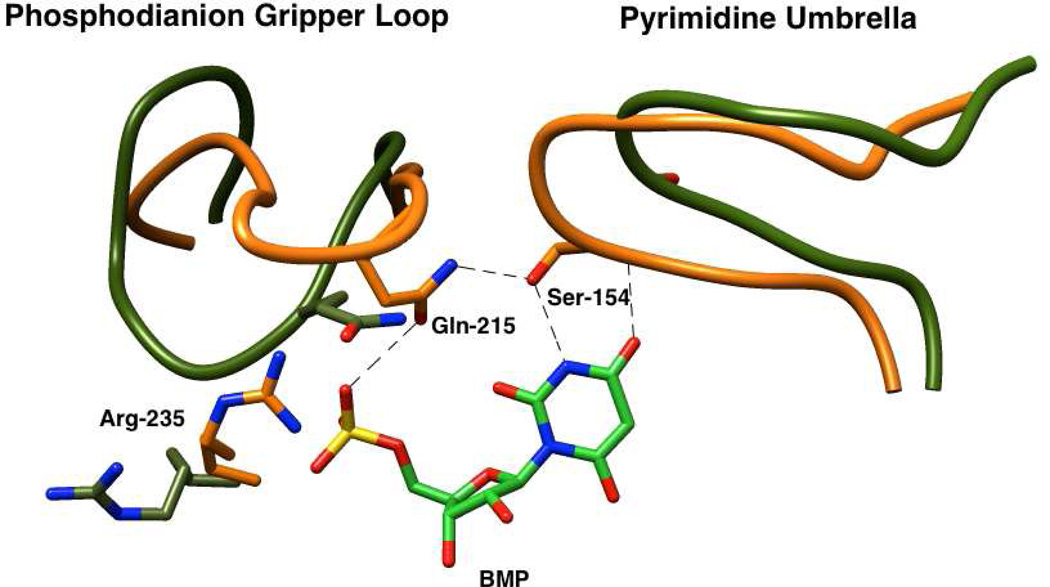
The X-ray crystal structure of OMPDC from Saccharomyces cerevisiae (ScOMPDC) liganded with 6-hydroxyuridine 5′-monophosphate (Figure 1) shows that the phosphodianion group of the ligand interacts directly with the side chains of Gln215 and Tyr217 that are part of a closed flexible loop, and with the guanidinium group of Arg235.2 The focus of this paper is the strong ion-pairing interaction between the phosphodianion and the guanidinium cation side chain of Arg235 that accounts for 50% of the total intrinsic phosphodianion binding energy.26,27 We are interested in determining whether these interactions are expressed at the transition state for the OMPDC-catalyzed deuterium exchange reaction of FUMP, in which case they would be utilized mainly in the stabilization of the vinyl carbanion intermediate common to the decarboxylation and deuterium exchange reactions.
Figure 1.
X-ray crystal structure of yeast OMPDC liganded with 6-hydroxyuridine 5'-monophosphate (Protein Data Bank entry 1DQX).2 The structure shows the interactions between the side chains of Gln215, Tyr217 and Arg235 of the protein with the bound phosphodianion group. Reprinted with permission from Ref. 19. Copyright 2012 American Chemical Society.
We report the effect of the R235A mutation of ScOMPDC on the kinetic parameters for the following enzymatic reactions: (1) The enzyme-catalyzed deuterium exchange reaction of FUMP. (2) The rescue, by guanidinium cation, of the activity of the R235A mutant of OMPDC for catalysis of the deuterium exchange reaction of FUMP. (3) The enzyme-catalyzed decarboxylation of FOMP and of the truncated substrate 1-(β-d-erythrofuranosyl) 5-fluoroorotic acid (FEO). These data are analyzed along with results from earlier studies of the effect of the R235A mutation on OMPDC-catalyzed decarboxylation of OMP and EO.19,28
EXPERIMENTAL SECTION
Materials
d-Ribose 5-phosphate (disodium salt ≥ 98%), 5-fluorouridine (99%), phosphoryl chloride (99%), phosphoenolpyruvate (monosodium salt, 98%), adenosine 5'-triphosphate (disodium salt, 99%), β-nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (disodium salt, 98%) and triethylamine (99.5%) were purchased from Sigma. 3-(N-morpholino) propanesulfonic acid (99.5%) and trimethyl phosphate (97%) were purchased from Fluka, and imidazole (99.5%), guanidinium hydrochloride (99%) and potassium phosphate (99.8%) were from Fisher. Ultrapure glycylglycine (> 99%) was obtained from USB Biochemicals. Dowex-50 (hydrogen form), DEAE Sephadex A-25 and Amberlite IR120 ion exchange resins were purchased from Sigma. The following deuterium labeled compounds were purchased from Cambridge Isotope Laboratories: D2O (99.9%), DCl (35% wt, 99.9% D), and NaOD (30% wt, 98%D). The water was distilled and purified on a MilliQ water purification system. The imidazole was recrystallized from benzene and dried under vacuum at room temperature for several days. Trimethylphosphate was dried over activated molecular sieves (4 Å) and distilled under reduced pressure. 5-Fluorouridine was dried at 50 °C under reduced pressure for twenty four hours prior to use. All other reagents were used without further purification.
l-lactate dehydrogenase, inorganic pyrophosphatase, adenylate kinase and pyruvate kinase were purchased from Sigma. Orotate phosphoribosyl transferase (ORTase) from Salmonella typhimurium was overexpressed in E. coli BL21 (DE3) transformed with the plasmid pOPRTase.29 The isolated OPRTase was purified according to a literature procedure.30 Phosphoribosylpyrophosphate (PRPP) synthetase from Escherichia coli was constituitively expressed from E. coli strain HO1702 harboring the plasmid pHO11 that was a generous gift from Professor Vern Schramm,31,32 and was purified according to a literature procedure.33 Published procedures were followed to prepare wildtype OMPDC from Saccharomyces cerevisiae (ScOMPDC) and the R235A mutant of ScOMPDC.27
Orotidine 5'-monophosphate was prepared by enzymatic methods from orotate and phosphoribosylpyrophosphate.34 This synthesis gave OMP that contained ammonium bicarbonate from purification by column chromatography that was removed by the following procedure. Stock solutions of OMP (~10–25 mM) were carefully titrated to pH 5 with 1.00 M HCl, and N2 was then bubbled through the solution to carry away CO2. The solution pH was adjusted to 7.1 and monitored for several hours. If an increase in pH was observed due to the evaporation of CO2, then additional 1.00 M HCl was added and the bubbling of nitrogen repeated. The concentration of NH4Cl in the final NH4CO3 free solution was determined as the concentration of HCl used to convert the HCO3− to CO2. The concentration of this salt was included in the calculation of the solution ionic strength.
The triethylammonium salt of FUMP was synthesized as described in earlier work,13 and was converted to the free acid by passage over Amberlite IR120 resin (H+-form) in methanol. 1-(β-d-erythrofuranosyl) 5-fluoroorotic acid (FEO) was synthesized as described in earlier work.28 5-Fluoroorotidine 5'-monophosphate (FOMP) was synthesized enzymatically by adaptation of the procedure for the enzymatic synthesis of UMP.35 A typical reaction mixture (10 mL, 30 °C) contained, initially, 0.25 mmol 5-fluoroorotic acid, 4 units PRPP synthase, 20 units of ORTase, 200 units of adenylate kinase, 200 units of pyruvate kinase, 300 units of yeast inorganic pyrophosphatase, 50 mM MgCl2, 3 mM ATP, 60 mM PEP and 3 mM DTT in 30 mM phosphate buffer at pH 7.5. The formation of FOMP was monitored in aliquots that were diluted 250-fold into an assay mixture for OMPDC, by determining the decrease in absorbance at 282 nm from OMPDC-catalyzed decarboxylation of FOMP. The yield of FOMP plateaued after 90 min, at which time an additional 0.25 mmol of 5-fluoroorotic acid was added. The reaction was monitored an additional 150 min, when the yield of FOMP again plateaued. The enzymes were removed by filtration using an Amicon Ultra-15 10 KDa MWCO membrane centrifugal filter, and the FOMP was purified by ion exchange chromatography over DEAE Sephadex A25, and eluting with a gradient of triethylammonium bicarbonate. The fractions that contained FOMP were pooled and the buffer salts removed on a rotary evaporator at reduced pressure, followed by lyophilization. The lyophilizate was suspended in 25 mL of methanol that contained 25 g of Amberlite IR120 resin (H+-form). This was stirred for 1 h at room temperature with gentle purging of Ar. The resin was then removed by filtration, washed with 200 mL of methanol, and the solvent removed under reduced pressure. The compound was dissolved in water, and colored material from the Amberlite resin removed by passage through a 3 mL Supelco reversed phase (LC-18) SEP tube. This gave the free acid of FOMP as a colorless solid in 40% yield.
NMR Analyses
19F NMR spectra were acquired on a Varian Unity Inova-500 spectrometer operating at 470 MHz. Spectra (64 transients), obtained to monitor enzyme-catalyzed deuterium exchange reactions, were recorded using a spectral width of 50000 Hz, a 90° pulse angle, a 2.6 s acquisition time and a relaxation delay between pulses of 28 s (> 7T1).20 The chemical shifts of the 19F NMR signals are referenced to the value of −78.5 ppm for a neat trifluoroacetic acid external standard.
Preparation of Solutions
Solution pH was determined at 25 °C using an Orion Model 720A pH meter equipped with a Radiometer pHC4006-9 combination electrode that was standardized at pH 7.00 and 10.00 at 25 °C. The pD of the buffers prepared in D2O was obtained by adding 0.4 to the reading on the pH meter.36 The acidic protons of GlyGly were exchanged for deuterium by dissolving the buffer in D2O, followed by evaporation and drying under vacuum at 55 °C. Buffered solutions of GlyGly were prepared by dissolving the buffer acid in D2O and adjusting to the required pD using 0.98 M NaOD. The concentration of FOMP and FUMP in 0.1 M HCl was determined from the absorbance at 271 nm (ε= 10200 M−1 cm−1) and 270 nm (ε = 9160 M−1 cm−1) respectively,13,28 Samples of R235A mutant ScOMPDC that had been stored at −80 °C were defrosted and dialyzed at 7 °C against 50 mM MOPS (45% free base) at pH 7.0 and I = 0.14 (NaCl) for the experiments with FEO. Samples of wildtype ScOMPDC were dialyzed at 7 °C against 10 mM MOPS at pH 7.1 and I = 0.10 (NaCl). Samples of R235A mutant ScOMPDC used to study catalysis of the deuterium exchange reaction were dialyzed at 7 °C against 10 mM MOPS at pH 7.1 and I = 0.10 (NaCl). This was followed by dialysis against several changes of 60 mM GlyGly (pD 8.15) at I = 0.14 (NaCl) in D2O using a D-tube dialyzer (10 kDa MWCO, Novagen) placed inside a narrow vessel that was isolated from atmospheric moisture using parafilm. The concentration of stock solutions of wildtype and R235A mutant ScOMPDC was determined from the absorbance at 280 nm using an extinction coefficient of 29,900 M−1 cm−1, calculated using the ProtParam tool available on the ExPASy server.37
Steady-State Enzyme Kinetics
The decarboxylation of OMP catalyzed by OMPDC was monitored spectrophotometrically by following the decrease in absorbance at 279 nm, 290 nm or 295 nm [Δε, α; −2400 M cm−1, 279 nm; −1620 M cm−1 290 nm; −842 M cm−1, 295 nm]. These wavelengths were chosen so that the initial absorbance Ai is ≤ 2.0. Assays (1 mL) contained OMP (0.05 – 1.5 mM) at pH 7.1 (30 mM MOPS), 25 °C and at I = 0.10 maintained with NaCl. The reactions were initiated by the addition of a stock solution of R235A mutant ScOMPDC to give a final enzyme concentration of 1 µM. The initial velocity vi (M s−1) was determined by monitoring the decrease in absorbance at the chosen wavelength. Values of kcat and Km were obtained from the nonlinear least squares fits of seven or more values of vi/[E] (s−1) to the Michaelis-Menten equation.
Assays of R235A mutant ScOMPDC-catalyzed decarboxylation of FOMP contained FOMP (0.10 – 1.0 mM) at pH 7.1 (10 mM MOPS), 25 °C and at I = 0.10 maintained with NaCl. Initial velocities, vo (M s−1), of the decarboxylation of FOMP catalyzed by R235A mutant ScOMPDC were determined spectrophotometrically by monitoring the decrease in absorbance at 290 nm (Δε = −1090 M−1 cm−1). Assays in a volume of 1 mL were initiated by the addition of 1 µL of a stock solution of R235A mutant ScOMPDC to give a final enzyme concentration of 15 – 20 nM. Values of kcat and Km for the R235A ScOMPDC-catalyzed decarboxylation reaction of FOMP were obtained from the nonlinear least squares fit of the values of vo/[E] to the Michaelis-Menten equation.
R235A ScOMPDC-Catalyzed Decarboxylation of FEO
The decarboxylation of FEO (0.14 mM) catalyzed by R235A mutant ScOMPDC (30µM) at pH 7.0 (25 mM MOPS), 25 °C, and an ionic strength of 0.14 (NaCl) was followed spectrophotometrically by monitoring the decrease in absorbance at 282 nm, as described in a previous study using wildtype ScOMPDC.28These reactions were monitored for ≥ 10 reaction halftimes (≤ 800 min), during which time ScOMPDC was shown by a standard enzyme assay to maintain full catalytic activity. Observed first-order rate constants kobs (s−1) for enzyme-catalyzed decarboxylation of FEO were obtained from the fits of reaction progress curves to an equation for a single exponential decay.18 Second-order rate constants (kcat/Km)obs were obtained using the relationship (kcat/Km)obs = kobs/[E].
R235A ScOMPDC-Catalyzed Deuterium Exchange at C-6 of h-FUMP Monitored by 19F NMR Spectroscopy
The C-6 deuterium exchange reactions of h-FUMP catalyzed by the R235A mutant of ScOMPDC in D2O at pD 8.15 were monitored by 19F NMR spectroscopy at 470 MHz. Reactions in a volume of 1 – 2 mL were initiated by addition of an aliquot of h-FUMP in D2O to a mixture of 50 mM GlyGly (20% free base) at pD 8.15, NaCl, and the R235A mutant of ScOMPDC in D2O to give final concentrations of 0.74 – 9.6 mM h-FUMP and of 0.2 – 0.9 mM mutant ScOMPDC at I = 0.14. In experiments where the effect of guanidinium cation on the velocity of the enzyme-catalyzed deuterium exchange reaction was examined, reactions in a volume of 1 – 2 mL were initiated by addition of an aliquot of h-FUMP in D2O to a mixture of 50 mM GlyGly at pD 8.15, NaCl, and ScOMPDC in D2O to give final concentrations of 0.74 mM h-FUMP, 12.5 – 82 mM guanidinium cation, and 0.08 – 0.12 mM ScOMPDC at I = 0.14. At timed intervals, during each set of experiments, 20 µL of neat deuterium labeled formic acid (DCOOD) was added to a measured aliquot that contains 0.38 or 0.75 µmol of h-FUMP + d-FUMP, in order to quench the reaction. The enzyme was removed by ultracentrifugation using an Amicon Ultrafiltration device (10 KDa MWCO), the volume of the filtrate was adjusted to 700 µL with D2O, and the solution was transferred to an NMR tube for analysis of the formation of d-FUMP. The enzyme-catalyzed deuterium exchange reactions were monitored for up to 2 days, during which time the activity of ScOMPDC was determined by a standard assay. In several cases, the enzyme was removed after completion of the reaction by the filtration procedures described above and the solution pD was determined. No significant loss in enzymatic activity (< 5%) or decrease in solution pD (<0.1 unit) was observed during the course of these enzyme-catalyzed deuterium exchange reactions.
The 19F NMR spectra were determined to give the integrated peak areas for the doublet with area (AH) at −165.36 ppm for h-FUMP and the broad upfield-shifted apparent singlet with area (AD) at −165.66 ppm for d-FUMP. The initial velocity (vi, eq 1) for the enzyme-catalyzed deuterium exchange reactions of h-FUMP was determined as the slopes of linear plots of fP[FUMP]o against time over the first 5 – 10% reaction, where fP = AD/(AH + AD) is the fraction of total FUMP labeled with deuterium at the C-6 position, and [FUMP]o is the initial concentration of h-FUMP.
| (1) |
RESULTS
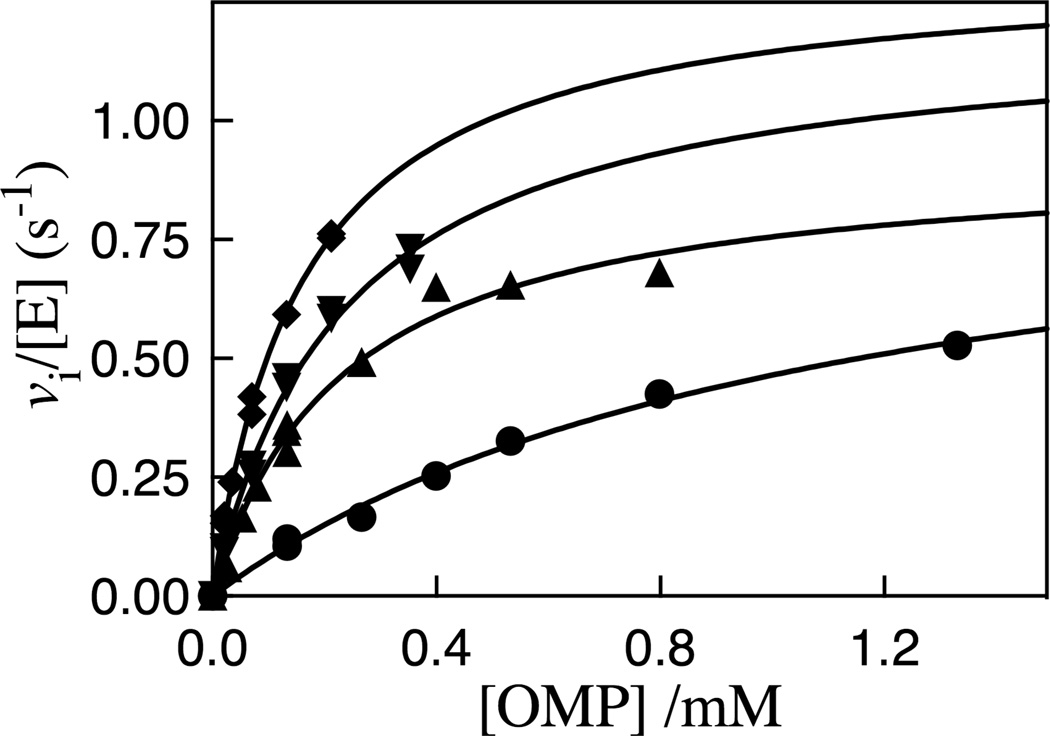
The decarboxylation of OMP catalyzed by the R235A mutant of ScOMPDC was monitored spectrophotometrically at wavelengths chosen to ensure that Ai < 2.0 for the initial absorbance of the OMP. Figure 2 shows the dependence of the initial velocity vi/[E] on [OMP] for decarboxylation reactions catalyzed by the R235A mutant of OMPDC at 25 °C, pH 7.1 (30 mM MOPS) and at different ionic strengths maintained with NaCl, and Table S1 from the Supporting Information reports the individual values of vi/[E] and the wavelengths monitored for these experiments. The solid lines for Figure 2 show the non-linear least squares fits of the experimental data to the Michaelis-Menten equation. The following values of kcat, Km and kcat/Km for decarboxylation of OMP catalyzed by R235A mutant ScOMPDC were obtained from these fits, where the quoted uncertainties represent the 95% confidence interval (●), I = 0.10, kcat = 1.0 ± 0.19 s−1, Km = (1.1 ± 0.36) × 10−3 M, kcat/Km = 910 M−1 s−1; (▲), I = 0.050, kcat = 0.93 ± 0.11 s−1, Km = (0.23 ± 0.065) × 10−3 M, kcat/Km = 4000 M−1 s−1;(▼), I = 0.035, kcat = 1.21 ± 0.15 s−1, Km = (0.23 ± 0.052) × 10−3 M, kcat/Km = 5300 M−1 s−1; (◆), I =0.020, kcat = 1.33 ± 0.10 s−1, Km = (0.16 ± 0.022) × 10−3 M, kcat/Km = 8300 M−1 s−1.
Figure 2.
Michaelis-Menten plots which show the dependence of vi/[E] for decarboxylation of OMP catalyzed by R235A mutant ScOMPDC on the concentration of OMP for reactions at 25 °C, pH 7.1 (30 mM MOPS) and at different ionic strengths maintained with NaCl: (●), I = 0.10; (▲), I = 0.050; (▼), I = 0.035; (◆), I =0.020.
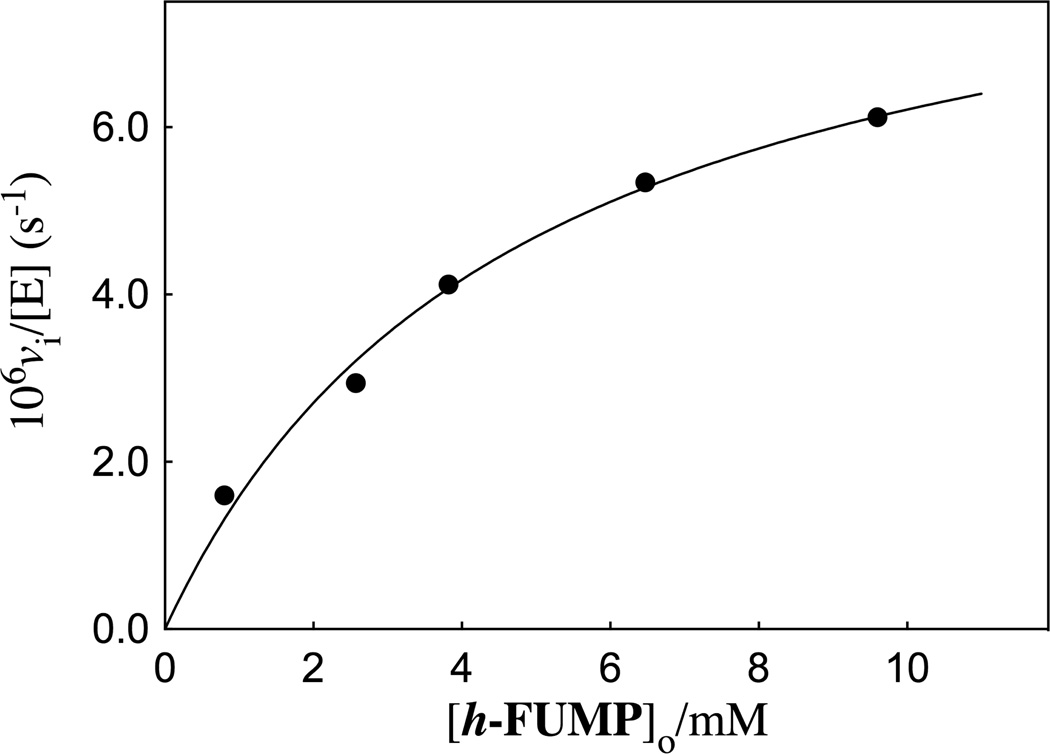
The R235A mutant ScOMPDC-catalyzed deuterium exchange reactions of h-FUMP in solutions buffered by 50 mM GlyGly in D2O at pD 8.15 and 25 °C were monitored by 19F NMR spectroscopy at 470 MHz, as described in an earlier study of the wildtype enzyme-catalyzed deuterium exchange reactions of 1-(β-d-erythrofuranosyl) 5′-fluorouracil (FEU).20 The initial reaction velocities (vi) were determined as described in the Experimental Section. The dependence of vi/[E] on the concentration of the substrate is shown in Figure 3. These data were fit to eq 2, derived for Scheme 3, to give the values for kex and Kd reported in Table 1.
| (2) |
Figure 3.
A Michaelis-Menten plot which shows the dependence of vi/[E] on the concentration of substrate h-FUMP for the deuterium exchange reaction catalyzed by the R235A mutant of ScOMPDC at pD 8.15 (20 mM GlyGly, 20% free base), and I = 0.14 (NaCl). The solid line shows the correlation of the experimental data to eq 2 derived for Scheme 3, using the values for the kinetic parameters reported in Table 1.
Scheme 3.
Table 1.
Kinetic Parameters for the Decarboxylation and Deuterium Exchange Reactions Catalyzed by Wildtype and R235A ScOMPDC.a
| kcat or kex (s−1) | Km or Kd (M) |
kcat/Km or kex/Kd (M−1 s−1) |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wildtype | R235A | Wildtype | R235A | Wildtype | R235A | |
| OMP b | 15 | 1.0 | 1.4 × 10−6 | 1.1 × 10−3 | 1.1 × 107 | 910 |
| Effect of mutation | 15-fold decrease | 790-fold increase | 12000-fold decrease | |||
| FOMP c | 95 | 92 | 8 ×10−6 | 5.8 × 10−4 | 1.2 × 107 | 1.6 × 105 |
| Effect of mutation | No effect | 73-fold increase | 75-fold decrease | |||
| h-FUMP d | 0.044 | 9.3 × 10−6 | 1.1 × 10−4 | 5.0 × 10−3 | 400 | 1.9 × 10−3 |
| Effect of mutation | 4700-fold decrease | 45-fold increase | 210000-fold decrease | |||
The kinetic parameters kcat and Km, and kex and Kd, respectively, are used for the ScOMPDC-catalyzed decarboxylation and deuterium exchange reactions.
At pH 7.1 (30 mM MOPS) 25 °C, and I = 0.10 (NaCl). Data for wildtype ScOMPDC is from Ref. 38.
At pH 7.1 (10 mM MOPS) 25 °C, and I = 0.10 (NaCl). Data for wildtype ScOMPDC is from Ref. 39.
At pD 8.15 (20 mM GlyGly, 20% free base), and I = 0.14 (NaCl). Data for wildtype ScOMPDC is from Ref. 13.
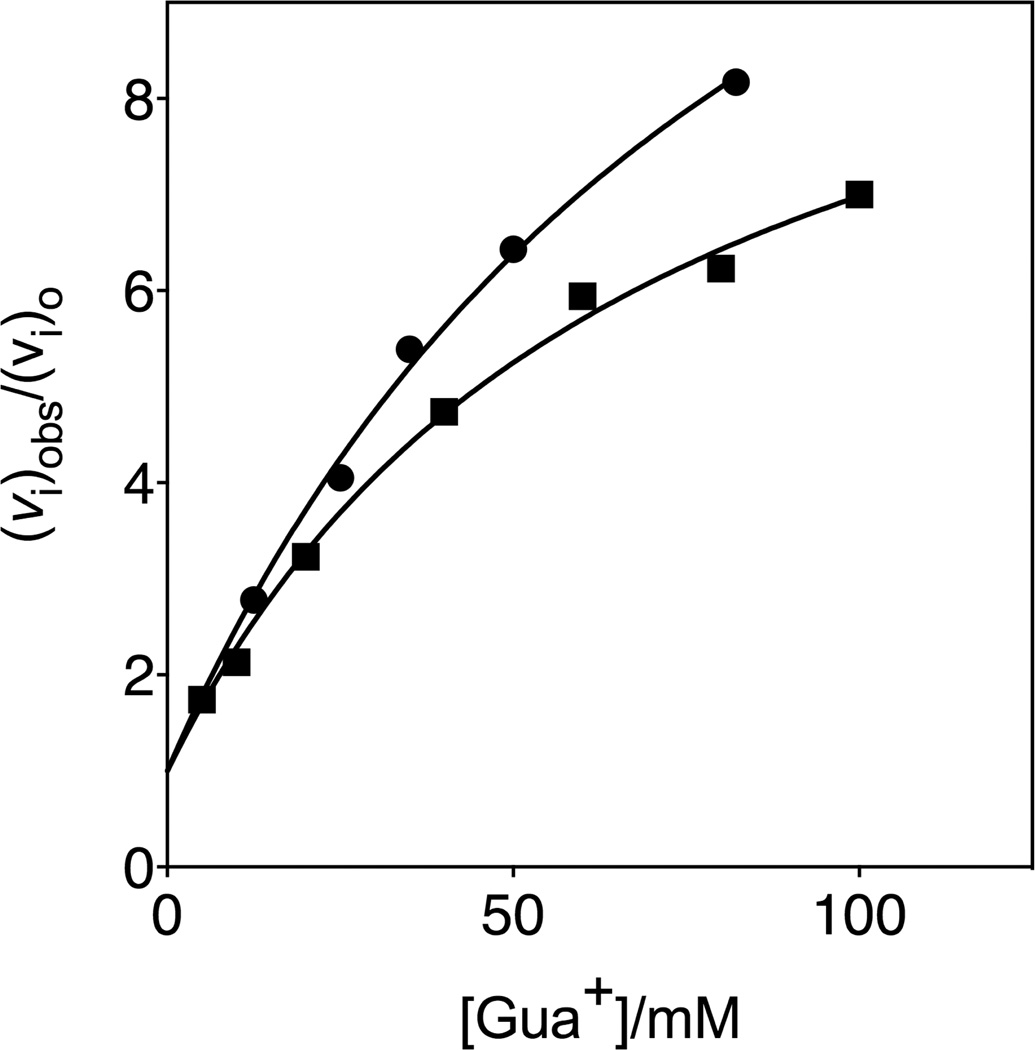
Figure 4 shows the effect of increasing concentrations of guanidinium cation (Gua+) on the relative initial velocity, (vi)obs/(vi)o, for the R235A mutant ScOMPDC-catalyzed deuterium exchange reaction of 0.74 mM h-FUMP at 25 °C in solutions buffered by 50 mM GlyGly at pD 8.15 and an ionic strength of 0.14 (NaCl), and for the decarboxylation reaction of 5 µM OMP reported in an earlier study. In each case, the substrate concentration [h-FUMP]o << Kd = 5 mM or [OMP]o << Kd = 1 mM is far below saturation, so that in the absence of Gua+ the enzyme exists mainly in the unliganded form. The data in Figure 4 show that Gua+ provides quantitatively similar activation of R235A ScOMPDC-catalyzed decarboxylation and deuterium exchange reactions. The protocol to monitor R235A mutant ScOMPDC-catalyzed deuterium exchange reactions of FUMP is labor intensive and consumes large amounts of enzyme. This prohibited the determination of kinetic parameters for activation of the mutant enzyme-catalyzed deuterium exchange reaction by Gua+, for comparison with previously published kinetic parameters for Gua+ activation of mutant enzyme-catalyzed decarboxylation of OMP.27
Figure 4.
Dependence of (vi)obs/(vi)o on the concentration guanidinium cation for R235A mutant ScOMPDC-catalyzed reactions, where (vi)o is the observed initial velocity in the absence of the cation activator: (●), the deuterium exchange reaction of 0.74 mM h-FUMP catalyzed by the R235A mutant of ScOMPDC at pD 8.15 (20 mM GlyGly, 20% free base), 25 °C and I = 0.14 (NaCl); (■), the decarboxylation reaction of 5 µM OMP at pH 7.1 (10 mM MOPS), 25 °C and I = 0.10 (NaCl).27
The initial velocity of R235A mutant ScOMPDC-catalyzed decarboxylation of FOMP at 25 °C was determined for reactions at several concentrations of FOMP between 0.10 and 1.0 mM in solutions buffered by 10 mM MOPS at pH 7.1 and at I = 0.10 (NaCl). Values of kcat and Km for R235A mutant enzyme-catalyzed decarboxylation of FOMP were obtained from the nonlinear least squares fits of the values of vo/[E] to the Michaelis-Menten equation (Table 1). The following parameters for ScOMPDC-catalyzed reactions, determined in earlier work at pH 7.1 and 25 °C, are reported in Table 1; kcat and Km for wildtype ScOMPDC-catalyzed decarboxylation of OMP38 and FOMP,39 and kex and Kd for the wildtype enzyme-catalyzed deuterium exchange reaction of h-FUMP.13
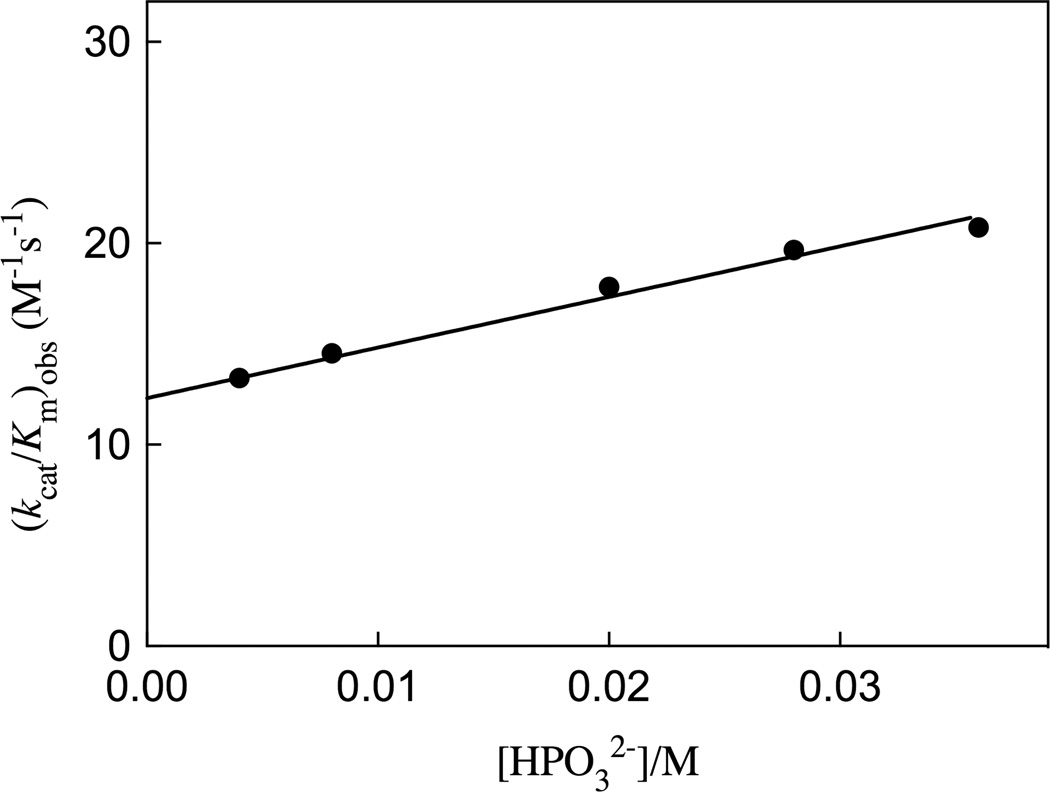
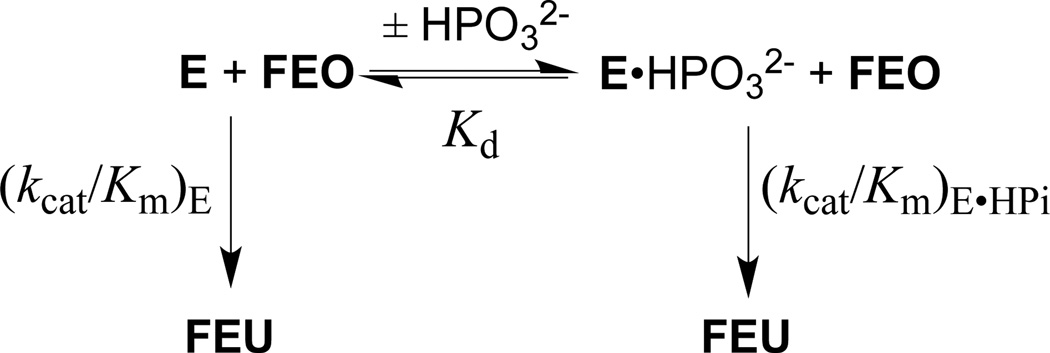
Figure 5 shows the increase, at increasing concentrations of phosphite dianion, in the apparent second-order rate constant (kcat/Km)obs for R235A mutant ScOMPDC-catalyzed decarboxylation of FEO at pH 7.0 (25 mM MOPS), 25 °C and an ionic strength of 0.14 (NaCl). A linear least squares fit of these data to eq 3, derived for Scheme 4 (Kd >> [HPO32−]), gives the values of (kcat/Km)E and [(kcat/Km)E•HPi]/Kd reported in Table 2. Table 2 also reports these kinetic parameters for wildtype ScOMPDC-catalyzed decarboxylation of FEO and for wildtype and R235A mutant ScOMPDC-catalyzed decarboxylation of EO, determined in earlier studies.19,28
| (3) |
Figure 5.
Dependence of the observed second-order rate constant (kcat/Km)obs for the R235A mutant of ScOMPDC-catalyzed decarboxylation of the truncated substrate FEO on the concentration of added phosphite dianion at pH 7.0, 25 °C and I = 0.14 (NaCl). The solid line shows the linear correlation of the experimental data to eq 3, derived for Scheme 4, using the values for the kinetic parameters reported in Table 2.
Scheme 4.
Table 2.
Kinetic Parameters from Scheme 4 for the Decarboxylation Reactions of the Substrate Pieces Catalyzed by Wildtype and R235A Mutant ScOMPDC.a
DISCUSSION
The 7-fold increase in Km (Figure 2) for decarboxylation of OMP catalyzed by the R235A mutant of ScOMPDC as the ionic strength is increased from 0.020 (Km = 0.16 × 10−3 M) to 0.10 (Km = 1.1 × 10−3 M) shows that great care must be exercised to maintain constant ionic strength in these experiments. A similar effect of changing ionic strength on Km has been reported for triosephosphate isomerase (TIM) catalyzed isomerization of glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate.40 This increase in Km is consistent with a decrease in the activity coefficient for the substrate phosphodianion at increasing ionic strength.41 The ScOMPDC-catalyzed deuterium exchange reactions of h-FUMP were carried at pD 8.15, because this is very close to the pH-optimum of kex/Kd for the deuterium exchange reactions catalyzed by wildtype ScOMPDC. Similar values of kcat/Km = 5.5 × 106 M−1 s−1 and 1.1 × 107 M−1 s−1 were determined for wildtype ScOMPDC-catalyzed decarboxylation of OMP at pD = 8.15 and at pH 7.1, respectively.20
Role of Arg235 in ScOMPDC-Catalyzed Decarboxylation and Deuterium Exchange Reactions
Table 3 summarizes the effects of the R235A mutation on the second-order rate constants kcat/Km for several ScOMPDC-catalyzed reactions, and the stabilizing interaction between the side chain cation and the different reaction transition states. The essentially full 13C kinetic isotope effect on kcat/Km for ScOMPDC-catalyzed decarboxylation of OMP is consistent with the expression of the entire side chain interaction at the rate-determining transition state.34 However, it has been determined that the rate constant k−d for breakdown of E•OMP to E + OMP is only 4-fold larger than kcat for turnover of OMP,42 so that substrate binding is weakly rate determining for the second order rate constant kcat/Km.29,42 We calculate that kcat/Km = 1.1 × 107 M−1 s−1 (Table 1) is 20% smaller than for a hypothetical reaction where OMP binds reversibly and chemistry is rate determining for decarboxylation. This gives an estimated interaction energy of 5.6 kcal/mol that is 0.1 kcal/mol larger than the value of 5.5 kcal/mol calculated using the observed value of kcat/Km = 1.1 × 107 M−1 s−1 (Table 3).
Table 3.
Apparent Interaction Energies of the Cationic Side Chain of Arg235 with the Rate-Determining Transition States for Several ScOMPDC-Catalyzed Reactions.
| Substrate |  |
|
|---|---|---|
| Interaction Energy (kcal/mol) |
||
| OMP a | 1.2 × 104 | 5.5 d |
| 5.6 e | ||
| FOMP a | 75 | 2.6 |
| h-FUMP a | 2.1 × 105 | 7.2 |
| EO b | 1 | 0 |
| FEO b | 0.8 | −0.1 |
| HPO32− (1 M) + EO c | 1.9 × 104 | 5.8 |
| HPO32− (1 M) + FEO c | 190 | 3.1 |
Calculated from data in Table 1.
Calculated from data in Table 2.
Calculated from the effect of the R235A mutation on (Table 2).
Observed stabilization of the rate-determining transition state.
Estimated stabilizing interaction if chemistry were fully rate determining for ScOMPDC-catalyzed decarboxylation of OMP.
The intrinsic phosphodianion binding energy may be utilized to induce electrostatic stress into the protein catalyst and/or substrate, which is relieved at the transition state for the enzyme-catalyzed decarboxylation reaction.42–44 However, such ground state destabilization would result in equal increases in kcat and Km, but should not affect the value of kcat/Km. It is therefore not relevant to our analysis of the effect of the R235A mutation on kcat/Km for the ScOMPDC-catalyzed reactions of OMP and FOMP summarized in Table 3. The utilization of phosphodianion binding energy to induce electrostatic stress between protein and substrate carboxylate anions, which is relieved in the vinyl carbanion-like transition state for the enzyme-catalyzed decarboxylation reaction, would result in a smaller effect of the R235A mutation on the kinetic parameter kcat for the enzyme-catalyzed deuterium exchange reaction of an unstrained Michaelis complex to FUMP through a vinyl carbanion-like transition state. We find, instead, that the R235A mutation results in a larger decrease in kex for the OMPDC-catalyzed deuterium exchange reaction of FUMP compared with kcat for enzyme-catalyzed decarboxylation of OMP.
The cationic side chain of Arg235 provides no stabilization of the transition states for enzyme-catalyzed decarboxylation of the truncated substrates EO and FEO, but large 5.6 and 7.2 kcal/mol stabilization, respectively, of the transition states for the decarboxylation and deuterium exchange reactions of phosphorylated substrates OMP and FUMP (Table 3) The absence of stabilizing interactions between this side chain and the decarboxylation transition state, when there is no substrate phosphodianion, shows that the large transition state stabilization observed for the OMPDC-catalyzed reactions of OMP and UMP is due entirely to stabilizing interactions expressed at the enzyme-phosphodianion ion pair (Figure 1). These are not only interactions expressed at the ground state Michaelis complex (Km effect), because the R235A mutation results in decreases in kcat and kex, respectively, for the ScOMPDC-catalyzed reactions of OMP and FUMP (Scheme 5).
Scheme 5.
We have proposed that the binding energy from the protein-phosphodianion pair isutilized to drive an enzyme conformational change that activates OMPDC for catalysis.19,25,28,43,44 This is shown by Scheme 5 for ScOMPDC-catalyzed reactions of OMP and h-FUMP, as the conversion of a dominant inactive open form of OMPDC (EO) to the active closed forms EC•OMP or EC•h-FUMP (Kc << 1).22,41 The utilization of the dianion binding interactions to stabilize EC results in enzyme activation, because of the increase in the fraction of total OMPDC present in reactive EC. The conformational change from EO•OMP to EC•OMP or from EO•h-FUMP to EC•h-FUMP includes closure of a phosphodianion gripper loop (Pro202 to Val220) and of a hydrophobic pyrimidine umbrella (Ala151 – Thr165) over O-4 and C-5 of the pyrimidine ring (Figure 6). The formation of a hydrogen bond at EC between the side chains of Gln 215 from the “gripper” loop and Ser154 from the “lid” shows that these structural elements act cooperatively during the enzyme conformational change.45 The mechanism for activation of OMPDC for catalysis of decarboxylation and deuterium exchange reactions, that we propose results from this conformational change, has not been determined. A minimal mechanism will include: (a) The utilization of substrate binding energy for the optimal positioning of amino acid residues at the enzyme active site.46,47 (b) The utilization of substrate binding energy to extrude solvent from the active site - this will reduce the effective dielectric constant at the active site cavity, to enhance stabilizing electrostatic interactions between the protein and transition state.43,46,47
Figure 6.
An image that superimposes the partial X-ray crystal structure of ScOMPDC complexed with BMP (PDB entry 1DQX) over the structure for unliganded ScOMPDC (PDB entry 1DQW). The movement of the phosphodianion gripper loop (Pro202 to Val220) towards the hydrophobic pyrimidine umbrella (Ala151 – Thr165) is shown for the unliganded (orange) and liganded (olive green) enzymes. The closure of these loops is proposed to be cooperative, and driven by the formation of a hydrogen bond between the side chains of Gln215 from “gripper” loop and of Ser 154 from the “umbrella”.
Effects on kcat and Km
The ion pair between the side chain cation of Arg235 and the phosphodianion of ligands (Figure 1) appears to stabilize the enzyme-ligand complex, so that strong phosphodianion binding interactions will favor tight substrate binding. On the other hand, binding energy that is utilized to drive an initially unfavorable, but activating, protein conformational change (Scheme 5) cannot be expressed as a decrease in Km, and must instead result in an increase in kcat conversion of the Michaelis complex to product.25
Removing the side chain cation-phosphodianion pair by the R235A mutation results in changes in both Km or Kd for formation of the Michaelis complex to OMP and h-FUMP, respectively, and in kcat or kex for conversion of the Michaelis complex to product (Table 1). The 7.2 kcal/mol stabilizing interaction between the side chain of Arg235 and the transition state for the ScOMPDC-catalyzed deuterium exchange reaction of h-FUMP (Table 3) reflects a 2.2 kcal/mol stabilization of the Michaelis complex (Kd effect) and a larger 5.0 kcal/mol decrease in the barrier for conversion of the Michaelis complex to the reaction transition state (kex effect). By contrast, the smaller 5.6 kcal/mol stabilizing interaction between the side chain of Arg235 and the transition state for the decarboxylation reaction reflects a large 4.0 kcal/mol stabilization of the Michaelis complex to OMP (Km effect) and only a 1.6 kcal/mol decrease in the barrier to turnover of this complex (kcat effect).
| (4) |
| (5) |
| (6) |
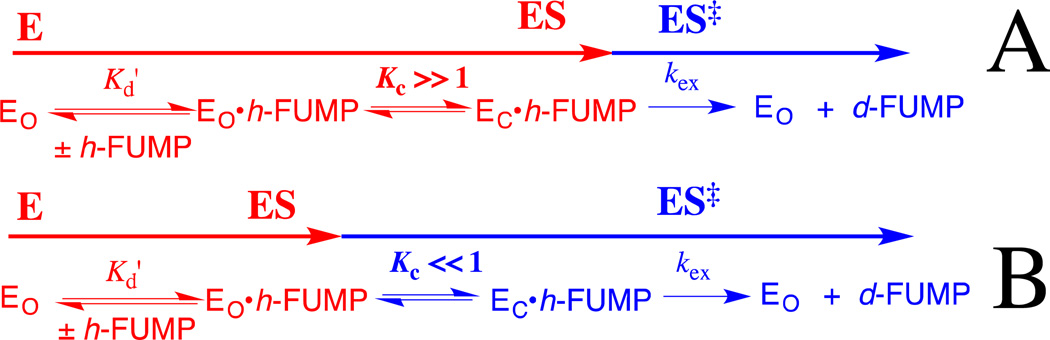
Figure 7 shows the complexes between h-FUMP and the open form (EO) and the closed form (EC) of ScOMPDC, that are interconverted with an equilibrium constant Kc. Eq 4 – 6 define the relationships between Kc, Kd' and kex from Figure 7 and the observed kinetic parameters (kex)obs and (Kd)obs for the ScOMPDC-catalyzed deuterium exchange reactions of h-FUMP. A similar set of equations for (kcat)obs and (Km)obs can be written for the ScOMPDC-catalyzed decarboxylation of OMP. Figure 7 shows limiting cases for the effect of a change in the protein cation-phosphodianion interaction, which affects the value of Kc, on the observed kinetic parameters. When EC• h-FUMP is the dominant complex (Kc >> 1, Figure 7A), then changes in Kc will be expressed as changes in the observed substrate affinity ((Kd)obs, eq 6); and, when unreactive EO• h-FUMP is the dominant complex (Kc <<1, Figure 7B), then changes in Kc will be expressed as changes in the apparent reactivity of the Michaelis complex ((kex)obs, eq 5), because the enzyme conformational change is a step on the pathway from the major complex EO• h-FUMP to the reaction transition state. Mutations that result in a change from Kc > 1 to Kc < 1 will be expressed as changes in both (Kd)obs and (kex)obs.
Figure 7.
Diagrams which illustrate the effect of a change in the equilibrium constant Kc for a conformational change, that converts OMPDC from an inactive [nonproductive] open form to an active [productive] closed form, on the kinetic parameters (kex)obs and (Kd)obs for the OMPDC-catalyzed deuterium exchange reaction of h-FUMP to form d-FUMP (eq 5 and 6).The steps leading to formation of the major Michaelis complex are shown in red, and the steps leading from this Michaelis complex to the transition state for OMPDC-catalyzed deuterium exchange are shown in blue. (A) Kc >>1. The major Michaelis complex is the productive complex EC•h-FUMP and a change in Kc affects (Kd)obs for substrate binding but not (kex)obs for turnover to form product (eq 6). (B) Kc <<1. The major Michaelis complex is the nonproductive complex EO•h-FUMP, so that the enzyme conformational change lies on the pathway from the major complex EO•h-FUMP to the reaction transition state. A change in Kc now results mainly in a change in (kex)obs for turnover of h-FUMP (eq 5).
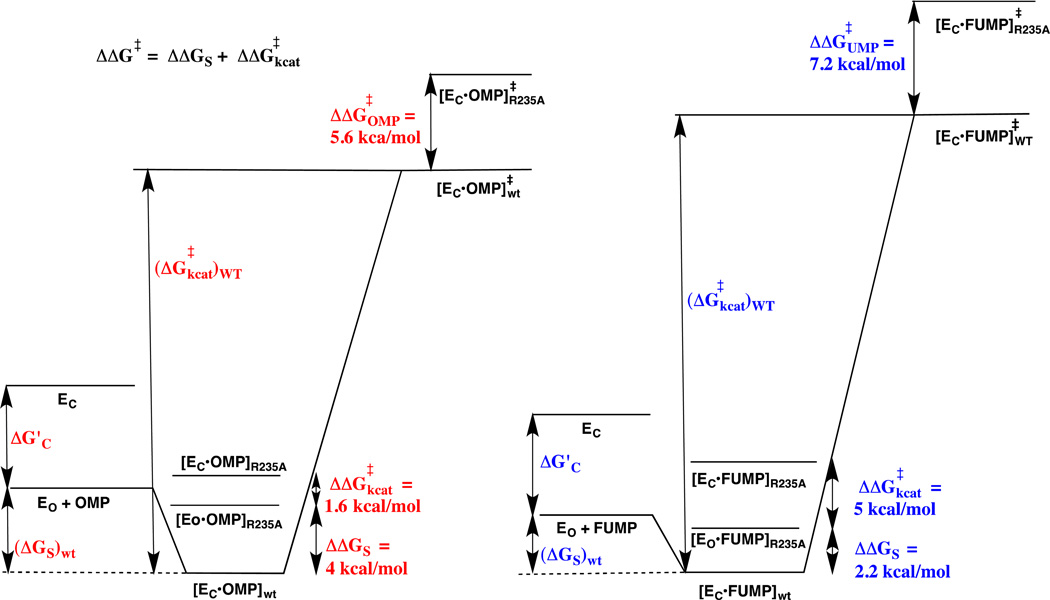
OMP and FUMP bind to different protonated and neutral forms of OMPDC with Kd =1.0 µM 42 and 20 µM,13 respectively. The ligand binding is proposed to be controlled by the protonation state of the cationic side-chain of Lys93.13 Now, the effect of the R235A mutation is expressed mainly as a change in (kex)obs for the ScOMPDC-catalyzed deuterium exchange reaction of h-FUMP. This is consistent with a small favorable thermodynamic driving force for the enzyme conformational change, from EO• h-FUMP to EC• h-FUMP, for wildtype ScOMPDC; and, a large barrier to this conformational change (Kc <<1) for the R235A mutant enzyme. The higher affinity of OMP, compared with UMP, for OMPDC reflects stabilizing binding interactions between the carboxylate side chain of OMP and the cationic side chain of Lys93.13 We propose that these and possibly other interactions with this –CO2− are part of an extended network of cooperative interactions that stabilize EC•OMP so that (Kc)OMP > (Kc)FUMP. This more favorable conformational change at the Michaelis complex to OMP compared with h-FUMP would result in the larger observed fractional expression of the effect of the R235A mutation on Km (4.0/5.6 = 0.71) and a corresponding smaller observed fractional expression on kcat (1.6/5.6 = 0.29) for the enzyme-catalyzed decarboxylation reaction of OMP compared with the fractional expression of the effect of the R235A mutation on Kd (2.2/7.2 = 0.31) and on kex (5.0/7.2 = 0.69) for the OMPDC-catalyzed deuterium exchange reaction of h-FUMP. The difference in the effects of the R235A mutation on the kinetic parameters for ScOMPDC-catalyzed decarboxylation of OMP and the deuterium exchange reaction of FUMP are illustrated by the two free energy profiles shown in Figure 8, and additional discussion for these differences is presented in the Figure legend.
Figure 8.
Free energy reaction profiles that illustrate the different effects of the R235A mutation on the kinetic parameters for ScOMPDC-catalyzed decarboxylation of OMP to form UMP (profile on left) and the deuterium exchange reaction of h-FUMP to form d-FUMP (profile on right). The binding energy of R235A and other residues in the phosphodianion gripper loop is utilized to drive the conversion of open enzyme EO to closed enzyme EC – this binding energy is partly expressed at the Michaelis complex when loop closure at the Michaelis complex is thermodynamically favorable (Kc > 1, eq 4 – 6). The substrate binding energy (ΔGS)wt of OMP is greater than for FUMP, and we propose that this reflects the utilization of the binding interactions with the -CO2− group of OMP to drive the conversion of EO to EC (ΔG’c). The overall effect of the R235A mutation on the barrier for the deuterium exchange (ΔΔG‡UMP = 7.2 kcal/mol) is larger than for the decarboxylation reaction (ΔΔG‡OMP = 5.6 kcal/mol). The R235A mutation results mainly in a decrease in ΔGS for the decarboxylation reaction (ΔΔGS = 4 kcal/mole). We propose that the Michaelis complex between OMP and the R235A mutant enzyme exists mainly in the nonproductive open form ([Eo•OMP]R235A), because there is insufficient binding energy at this Michaelis complex enzyme to drive the enzyme conformational change (Kc < 1, eq 4–6). The effect of the R235A mutation on kcat (ΔΔG‡kcat = 1.6 kcal/mol) is shown as the 1.6 kcal/mol barrier for conversion of [Eo•OMP]R235A to the productive complex ([EC•OMP]R235A). The smaller binding energy from FUMP compared with OMP available to drive the enzyme conformational change ((Kc)FUMP < (Kc)OMP, eq 4 – 6) results in the smaller the effect of the R235A mutation on ΔGS (ΔΔGS = 2.2 kcal/mol) and a large 5 kcal/mol barrier to conversion of nonproductive [Eo•FUMP]R235A to productive ([EC•FUMP]R235A that is added to the barrier for conversion of [Eo•FUMP]R235A to product (ΔΔG‡kcat = 5 kcal/mol).
In summary, a mutation that destabilizes the closed form of wildtype OMPDC by weakening the interactions with the substrate phosphodianion will result in a decrease in substrate affinity (Figure 7A, Kd effect) up to the point where Kc = 1 and . A further destabilization of the closed enzyme will then be expressed as an increase in the barrier for conversion of EO•h-FUMP to the rate-determining transition state (Figure 7B, kex effect). The partitioning of the overall effect on kcat/Km or kex/Kd into effects on substrate binding and catalysis depends upon the initial value of Kc for the conformational change at the Michaelis complex, and we propose that this is more favorable for the binding and reaction of OMP compared with h-FUMP.
Stabilization of Vinyl Carbanion-Like Transition States
Binding interactions between the phosphodianion and the side chain cation of Arg235 provide a strong stabilization of the vinyl carbanion-like transition states for both enzyme-catalyzed decarboxylation and deuterium exchange reactions (Table 1). Similarly, interactions between the phosphodianion and exogenous guanidinium cation provide similar activation of R235A mutant enzyme-catalyzed decarboxylation and deuterium exchange reactions (Figure 4). This result is consistent with a similar stabilization of these two vinyl carbanion-like transition states by interaction with Gua+.13,14,20 This limited set of data show that the deuterium exchange and decarboxylation reactions catalyzed by this mutant OMPDC are activated to a similar degree by Gua+, and that the side-chain shows similar effective molarities in the two reactions.27
The apparent interaction of the cationic side chain of Arg235 with the transition state for the ScOMPDC-catalyzed deuterium exchange reaction (7.2 kcal/mol) is larger than the interaction with the transition state for the enzyme-catalyzed decarboxylation reaction (5.6 kcal/mol); but, the 5.6 kcal/mol interaction energy is 50% of the total 11.2 kcal/mol contribution of the phosphodianion binding energy to the stabilization of the decarboxylation transition state,18 while the 7.2 kcal/mol interaction is a larger 78% of the total 9.2 kcal/mol contribution of the phosphodianion binding energy to the stabilization of the exchange transition state.20
We speculate that the 2 kcal/mol larger phosphodianion binding energy utilized to stabilize the transition state for OMPDC-catalyzed decarboxylation of OMP compared with the deuterium exchange reaction of h-FUMP reflects the tighter fit of OMP at the enzyme active site. This minimizes the entropic cost to formation of a network of hydrogen bonding and ionic interactions with the substrate phosphodianion.48,49 We propose that there is a related greater cooperativity for FUMP compared with OMP in the expression of the phosphodianion binding interactions with the amino acid side chains of Gln215, Tyr217 and Arg235 (Figure 1); and, that the large 7.2 kcal/mol effect of the R235A mutation on the stability of the transition state for the deuterium exchange reaction of h-FUMP reflects not only the loss of the interactions with the excised side chain (≈ 5.6 kcal/mol determined for the reaction of OMP), but also a ca. 1.6 kcal/mol weakening of interactions between the phosphodianion and the side chains of the remaining gripper residues Gln215 and Tyr217 (Figure 1).50 Once again, the phosphodianion binding interactions are more fully maintained at the transition state for the R235A mutant ScOMPDC-catalyzed decarboxylation, compared with the deuterium exchange reaction, because the interactions between OMPDC and the pyrimidine carboxylate have the effect of reducing the entropy of the bound substrate by “locking” the ligand into a rigid reactive conformation.49
ScOMPDC-Catalyzed Decarboxylation of FOMP and FEO
The cationic side chain of Arg235 provides similar 5.6 and 5.8 kcal/mol stabilization, respectively, of the transition states for the ScOMPDC-catalyzed reactions of OMP and the substrate pieces EO + HPO32−, respectively; and, smaller but likewise similar, 2.6 and 3.1 kcal/mol stabilization of the transition states for the enzyme-catalyzed reactions of FOMP and the substrate pieces FEO + HPO32− (Table 3). The similar interaction of this side chain with the transition states for the reactions of the whole substrates OMP or FOMP and the corresponding substrate pieces EO + HPO32− or FEO + HPO32− is consistent with the conclusion that the transition states for reactions of related whole substrates and substrate pieces show essentially the same interaction with the protein catalyst.18–20,45 The main effect of this covalent attachment is to reduce the entropic barrier for the unimolecular reaction of the whole substrate, compared with the bimolecular reaction of the corresponding pieces.48,51
The difference in the stabilization of the transition states for ScOMPDC-catalyzed reactions of FOMP or FEO + HPO32− compared with OMP or EO + HPO32− by interaction with the cationic side chain of Arg235 reflects the different rate determining steps for the wildtype enzyme-catalyzed reactions of the two types of substrates.28,29,34 The values of the kinetic parameters kcat/Km (Table 1) or [(kcat/Km)E•Pi]/Kd] (Table 2) for the wildtype ScOMPDC-catalyzed reactions of OMP or EO + HPO32−, respectively, are limited by the rate of the chemical decarboxylation step, while these values for the wildtype enzyme-catalyzed reactions of FOMP or FEO + HPO32− are limited by rate constant for formation of the Michaelis complex to substrate.28,29,34 The effect of the loss of the side chain interaction at the R235A mutant enzyme is essentially entirely expressed as the change in the values of the kinetic parameters for the wildtype ScOMPDC-catalyzed reactions of substrates OMP or EO + HPO32−, for which the chemical step is rate determining. By comparison, the effect of the R235A mutation should not result in a decrease in kcat/Km or [(kcat/Km)E•Pi]/Kd] for the reactions of FOMP or FEO + HPO32−, until there is a change in the rate-determining step. Our results show that this change in rate determining step only occurs after there is a ca 3 kcal/mol increase in the barrier to the decarboxylation of enzyme-bound FOMP or FEO + HPO32.
Summary
We have rationalized these data by a model in which: (1) The Michaelis complex between FUMP and R235A mutant OMPDC exists mainly in the open conformation (Figure 7B), so that the interactions with the cationic side chain of R235 at wildtype OMPDC result mainly in an increase in kex for the deuterium exchange reaction (Figure 8). (2) The stabilizing interactions between OMPDC and the -CO2− group of OMP result in a shift in this conformational equilibrium to the closed form of OMPDC, so that the interactions with the cationic side chain of R235 at wildtype OMPDC now result mainly in a decrease in Km for decarboxylation (Figure 8). (3) The stabilizing interactions between OMPDC and the -CO2− group of OMP are utilized to immobilize the substrate in ScOMPDC: the removal of the -CO2− group results in a greater conformational flexibility of enzyme bound FUMP, a larger requirement for the utilization of the phosphodianion binding interactions to immobilize this substrate with the result that a smaller fraction of the total dianion binding energy is available to stabilize of the transition state for the ScOMPDC-catalyzed deuterium exchange reaction of FUMP compared with the OMPDC-catalyzed decarboxylation reaction.49
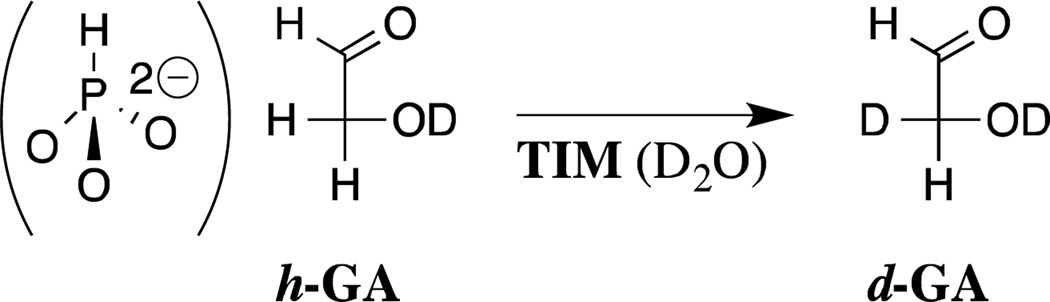
There are interesting differences in the mechanisms for the utilization of dianion binding interactions in the activation of triosephosphate isomerase for catalysis of the truncated substrate glycolaldehyde (GA, Scheme 6) and of OMPDC for catalysis of the decarboxylation and deuterium exchange reactions of EO and FEU, respectively (Scheme 2).18,20,22 The binding loci for the small carbon acid GA and for HPO32− are overlapping.52,53 The sites behave independently to the extent that some structural mutations, which have little effect on enzyme activation by phosphite dianion, result in a decrease in the enzyme reactivity towards deprotonation of glycolaldehyde.54 Binding of dianion activators to TIM triggers movement of active site loops 6 and loop 7. This places the active site base from Glu167 in a reactive conformation and swings the side chain of Ile172 towards the catalytic base,52,53 with the effect of shielding the substrate and the catalytic carboxylate from interaction with bulk solvent.52 The results of studies on the effect of the I172A mutation on the kinetic parameters for the TIM-catalyzed reactions of GA and HPO32− provide strong evidence for the conclusion that interactions between the hydrophobic side chain of I172 and the catalytic carboxylate from Glu167 activate TIM for catalysis of deprotonation of carbon by enhancing the basicity of this carboxylate ion.55–57
Scheme 6.
By comparison to TIM, the binding loci for EO and HPO32− are well separated at the active site of OMPDC. Binding of the dianion activator also triggers large movement of a phosphodianion gripper loop, but this loop appears too remote from the pyrimidine binding site to result in a large activation of OMPDC for catalysis of decarboxylation of EO (Figures 1 and 6). The results reported in this paper provide support for the conclusion that binding of the dianion activator triggers a much more extensive cooperative conformational change, which includes not only movement of the phosphodianion gripper loop but also the enzyme-activating closure of the pyrimidine umbrella. The dense network of hydrogen bonds that involve Ser154, from the pyrimidine umbrella, and Gln215, from the gripper loop should promote cooperative closure of these structural elements (Figure 6).2,45
Supplementary Material
Abbreviations
- ScOMPDC
orotidine 5'-monophosphate decarboxylase from Saccharomyces cerevisiae
- PRPP synthase
phosphoribosylpyrophosphate synthase
- ORTase
orotate phosphoribosyl transferase
- TIM
triosephosphate isomerase
- OMP
orotidine 5'-monophosphate
- UMP
uridine 5'-monophosphate
- FOMP
5-fluoroorotidine 5'-monophosphate
- FUMP
5-fluorouridine 5'-monophosphate
- h-FUMP
FUMP labeled with hydrogen at C-6
- d-FUMP
FUMP labeled with deuterium at C-6
- BMP
6-hydroxyuridine 5’-monophosphate EO, 1-(β-d-erythrofuranosyl)orotic acid
- EU
1-(β-d-erythrofuranosyl)uracil
- FEO
1-(β-d-erythrofuranosyl)-5-fluoroorotic acid
- FEU
1-(β-d-erythrofuranosyl)-5-fluorouracil
- Gua+
guanidinium cation
- GA
glycolaldehyde, LDA, lithium diisopropylamide
- BuLi
butyllithium
- THF
tetrahydrofuran
- MOPS
3-(N-morpholino)propanesulfonic acid
- NMR
nuclear magnetic resonance
Footnotes
This work was supported by Grants GM 039754 to J.P.R and GM 065155 to J.A.G. from the National Institutes of Health
SUPPORTING INFORMATION. Table S1: The UV-wavelengths monitored in determining the initial velocity data reported in Figure 2 for R235A ScOMPDC-catalyzed decarboxylation of OMP at different ionic strength. This material is available free of charge via the Internet at http://pubs.acs.org.
REFERENCES
- 1.Radzicka A, Wolfenden R. A proficient enzyme. Science. 1995;267:90–93. doi: 10.1126/science.7809611. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Miller BG, Hassell AM, Wolfenden R, Milburn MV, Short SA. Anatomy of a proficient enzyme: the structure of orotidine 5'-monophosphate decarboxylase in the presence and absence of a potential transition state analog. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2000;97:2011–2016. doi: 10.1073/pnas.030409797. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Sievers A, Wolfenden R. Equilibrium of Formation of the 6-Carbanion of UMP, a Potential Intermediate in the Action of OMP Decarboxylase. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002;124:13986–13987. doi: 10.1021/ja021073g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Wong FM, Capule CC, Wu W. Stability of the 6-Carbanion of Uracil Analogues: Mechanistic Implications for Model Reactions of Orotidine-5'-monophosphate Decarboxylase. Org. Lett. 2006;8:6019–6022. doi: 10.1021/ol0624981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Levine HL, Brody RS, Westheimer FH. Inhibition of orotidine-5'-phosphate decarboxylase by 1-(5'-phospho-β-D-ribofuranosyl)barbituric acid, 6-azauridine 5'-phosphate, and uridine 5'-phosphate. Biochemistry. 1980;19:4993–4999. doi: 10.1021/bi00563a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Houk KN, Lee JK, Tantillo DJ, Bahmanyar S, Hietbrink BN. Crystal structures of orotidine monophosphate decarboxylase: does the structure reveal the mechanism of nature's most proficient enzyme? ChemBioChem. 2001;2:113–118. doi: 10.1002/1439-7633(20010202)2:2<113::AID-CBIC113>3.0.CO;2-T. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Lee T-S, Chong LT, Chodera JD, Kollman PA. An alternative explanation for the catalytic proficiency of orotidine 5'-phosphate decarboxylase. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2001;123:12837–12848. doi: 10.1021/ja011096f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Silverman RB, Groziak MP. Model chemistry for a covalent mechanism of action of orotidine 5'-phosphate decarboxylase. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1982;104:6434–6439. [Google Scholar]
- 9.Beak P, Siegel B. Mechanism of decarboxylation of 1,3-dimethylorotic acid. A model for orotidine 5'-phosphate decarboxylase. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1976;98:3601–3606. doi: 10.1021/ja00428a035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Shostak K, Jones ME. Orotidylate decarboxylase: insights into the catalytic mechanism from substrate specificity studies. Biochemistry. 1992;31:12155–12161. doi: 10.1021/bi00163a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Appleby TC, Kinsland C, Begley TP, Ealick SE. The crystal structure and mechanism of orotidine 5'-monophosphate decarboxylase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2000;97:2005–2010. doi: 10.1073/pnas.259441296. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Lee JK, Houk KN. A proficient enzyme revisited: the predicted mechanism for orotidine monophosphate decarboxylase. Science (New York, NY) 1997;276:942–945. doi: 10.1126/science.276.5314.942. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Tsang W-Y, Wood BM, Wong FM, Wu W, Gerlt JA, Amyes TL, Richard JP. Proton Transfer from C-6 of Uridine 5'-Monophosphate Catalyzed by Orotidine 5'-Monophosphate Decarboxylase: Formation and Stability of a Vinyl Carbanion Intermediate and the Effect of a 5-Fluoro Substituent. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012;134:14580–14594. doi: 10.1021/ja3058474. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Amyes TL, Wood BM, Chan K, Gerlt JA, Richard JP. Formation and Stability of a Vinyl Carbanion at the Active Site of Orotidine 5'-Monophosphate Decarboxylase: pKa of the C-6 Proton of Enzyme-Bound UMP. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008;130:1574–1575. doi: 10.1021/ja710384t. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Chan KK, Wood BM, Fedorov AA, Fedorov EV, Imker HJ, Amyes TL, Richard JP, Almo SC, Gerlt JA. Mechanism of the Orotidine 5'-Monophosphate Decarboxylase-Catalyzed Reaction: Evidence for Substrate Destabilization. Biochemistry. 2009;48:5518–5531. doi: 10.1021/bi900623r. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Toth K, Amyes TL, Wood BM, Chan K, Gerlt JA, Richard JP. Product Deuterium Isotope Effects for Orotidine 5'-Monophosphate Decarboxylase: Effect of Changing Substrate and Enzyme Structure on the Partitioning of the Vinyl Carbanion Reaction Intermediate. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010;132:7018–7024. doi: 10.1021/ja102408k. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Toth K, Amyes TL, Wood BM, Chan K, Gerlt JA, Richard JP. Product Deuterium Isotope Effect for Orotidine 5'-Monophosphate Decarboxylase: Evidence for the Existence of a Short-Lived Carbanion Intermediate. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007;129:12946–12947. doi: 10.1021/ja076222f. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Amyes TL, Richard JP, Tait JJ. Activation of orotidine 5'-monophosphate decarboxylase by phosphite dianion: The whole substrate is the sum of two parts. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005;127:15708–15709. doi: 10.1021/ja055493s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Amyes TL, Ming SA, Goldman LM, Wood BM, Desai BJ, Gerlt JA, Richard JP. Orotidine 5'-monophosphate decarboxylase: Transition state stabilization from remote protein-phosphodianion interactions. Biochemistry. 2012;51:4630–4632. doi: 10.1021/bi300585e. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Goryanova B, Amyes TL, Gerlt JA, Richard JP. OMP Decarboxylase: Phosphodianion Binding Energy Is Used To Stabilize a Vinyl Carbanion Intermediate. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011;133:6545–6548. doi: 10.1021/ja201734z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Tsang W-Y, Amyes TL, Richard JP. A Substrate in Pieces: Allosteric Activation of Glycerol 3-Phosphate Dehydrogenase (NAD+) by Phosphite Dianion. Biochemistry. 2008;47:4575–4582. doi: 10.1021/bi8001743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Amyes TL, Richard JP. Enzymatic catalysis of proton transfer at carbon: activation of triosephosphate isomerase by phosphite dianion. Biochemistry. 2007;46:5841–5854. doi: 10.1021/bi700409b. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Amyes TL, O'Donoghue AC, Richard JP. Contribution of phosphate intrinsic binding energy to the enzymatic rate acceleration for triosephosphate isomerase. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2001;123:11325–11326. doi: 10.1021/ja016754a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Richard JP. A Paradigm for Enzyme-Catalyzed Proton Transfer at Carbon: Triosephosphate Isomerase. Biochemistry. 2012;51:2652–2661. doi: 10.1021/bi300195b. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Amyes TL, Richard JP. Specificity in Transition State Binding: The Pauling Model Revisited. Biochemistry. 2013;52:2021–2035. doi: 10.1021/bi301491r. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Miller BG, Snider MJ, Short SA, Wolfenden R. Contribution of Enzyme-Phosphoribosyl Contacts to Catalysis by Orotidine 5'-Phosphate Decarboxylase. Biochemistry. 2000;39:8113–8118. doi: 10.1021/bi000818x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Barnett SA, Amyes TL, McKay Wood B, Gerlt JA, Richard JP. Activation of R235A Mutant Orotidine 5'-Monophosphate Decarboxylase by the Guanidinium Cation: Effective Molarity of the Cationic Side Chain of Arg-235. Biochemistry. 2010;49:824–826. doi: 10.1021/bi902174q. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Goryanova B, Spong K, Amyes TL, Richard JP. Catalysis by Orotidine 5'-Monophosphate Decarboxylase: Effect of 5-Fluoro and 4'-Substituents on the Decarboxylation of Two-Part Substrates. Biochemistry. 2013;52:537–546. doi: 10.1021/bi301650d. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Wood BM, Chan KK, Amyes TL, Richard JP, Gerlt JA. Mechanism of the Orotidine 5'-Monophosphate Decarboxylase-Catalyzed Reaction: Effect of Solvent Viscosity on Kinetic Constants. Biochemistry. 2009;48:5510–5517. doi: 10.1021/bi9006226. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Bhatia MB, Vinitsky A, Grubmeyer C. Kinetic Mechanism of Orotate Phosphoribosyltransferase from Salmonella typhimurium. Biochemistry. 1990;29:10480–10487. doi: 10.1021/bi00498a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Hove-Jensen B. Cloning and characterization of the prs gene encoding phosphoribosylpyrophosphate synthetase of Escherichia coli. Mol. Gen. Genet. 1985;201:269–276. doi: 10.1007/BF00425670. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Tolbert TJ, Williamson JR. Preparation of specifically deuterated RNA for NMR studies using a combination of chemical and enzymatic synthesis. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1996;118:7929–7940. [Google Scholar]
- 33.Bower SG, Harlow KW, Switzer RL, Hove-Jensen B. Characterization of the Escherichia coli prsA1-encoded Mutant Phosphoribosylpyrophosphate Synthetase Identifies a Divalent Cation-Nucleotide Binding Site. J. Biol. Chem. 1989;264:10287–10291. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Van Vleet JL, Reinhardt LA, Miller BG, Sievers A, Cleland WW. Carbon isotope effect study on orotidine 5'-monophosphate decarboxylase: support for an anionic intermediate. Biochemistry. 2008;47:798–803. doi: 10.1021/bi701664n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Gross A, Abril O, Lewis JM, Geresh S, Whitesides GM. Practical synthesis of 5-phospho-D-ribosyl α-1-pyrophosphate (PRPP): enzymatic routes from ribose 5-phosphate or ribose. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013;105:7428–7435. [Google Scholar]
- 36.Glasoe PK, Long FA. Use of glass electrodes to measure acidities in deuterium oxide. J. Phys. Chem. 1960;64:188–190. [Google Scholar]
- 37.Gasteiger E, Gattiker A, Hoogland C, Ivanyi I, Appel RD, Bairoch A. ExPASy: The proteomics server for in-depth protein knowledge and analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003;31:3784–3788. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkg563. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Toth K, Amyes TL, Wood BM, Chan KK, Gerlt JA, Richard JP. An Examination of the Relationship between Active Site Loop Size and Thermodynamic Activation Parameters for Orotidine 5'-Monophosphate Decarboxylase from Mesophilic and Thermophilic Organisms. Biochemistry. 2009;48:8006–8013. doi: 10.1021/bi901064k. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Barnett SA. Ph.D. Thesis. Buffalo, New York: University at Buffalo; 2009. Studies on the Mechanism of Action of Orotidine 5'-Monophosphate Decarboxylase. [Google Scholar]
- 40.Hartman F, Lamuraglia G, Tomozawa Y, Wolfenden R. Influence of pH on the interaction of inhibitors with triosephosphate isomerase and determination of the pKa of the active-site carboxyl group. Biochemistry. 1975;14:5274–5279. doi: 10.1021/bi00695a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Nolte H-J, Rosenberry TL, Neumann E. Effective charge on acetylcholinesterase active sites determined from the ionic strength dependence of association rate constants with cationic ligands. Biochemistry. 1980;19:3705–3711. doi: 10.1021/bi00557a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Porter DJT, Short SA. Yeast Orotidine-5'-Phosphate Decarboxylase: Steady-State and Pre-Steady-State Analysis of the Kinetic Mechanism of Substrate Decarboxylation. Biochemistry. 2000;39:11788–11800. doi: 10.1021/bi001199v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Malabanan MM, Amyes TL, Richard JP. A role for flexible loops in enzyme catalysis. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2010;20:702–710. doi: 10.1016/j.sbi.2010.09.005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Go MK, Amyes TL, Richard JP. Hydron Transfer Catalyzed by Triosephosphate Isomerase. Products of the Direct and Phosphite-Activated Isomerization of [1-13C]-Glycolaldehyde in D2O. Biochemistry. 2009;48:5769–5778. doi: 10.1021/bi900636c. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Barnett SA, Amyes TL, Wood BM, Gerlt JA, Richard JP. Dissecting the Total Transition State Stabilization Provided by Amino Acid Side Chains at Orotidine 5'-Monophosphate Decarboxylase: A Two-Part Substrate Approach. Biochemistry. 2008;47:7785–7787. doi: 10.1021/bi800939k. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Warshel A. Electrostatic Origin of the Catalytic Power of Enzymes and the Role of Preorganized Active Sites. J. Biol. Chem. 1998;273:27035–27038. doi: 10.1074/jbc.273.42.27035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Cannon WR, Benkovic SJ. Solvation, Reorganization Energy, and Biological Catalysis. J. Biol. Chem. 1998;273:26257–26260. doi: 10.1074/jbc.273.41.26257. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Jencks WP. On the attribution and additivity of binding energies. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 1981;78:4046–4050. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.7.4046. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Adams H, Chekmeneva E, Hunter CA, Misuraca MC, Navarro C, Turega SM. Quantification of the Effect of Conformational Restriction on Supramolecular Effective Molarities. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013;135:1853–1863. doi: 10.1021/ja310221t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Horovitz A, Fersht AR. Strategy for analyzing the cooperativity of intramolecular interactions in peptides and proteins. J. Mol. Biol. 1990;214:613–617. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(90)90275-Q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Page MI, Jencks WP. Entropic contributions to rate accelerations in enzymic and intramolecular reactions and the chelate effect. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. U. S. 1971;68:1678–1683. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.8.1678. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Kursula I, Wierenga RK. Crystal structure of triosephosphate isomerase complexed with 2-phosphoglycolate at 0.83-Åresolution. J. Biol. Chem. 2003;278:9544–9551. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M211389200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Jogl G, Rozovsky S, McDermott AE, Tong L. Optimal alignment for enzymatic proton transfer: structure of the Michaelis complex of triosephosphate isomerase at 1.2-Å resolution. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2003;100:50–55. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0233793100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Zhai X, Amyes TL, Wierenga RK, Loria JP, Richard JP. Structural Mutations That Probe the Interactions between the Catalytic and Dianion Activation Sites of Triosephosphate Isomerase. Biochemistry. 2013;52:5928–5940. doi: 10.1021/bi401019h. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Malabanan MM, Nitsch-Velasquez L, Amyes TL, Richard JP. Magnitude and origin of the enhanced basicity of the catalytic glutamate of triosephosphate isomerase. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013;135:5978–5981. doi: 10.1021/ja401504w. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Malabanan MM, Koudelka AP, Amyes TL, Richard JP. Mechanism for Activation of Triosephosphate Isomerase by Phosphite Dianion: The Role of a Hydrophobic Clamp. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012;134:10286–10298. doi: 10.1021/ja303695u. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Richard JP. The Enhancement of Enzymic Rate Accelerations by Brøsted Acid-Base Catalysis. Biochemistry. 1998;37:4305–4309. doi: 10.1021/bi972655r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.