Abstract
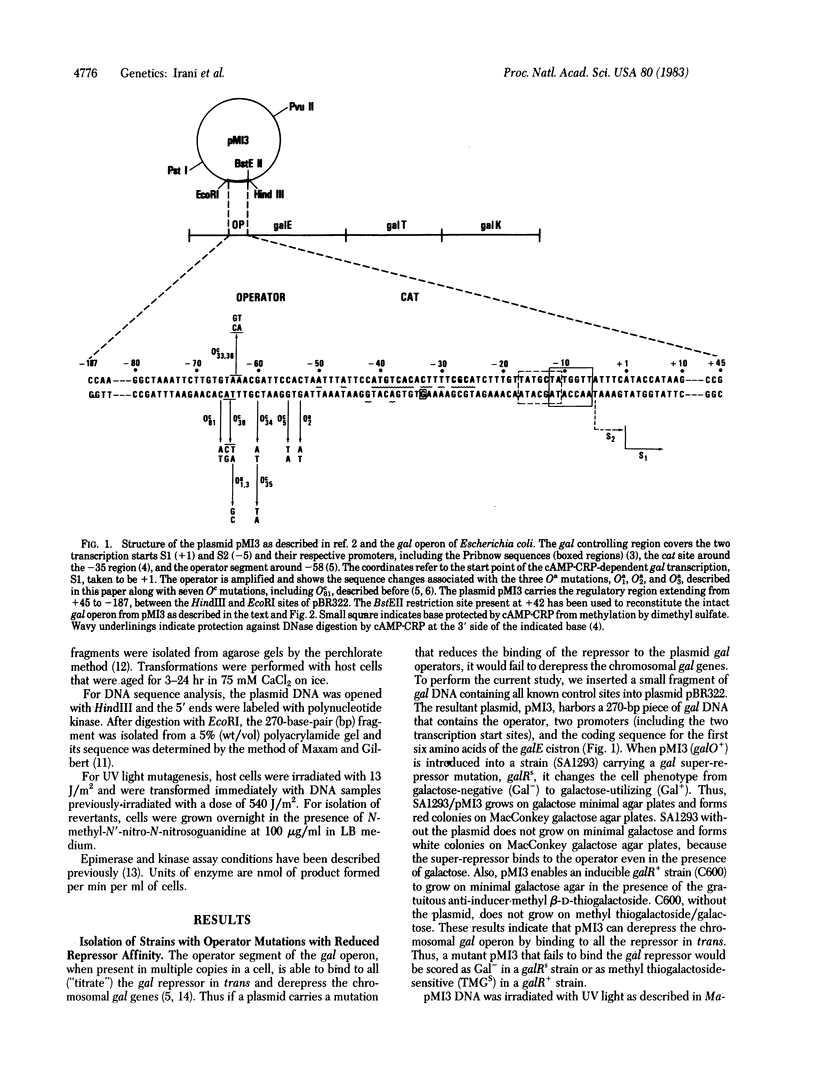
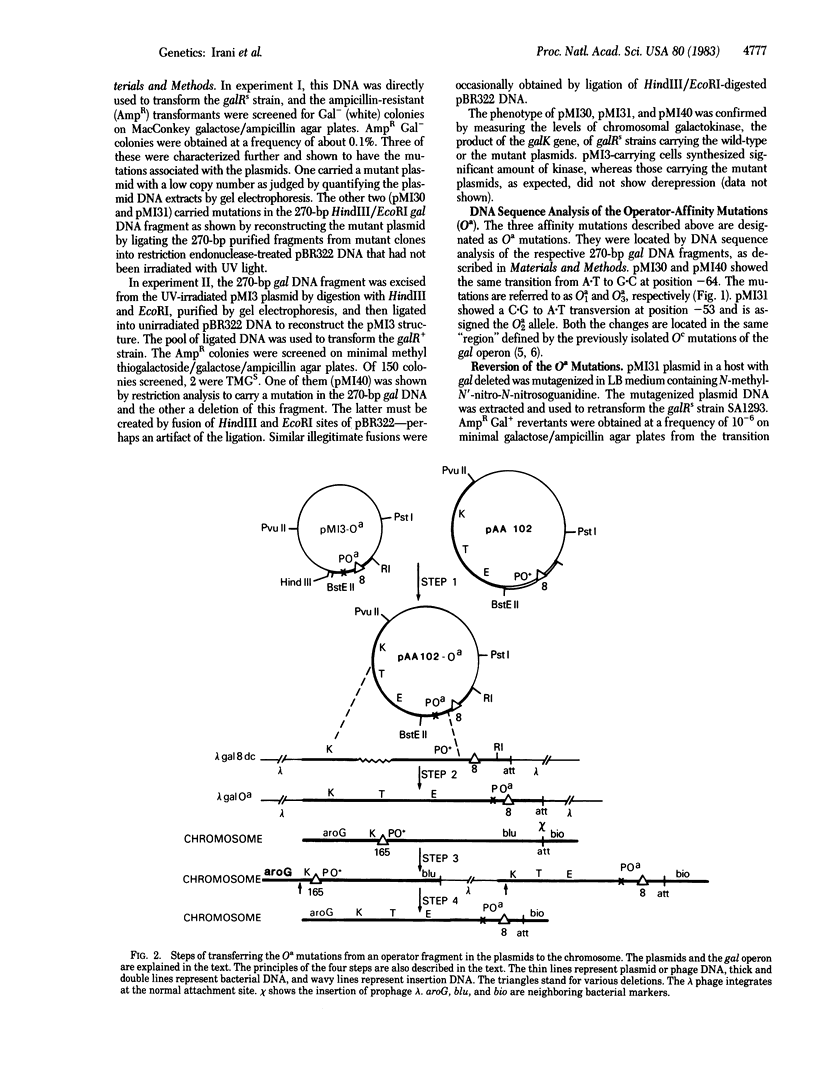
When the gal operator region is present in a multicopy plasmid it binds to all ("titrates") the gal repressor and "induces" the chromosomal gal operon. To make operator mutations (Oa) with reduced affinity toward the repressor, plasmid DNA was irradiated with UV light and mutant derivatives were isolated that were unable to release the chromosomal gal genes from repression. Then with such an Oa plasmid operator revertants were isolated that had reacquired the ability to release repression. Both sets of mutations have been localized by DNA sequence analysis. When the Oa mutations were transferred from the plasmid to the chromosome by recombination these mutant operators were found to make gal expression constitutive (independent of repressor) but still dependent on cAMP, whereas the previously reported gal operator mutants (Oc) are constitutive both in the presence and in the absence of cAMP. The titration method of isolating mutants enables the isolation of strains with operator mutations that also affect normal promoter activity, and it provides an easy way to isolate revertants of operator mutations.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adhya S., Miller W. Modulation of the two promoters of the galactose operon of Escherichia coli. Nature. 1979 Jun 7;279(5713):492–494. doi: 10.1038/279492a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aiba H., Adhya S., de Crombrugghe B. Evidence for two functional gal promoters in intact Escherichia coli cells. J Biol Chem. 1981 Nov 25;256(22):11905–11910. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BUTTIN G. M'ECANISMES R'EGULATEURS DANS LA BIOSYNTH'ESE DES ENZYMES DU M'ETABOLISME DU GALACTOSE CHEZ ESCHERICHIA COLI K12. II. LE D'ETERMINISME G'EN'ETIQUE DE LA R'EGULATION. J Mol Biol. 1963 Aug;7:183–205. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(63)80045-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Busby S., Irani M., Crombrugghe B. Isolation of mutant promoters in the Escherichia coli galactose operon using local mutagenesis on cloned DNA fragments. J Mol Biol. 1982 Jan 15;154(2):197–209. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90060-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen C. W., Thomas C. A., Jr Recovery of DNA segments from agarose gels. Anal Biochem. 1980 Jan 15;101(2):339–341. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90197-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiLauro R., Taniguchi T., Musso R., de Crombrugghe B. Unusual location and function of the operator in the Escherichia coli galactose operon. Nature. 1979 Jun 7;279(5713):494–500. doi: 10.1038/279494a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irani M. H., Orosz L., Adhya S. A control element within a structural gene: the gal operon of Escherichia coli. Cell. 1983 Mar;32(3):783–788. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90064-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Musso R. E., Di Lauro R., Adhya S., de Crombrugghe B. Dual control for transcription of the galactose operon by cyclic AMP and its receptor protein at two interspersed promoters. Cell. 1977 Nov;12(3):847–854. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90283-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakanishi S., Adhya S., Gottesman M., Pastan I. Studies on the mechanism of action of the gal repressor. J Biol Chem. 1973 Sep 10;248(17):5937–5942. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nisseley S. P., Anderson W. B., Gottesman M. E., Perlman R. L., Pastan I. In vitro transcription of the gal operon requires cyclic adenosine monophosphate and cyclic adenosine monophosphate receptor protein. J Biol Chem. 1971 Aug 10;246(15):4671–4678. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taniguchi T., O'Neill M., de Crombrugghe B. Interaction site of Escherichia coli cyclic AMP receptor protein on DNA of galactose operon promoters. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):5090–5094. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.5090. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullmann A., Joseph E., Danchin A. Cyclic AMP as a modulator of polarity in polycistronic transcriptional units. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jul;76(7):3194–3197. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.7.3194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willard M., Echols H. Role of bacteriophage DNA replication in lambda-dg escape synthesis. J Mol Biol. 1968 Feb 28;32(1):37–46. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90143-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto T., Sobel M. E., Adams S. L., Avvedimento V. E., DiLauro R., Pastan I., de Crombrugghe B., Showalter A., Pesciotta D., Fietzek P. Construction of a recombinant bacterial plasmid containing pro-alpha 1(I) collagen DNA sequences. J Biol Chem. 1980 Mar 25;255(6):2612–2615. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



