Abstract
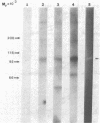
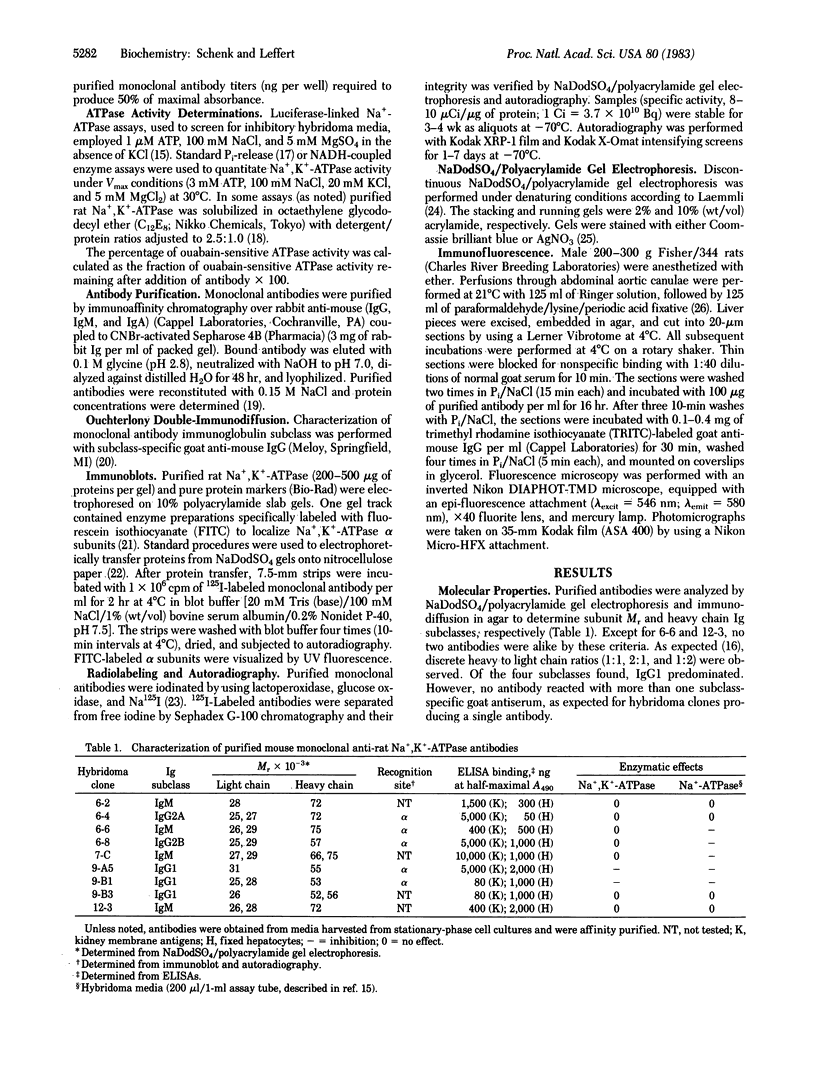
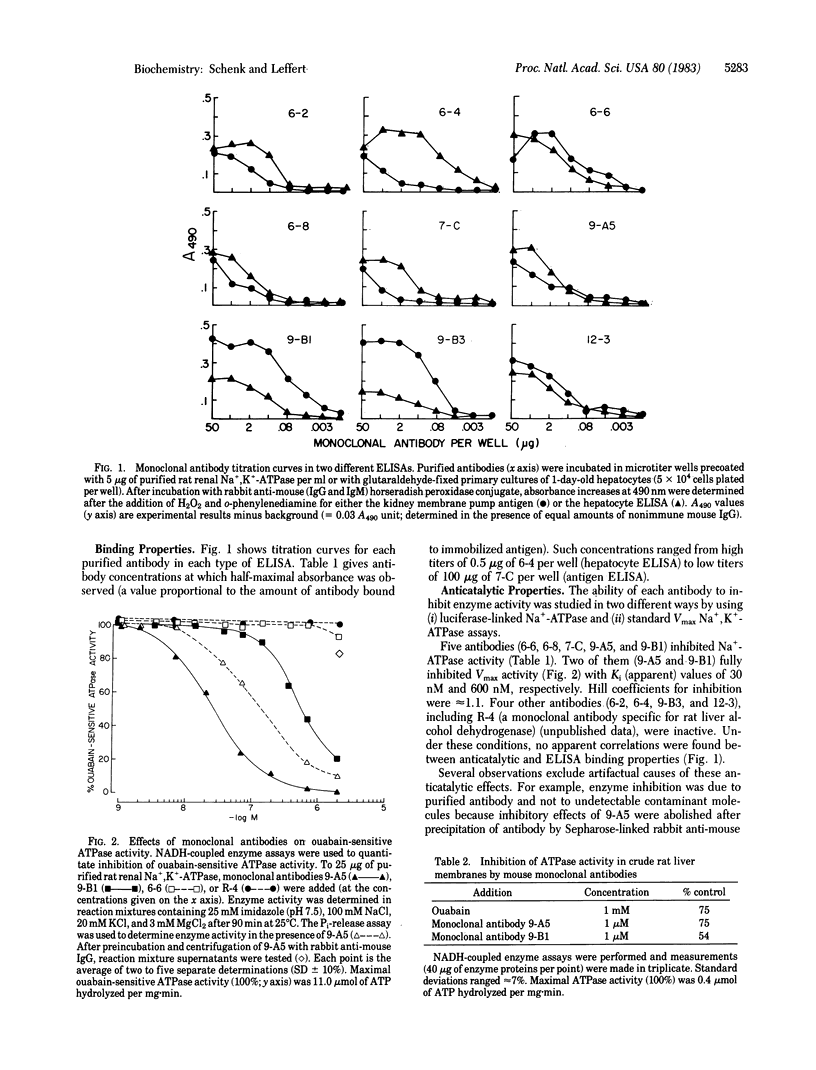
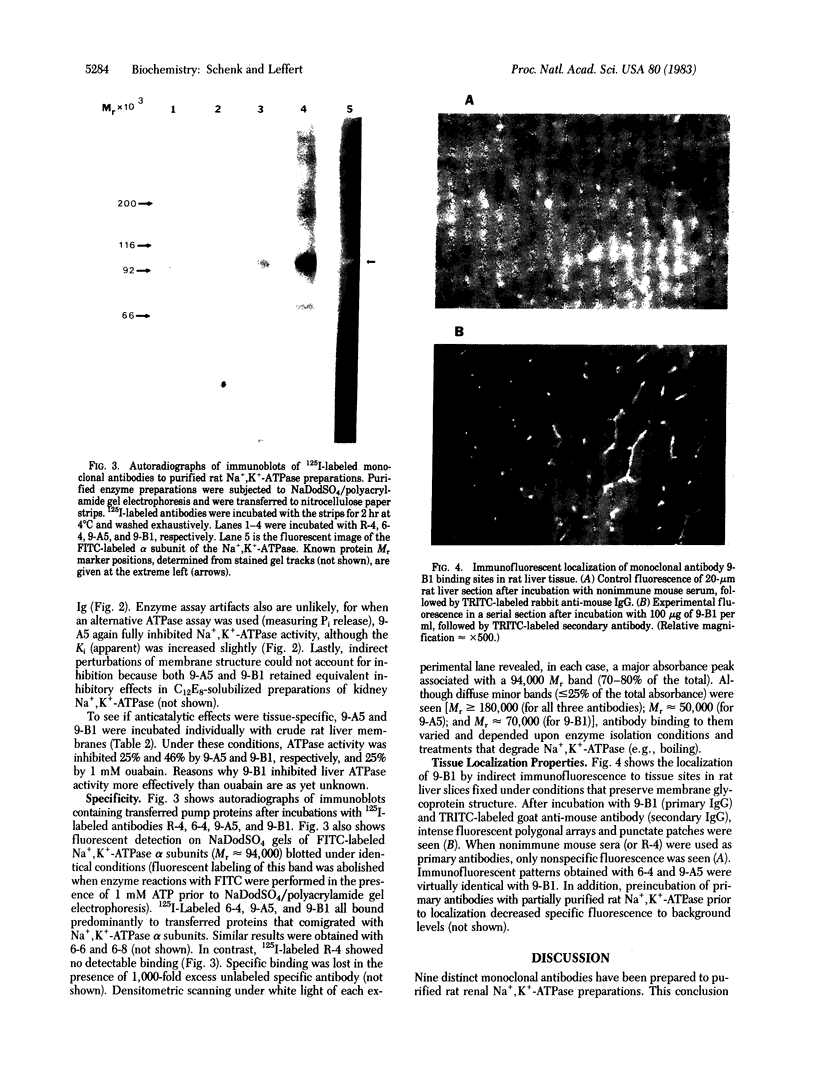
A panel of nine mouse monoclonal antibodies has been prepared against purified preparations of rat kidney Na+,K+-ATPase (EC 3.6.1.3). Selection for specific antibody was based upon the ability of crude hybridoma fluids to inhibit Na+-ATPase activity (using luciferase-linked ATPase assays) and upon antibody binding to both the purified kidney membrane enzyme and to glutaraldehyde-fixed hepatocytes by using standard enzyme-linked immunoadsorbent assays. After immunoaffinity purification, two of the antibodies (both of the IgG1 subclass) fully inhibit kidney and liver membrane Na+,K+-ATPase activity with Ki (apparent) values of 30 nM ("9-A5") and 600 nM ("9-B1"). Immunoblots demonstrate directly that three different 125I-labeled antibodies (6-4, 9-A5, and 9-B1) bind predominantly to a 94,000 Mr protein that comigrates in NaDodSO4/polyacrylamide gels with the fluorescein isothiocyanate-labeled alpha subunit of the Na+,K+-ATPase. Indirect immunofluorescence studies with these antibodies on paraformaldehyde-fixed liver slices reveal staining patterns congruent with bile canalicular membrane domains. These results together suggest that the antibodies exert inhibitory effects by recognizing alpha subunits of both liver and kidney Na+ pumps in their native conformations.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baker P. F., Willis J. S. Binding of the cardiac glycoside ouabain to intact cells. J Physiol. 1972 Jul;224(2):441–462. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009904. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ball W. J., Schwartz A., Lessard J. L. Isolation and characterization of monoclonal antibodies to (Na+ + K+)-ATPase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Dec 17;719(3):413–423. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(82)90228-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blitzer B. L., Boyer J. L. Cytochemical localization of Na+, K+-ATPase in the rat hepatocyte. J Clin Invest. 1978 Nov;62(5):1104–1108. doi: 10.1172/JCI109216. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnette W. N. "Western blotting": electrophoretic transfer of proteins from sodium dodecyl sulfate--polyacrylamide gels to unmodified nitrocellulose and radiographic detection with antibody and radioiodinated protein A. Anal Biochem. 1981 Apr;112(2):195–203. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90281-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carilli C. T., Farley R. A., Perlman D. M., Cantley L. C. The active site structure of Na+- and K+-stimulated ATPase. Location of a specific fluorescein isothiocyanate reactive site. J Biol Chem. 1982 May 25;257(10):5601–5606. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craig W. S. Determination of the distribution of sodium and potassium ion activated adenosinetriphosphatase among the various oligomers formed in solutions of nonionic detergents. Biochemistry. 1982 May 25;21(11):2667–2674. doi: 10.1021/bi00540a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galfrè G., Milstein C. Preparation of monoclonal antibodies: strategies and procedures. Methods Enzymol. 1981;73(Pt B):3–46. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(81)73054-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graf E., Verma A. K., Gorski J. P., Lopaschuk G., Niggli V., Zurini M., Carafoli E., Penniston J. T. Molecular properties of calcium-pumping ATPase from human erythrocytes. Biochemistry. 1982 Aug 31;21(18):4511–4516. doi: 10.1021/bi00261a049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jorgensen P. L. Purification and characterization of (Na+ plus K+ )-ATPase. 3. Purification from the outer medulla of mammalian kidney after selective removal of membrane components by sodium dodecylsulphate. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Jul 12;356(1):36–52. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(74)90292-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch K. S., Leffert H. L. Increased sodium ion influx is necessary to initiate rat hepatocyte proliferation. Cell. 1979 Sep;18(1):153–163. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90364-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyte J. Purification of the sodium- and potassium-dependent adenosine triphosphatase from canine renal medulla. J Biol Chem. 1971 Jul 10;246(13):4157–4165. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leffert H. L., Koch K. S., Fehlmann M., Heiser W., Lad P. J., Skelly H. Amiloride blocks cell-free protein synthesis at levels attained inside cultured rat hepatocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Sep 30;108(2):738–745. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)90891-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Low M. G., Finean J. B. Specific release of plasma membrane enzymes by a phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Apr 20;508(3):565–570. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(78)90100-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lubin M., Cahn F., Coutermarsh B. A. Amiloride, protein synthesis, and activation of quiescent cells. J Cell Physiol. 1982 Nov;113(2):247–251. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041130210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mancini G., Carbonara A. O., Heremans J. F. Immunochemical quantitation of antigens by single radial immunodiffusion. Immunochemistry. 1965 Sep;2(3):235–254. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(65)90004-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCans J. L., Lindenmayer G. E., Pitts B. J., Ray M. V., Raynor B. D., Butler V. P., Jr, Schwartz A. Antigenic differences in (Na+, K+)-ATPase preparations isolated from various organs and species. J Biol Chem. 1975 Sep 25;250(18):7257–7265. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLean I. W., Nakane P. K. Periodate-lysine-paraformaldehyde fixative. A new fixation for immunoelectron microscopy. J Histochem Cytochem. 1974 Dec;22(12):1077–1083. doi: 10.1177/22.12.1077. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrissey J. H. Silver stain for proteins in polyacrylamide gels: a modified procedure with enhanced uniform sensitivity. Anal Biochem. 1981 Nov 1;117(2):307–310. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90783-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mummery C. L., Boonstra J., van der Saag P. T., de Laat S. W. Modulations of Na+ transport during the cell cycle of neuroblastoma cells. J Cell Physiol. 1982 Jul;112(1):27–34. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041120106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neville D. M., Jr Isolation of an organ specific protein antigen from cell-surface membrane of rat liver. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Apr 9;154(3):540–552. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(68)90014-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhee H. M., Hokin L. E. Inhibition of ouabain-binding to (Na+ + K+)ATPase by antibody against the catalytic subunit but not by antibody against the glycoprotein subunit. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Nov 16;558(1):108–112. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(79)90319-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson J. D., Flashner M. S. The (Na+ + K+)-activated ATPase. Enzymatic and transport properties. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Aug 17;549(2):145–176. doi: 10.1016/0304-4173(79)90013-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rozengurt E., Mendoza S. Monovalent ion fluxes and the control of cell proliferation in cultured fibroblasts. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1980;339:175–190. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1980.tb15977.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sachs G., Chang H. H., Rabon E., Schackman R., Lewin M., Saccomani G. A nonelectrogenic H+ pump in plasma membranes of hog stomach. J Biol Chem. 1976 Dec 10;251(23):7690–7698. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schenk D. B., Grosse R., Ellisman M. H., Bradshaw V., Leffert H. L. (Na+,K+)-ATPase: a new assay of Na+-ATPase reveals covert anti-pump antibodies. Anal Biochem. 1982 Sep 1;125(1):189–196. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90401-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz A., Allen J. C., Harigaya S. Possible involvement of cardiac Na+, K+-adenosine triphosphatase in the mechanism of action of cardiac glycosides. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1969 Jul;168(1):31–41. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trowbridge I. S., Ralph P., Bevan M. J. Differences in the surface proteins of mouse B and T cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jan;72(1):157–161. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.1.157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]