Abstract
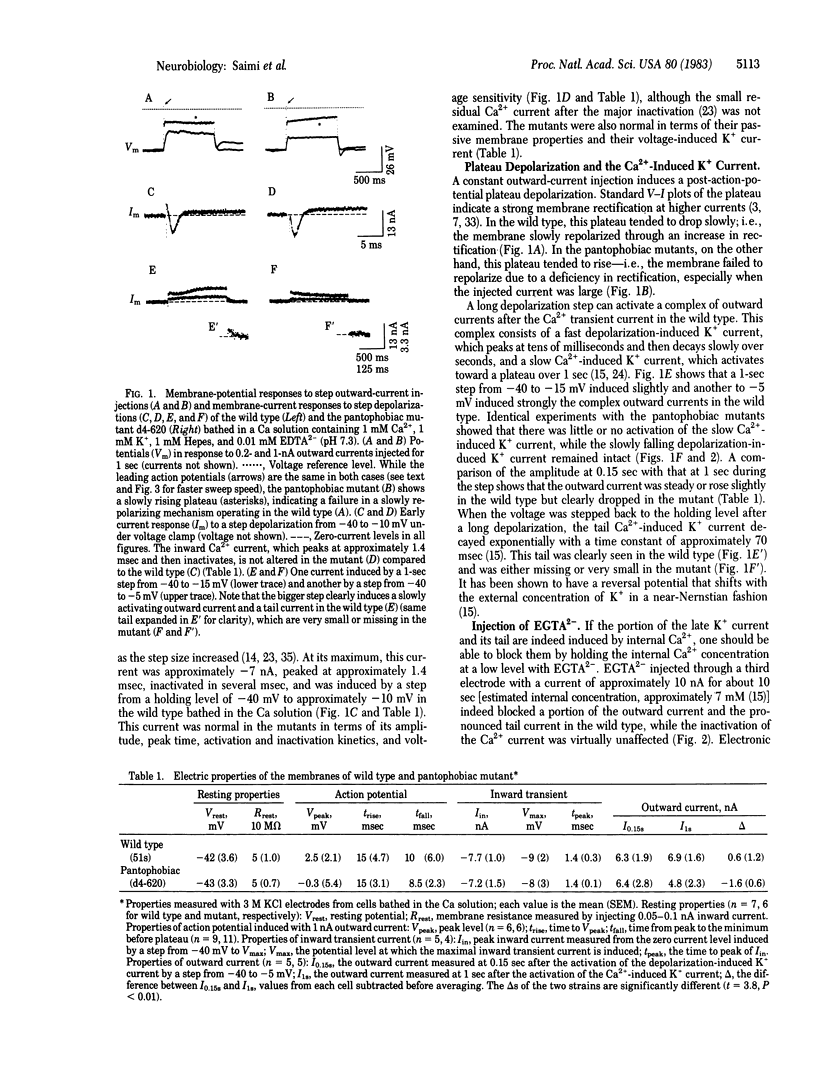
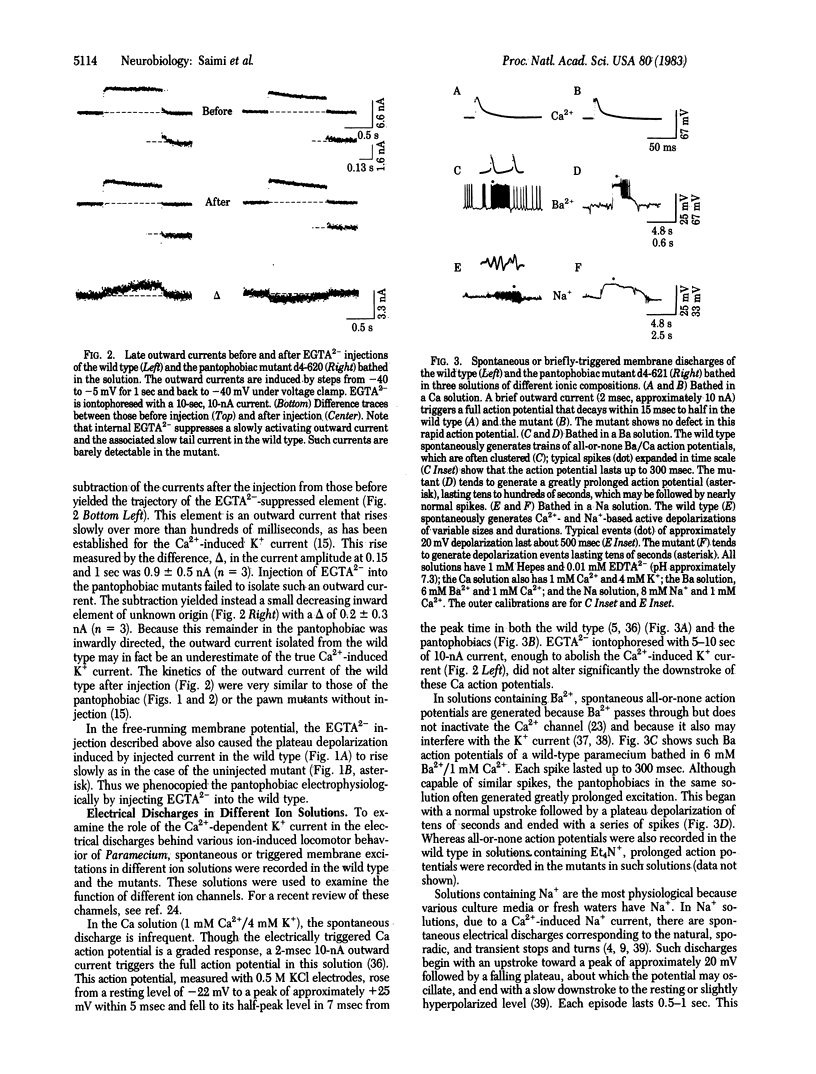
Two mutants of Paramecium tetraurelia, called "pantophobiacs," were found to lack most of the slow Ca2+-induced K+ outward current. Passive properties, the transient Ca2+ inward current, and the fast depolarization-induced K+ outward current remain normal. The mutant defect reduces the ability to shut off a normal, excited state of the membrane and results in repeated, long backward swimming instead of the wild-type jerks in response to a variety of ions, to heat, and to touch.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adoutte A., Ling K. Y., Forte M., Ramanathan R., Nelson D., Kung C. Ionic channels of Paramecium: from genetics and electrophysiology to biochemistry. J Physiol (Paris) 1981 May;77(9):1145–1159. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong C. M., Swenson R. P., Jr, Taylor S. R. Block of squid axon K channels by internally and externally applied barium ions. J Gen Physiol. 1982 Nov;80(5):663–682. doi: 10.1085/jgp.80.5.663. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brehm P., Dunlap K., Eckert R. Calcium-dependent repolarization in Paramecium. J Physiol. 1978 Jan;274:639–654. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Browning J. L., Nelson D. L., Hansma H. G. Ca2+ influx across the excitable membrane of behavioural mutants of Paramecium. Nature. 1976 Feb 12;259(5543):491–494. doi: 10.1038/259491a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eckert R., Brehm P. Ionic mechanisms of excitation in Paramecium. Annu Rev Biophys Bioeng. 1979;8:353–383. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.08.060179.002033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forte M., Satow Y., Nelson D., Kung C. Mutational alteration of membrane phospholipid composition and voltage-sensitive ion channel function in paramecium. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Nov;78(11):7195–7199. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.11.7195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman A. L., Hermann A., Thomas M. V. Ionic requirements for membrane oscillations and their dependence on the calcium concentration in a molluscan pace-maker neurone. J Physiol. 1982 Jun;327:185–217. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haga N., Forte M., Saimi Y., Kung C. Microinjection of cytoplasm as a test of complementation in Paramecium. J Cell Biol. 1982 Feb;92(2):559–564. doi: 10.1083/jcb.92.2.559. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall J. C. Genetics of the nervous system in Drosophila. Q Rev Biophys. 1982 May;15(2):223–479. doi: 10.1017/s0033583500004844. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kung C., Chang S. Y., Satow Y., Houten J. V., Hansma H. Genetic dissection of behavior in paramecium. Science. 1975 May 30;188(4191):898–904. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kung C., Eckert R. Genetic modification of electric properties in an excitable membrane (paramecium-calcium conductance-electrophysiological measurements-membrane mutant). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jan;69(1):93–97. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.1.93. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kung C. Genic mutants with altered system of excitation in Paramecium aurelia. II. Mutagenesis, screening and genetic analysis of the mutants. Genetics. 1971 Sep;69(1):29–45. doi: 10.1093/genetics/69.1.29. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kung C., Saimi Y. The physiological basis of taxes in Paramecium. Annu Rev Physiol. 1982;44:519–534. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.44.030182.002511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Latorre R., Vergara C., Hidalgo C. Reconstitution in planar lipid bilayers of a Ca2+-dependent K+ channel from transverse tubule membranes isolated from rabbit skeletal muscle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Feb;79(3):805–809. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.3.805. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ling K. Y., Kung C. Ba2+ influx measures the duration of membrane excitation in Paramecium. J Exp Biol. 1980 Feb;84:73–87. doi: 10.1242/jeb.84.1.73. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meech R. W. Calcium-dependent potassium activation in nervous tissues. Annu Rev Biophys Bioeng. 1978;7:1–18. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.07.060178.000245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merkel S. J., Kaneshiro E. S., Gruenstein E. I. Characterization of the cilia and ciliary membrane proteins of wild-type Paramecium tetraurelia and a pawn mutant. J Cell Biol. 1981 May;89(2):206–215. doi: 10.1083/jcb.89.2.206. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naitoh Y., Eckert R., Friedman K. A regenerative calcium response in Paramecium. J Exp Biol. 1972 Jun;56(3):667–681. doi: 10.1242/jeb.56.3.667. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naitoh Y., Eckert R. Ionic mechanisms controlling behavioral responses of paramecium to mechanical stimulation. Science. 1969 May 23;164(3882):963–965. doi: 10.1126/science.164.3882.963. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oertel D., Schein S. J., Kung C. Separation of membrane currents using a Paramecium mutant. Nature. 1977 Jul 14;268(5616):120–124. doi: 10.1038/268120a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saimi Y., Kung C. A Ca-induced Na-current in Paramecium. J Exp Biol. 1980 Oct;88:305–325. doi: 10.1242/jeb.88.1.305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saimi Y., Kung C. Are ions involved in the gating of calcium channels? Science. 1982 Oct 8;218(4568):153–156. doi: 10.1126/science.6289432. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Satow Y. Internal calcium concentration and potassium permeability in Paramecium. J Neurobiol. 1978 Jan;9(1):81–91. doi: 10.1002/neu.480090107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Satow Y., Kung C. A 'TEA+-insensitive' mutant with increased potassium conductance in Paramecium aurelia. J Exp Biol. 1976 Aug;65(1):51–63. doi: 10.1242/jeb.65.1.51. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Satow Y., Kung C. Ca-induced K+-outward current in Paramecium tetraurelia. J Exp Biol. 1980 Oct;88:293–303. doi: 10.1242/jeb.88.1.293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Satow Y., Kung C. Genetic dissection of active electrogenesis in Paramecium aurelia. Nature. 1974 Jan 4;247(5435):69–71. doi: 10.1038/247069a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Satow Y., Kung C. Membrane currents of pawn mutants of the pwA group in Paramecium tetraurelia. J Exp Biol. 1980 Feb;84:57–71. doi: 10.1242/jeb.84.1.57. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Satow Y., Kung C. Possible reduction of surface charge by a mutation in Paramecium tetraurelia. J Membr Biol. 1981 Apr 30;59(3):179–190. doi: 10.1007/BF01875424. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwarz W., Passow H. Ca2+-activated K+ channels in erythrocytes and excitable cells. Annu Rev Physiol. 1983;45:359–374. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.45.030183.002043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi M., Naitoh Y. Behavioural mutants of Paramecium caudatum with defective membranes electrogenesis. Nature. 1978 Feb 16;271(5646):656–659. doi: 10.1038/271656a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thiele J., Schultz J. E. Ciliary membrane vesicles of paramecium contain the voltage-sensitive calcium channel. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3688–3691. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3688. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


