Abstract
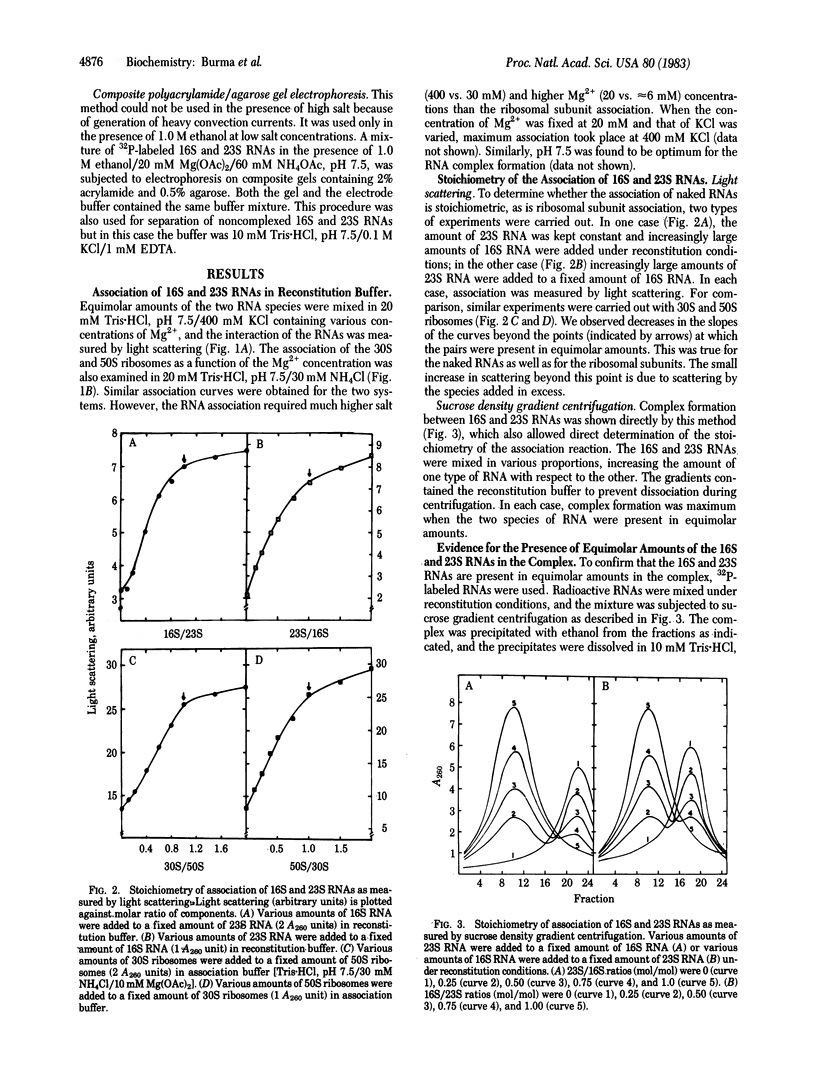
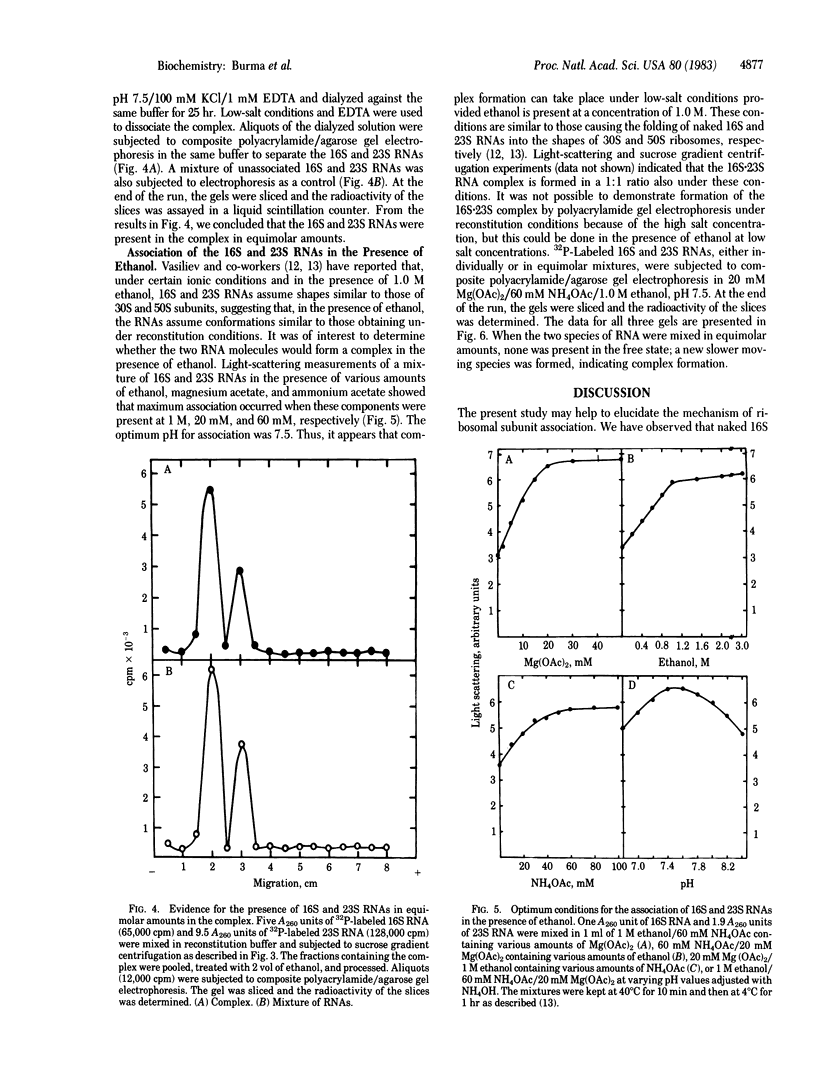
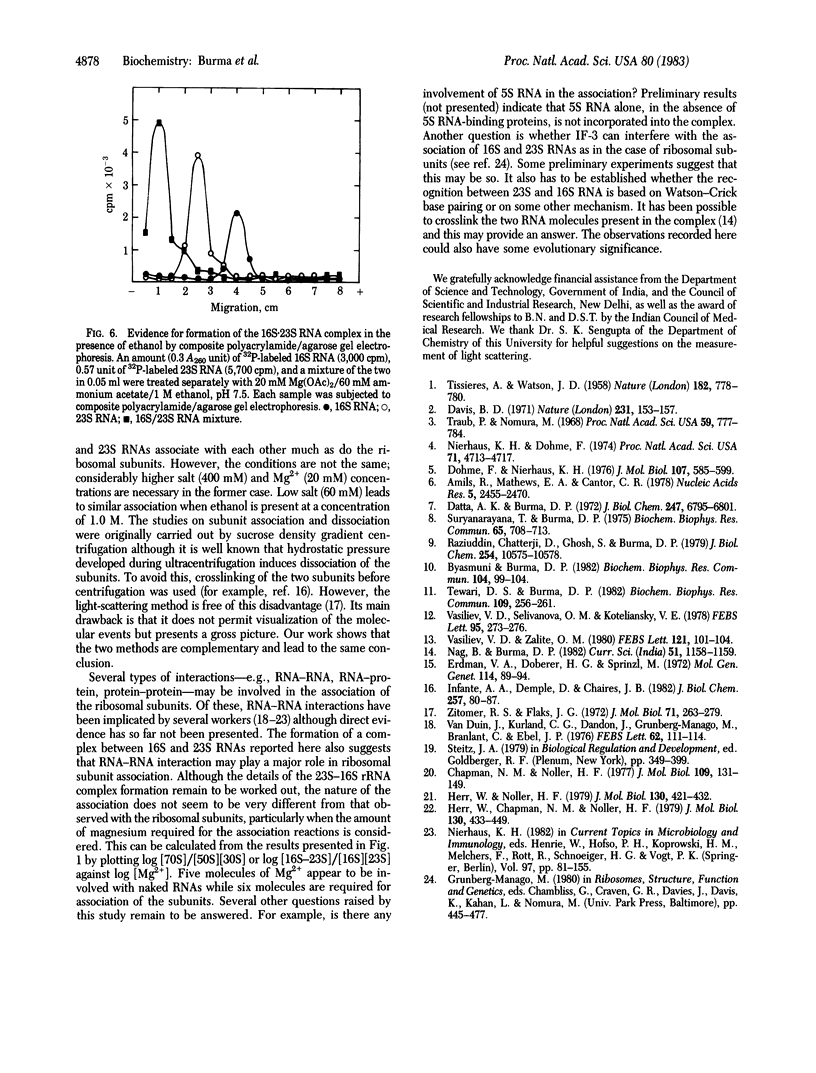
Association of the 30S and 50S subunits to generate the 70S ribosomes of Escherichia coli has long been known but the mechanism of this interaction remains obscure. Light-scattering studies indicate that naked 16S and 23S RNAs can also associate under conditions similar to those required for the assembly of ribosomes from the constituent RNAs and proteins. The RNA-RNA association also takes place in the presence of ethanol, which promotes folding of 16S and 23S RNAs into specific compact structures with the morphological features of 30S and 50S ribosomes, respectively. Equimolar amounts of the two RNAs are involved in the association. The formation of a stoichiometric complex was shown by light scattering, sucrose density gradient centrifugation, and composite polyacrylamide/agarose gel electrophoresis. The presence of the two species of RNA in the complex was also shown by gel electrophoresis. The association of naked 16S and 23S RNAs suggests that RNA-RNA interaction may play an important role in the association of 30S and 50S subunits.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amils R., Matthews E. A., Cantor C. R. An efficient in vitro total reconstitution of the Escherichia coli 50S ribosomal subunit. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Jul;5(7):2455–2470. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.7.2455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byasmuni, Burma D. P. Structural alteration of rRNA in the L7/L12 region of 50s ribosome on removal of L7/L12 proteins. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Jan 15;104(1):99–104. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)91945-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapman N. M., Noller H. F. Protection of specific sites in 16 S RNA from chemical modification by association of 30 S and 50 S ribosomes. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jan 5;109(1):131–149. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(77)80049-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Datta A. K., Burma D. P. Association of ribonuclease I with ribosomes and their subunits. J Biol Chem. 1972 Nov 10;247(21):6795–6801. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis B. D. Role of subunits in the ribosome cycle. Nature. 1971 May 21;231(5299):153–157. doi: 10.1038/231153a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dohme F., Nierhaus K. H. Total reconstitution and assembly of 50 S subunits from Escherichia coli Ribosomes in vitro. J Mol Biol. 1976 Nov 15;107(4):585–599. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(76)80085-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erdmann V. A., Doberer H. G. Structure and function of 5S RNA: the role of the 3' terminus in 5S RNA function. Mol Gen Genet. 1972;114(2):89–94. doi: 10.1007/BF00332779. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herr W., Chapman N. M., Noller H. F. Mechanism of ribosomal subunit association: discrimination of specific sites in 16 S RNA essential for association activity. J Mol Biol. 1979 Jun 5;130(4):433–449. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90433-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herr W., Noller H. F. Protection of specific sites in 23 S and 5 S RNA from chemical modification by association of 30 S and 50 S ribosomes. J Mol Biol. 1979 Jun 5;130(4):421–432. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90432-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Infante A. A., Demple B., Chaires J. B. Analysis of the Escherichia coli ribosome-ribosomal subunit equilibrium using pressure-induced dissociation. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jan 10;257(1):80–87. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nierhaus K. H., Dohme F. Total reconstitution of functionally active 50S ribosomal subunits from Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Dec;71(12):4713–4717. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.12.4713. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raziuddin, Chatterji D., Ghosh S., Burma D. P. Site of action of RNase I on the 50 S ribosome of Escherichia coli and the association of the enzyme with the partially degraded subunit. J Biol Chem. 1979 Nov 10;254(21):10575–10578. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suryanarayana T., Burma D. P. Effects of intercalating agents on the structure of the ribosome. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Jul 22;65(2):708–713. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(75)80203-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TISSIERES A., WATSON J. D. Ribonucleoprotein particles from Escherichia coli. Nature. 1958 Sep 20;182(4638):778–780. doi: 10.1038/182778b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tewari D. S., Burma D. P. 5S RNA may not have highly ordered structure like 4S RNAS. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Nov 16;109(1):256–261. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)91593-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traub P., Nomura M. Structure and function of E. coli ribosomes. V. Reconstitution of functionally active 30S ribosomal particles from RNA and proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Mar;59(3):777–784. doi: 10.1073/pnas.59.3.777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Duin J., Kurland C. G., Dondon J., Grunberg-Mangago M., Branlant C., Ebel J. P. New aspects of the IF3-ribosome interaction. FEBS Lett. 1976 Feb 15;62(2):111–114. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(76)80030-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vasiliev V. D., Selivanova O. M., Koteliansky V. E. Specific selfpacking of the ribosomal 16 S RNA. FEBS Lett. 1978 Nov 15;95(2):273–276. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)81009-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vasiliev V. D., Zalite O. M. Specific compact selfpacking of the ribosomal 23 S RNA. FEBS Lett. 1980 Nov 17;121(1):101–104. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)81275-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zitomer R. S., Flaks J. G. Magnesium dependence and equilibrium of the Escherichia coli ribosomal subunit association. J Mol Biol. 1972 Nov 14;71(2):263–279. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90350-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


