Abstract
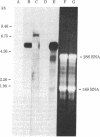
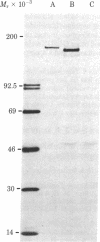
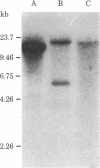
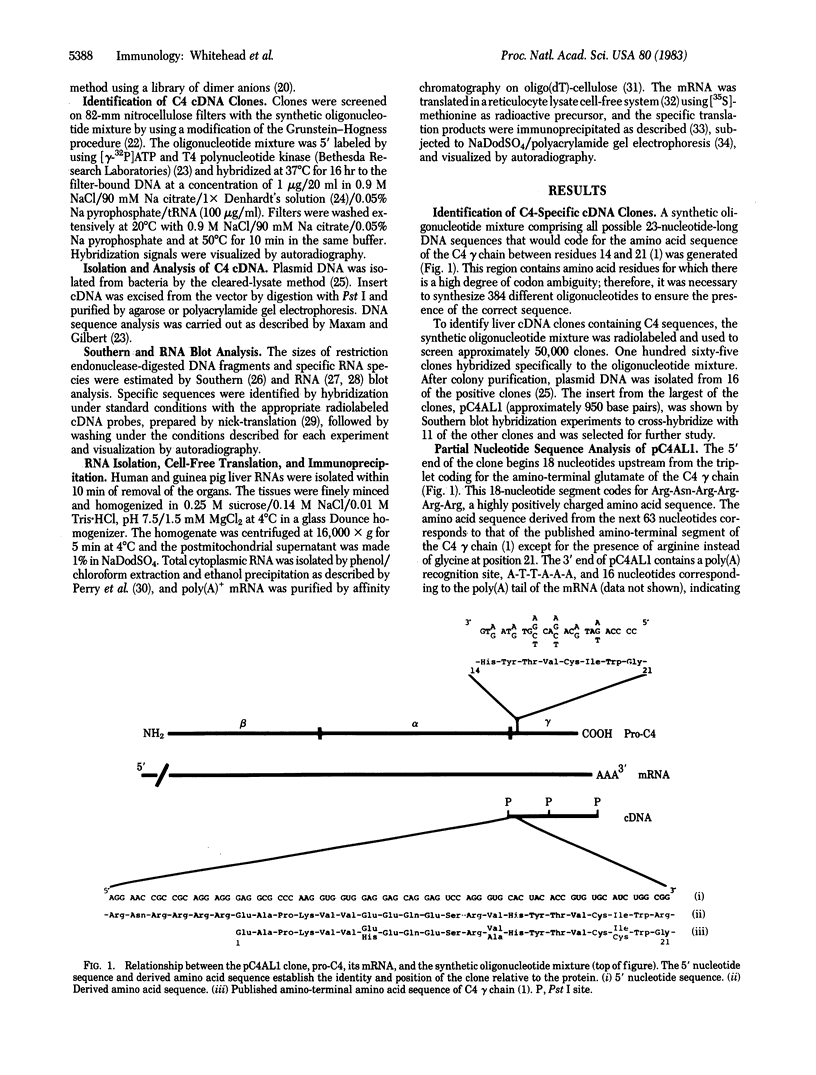
A cDNA clone for the fourth complement component (C4), pC4AL1, has been isolated from a human adult liver cDNA library by using a synthetic oligonucleotide mixture containing all 384 possible sequences coding for residues 14-21 of the C4 gamma-chain amino acid sequence. This clone spans the entire C4 gamma-chain coding sequence and includes a short 3' untranslated region, a poly(A) recognition site, and 16 nucleotides of the poly(A) tail. The 5' end of the clone begins 18 nucleotides upstream from the amino terminus of the C4 gamma chain and codes for Arg-Asn-Arg-Arg-Arg-Arg, a highly charged proteolytic cleavage site involved in the processing of pro-C4 to native C4. Liver mRNA preparations from C4-deficient guinea pigs were incapable of directing synthesis of pro-C4 or C4 peptides in cell-free translation experiments. Southern blot analysis using pC4AL1 as a hybridization probe of C4-deficient guinea pig DNA established that the deficiency is not the result of deletion of the entire C4 gene. RNA blot analysis using pC4AL1 as a hybridization probe of normal guinea pig liver mRNA revealed a C4 mRNA of 5.0 kilobases (kb). No such mRNA species was observed in C4-deficient guinea pig liver mRNA; however, a 7.0-kb RNA was detected, indicating the presence of a C4 precursor RNA. These results suggest that the basis of C4 deficiency in the guinea pig is a post-transcriptional defect in the processing of C4 precursor RNA to mature C4 mRNA.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aviv H., Leder P. Purification of biologically active globin messenger RNA by chromatography on oligothymidylic acid-cellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1408–1412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Awdeh Z. L., Alper C. A. Inherited polymorphism of human C4 as revealed by desialyzation. Immunobiology. 1980;158(1-2):35–41. doi: 10.1016/s0171-2985(80)80035-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carroll M. C., Porter R. R. Cloning of a human complement component C4 gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(1):264–267. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.1.264. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clewell D. B., Helinski D. R. Supercoiled circular DNA-protein complex in Escherichia coli: purification and induced conversion to an opern circular DNA form. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Apr;62(4):1159–1166. doi: 10.1073/pnas.62.4.1159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colten H. R. Biosynthesis of the MHC-linked complement proteins (C2, C4 and factor B) by mononuclear phagocytes. Mol Immunol. 1982 Oct;19(10):1279–1285. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(82)90294-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colten H. R., Frank M. M. Biosynthesis of the second (C2) and fourth (C4) components of complement in vitro by tissues isolated from guinea-pigs with genetically determined C4 deficiency. Immunology. 1972 Jun;22(6):991–999. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denhardt D. T. A membrane-filter technique for the detection of complementary DNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1966 Jun 13;23(5):641–646. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(66)90447-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Domdey H., Wiebauer K., Kazmaier M., Müller V., Odink K., Fey G. Characterization of the mRNA and cloned cDNA specifying the third component of mouse complement. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(24):7619–7623. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.24.7619. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellman L., Green I., Frank M. Genetically controlled total deficiency of the fourth component of complement in the guinea pig. Science. 1970 Oct 2;170(3953):74–75. doi: 10.1126/science.170.3953.74. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira A., Takahashi M., Nussenzweig V. Purificaiton and characterization of mouse serum protein with specific binding affinity for C4 (Ss protein). J Exp Med. 1977 Oct 1;146(4):1001–1008. doi: 10.1084/jem.146.4.1001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fey G., Colten H. R. Biosynthesis of complement components. Fed Proc. 1981 May 15;40(7):2099–2104. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gigli I. A single chain precursor of C4 in human serum. Nature. 1978 Apr 27;272(5656):836–837. doi: 10.1038/272836a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg D. A. Isolation and partial characterization of the Drosophila alcohol dehydrogenase gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Oct;77(10):5794–5798. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.10.5794. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberger G., Abraham G. N., Williams J., Colten H. R. NH2-terminal sequence analysis of pro-C4, the precursor of the fourth component of guinea pig complement. J Biol Chem. 1980 Aug 10;255(15):7071–7074. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberger G., Colten H. R. Precursor complement protein (pro-C4) is converted in vitro to native C4 by plasmin. Nature. 1980 Jul 31;286(5772):514–516. doi: 10.1038/286514a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberger G., Thomas M. L., Tack B. F., Williams J., Colten H. R., Abraham G. N. NH2-terminal structure and cleavage of guinea pig pro-C3, the precursor of the third complement component. J Biol Chem. 1981 Dec 25;256(24):12617–12619. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross-Bellard M., Oudet P., Chambon P. Isolation of high-molecular-weight DNA from mammalian cells. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Jul 2;36(1):32–38. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb02881.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grunstein M., Hogness D. S. Colony hybridization: a method for the isolation of cloned DNAs that contain a specific gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Oct;72(10):3961–3965. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.10.3961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall R. E., Colten H. R. Cell-free synthesis of the fourth component of guinea pig complement (C4): identification of a precursor of serum C4 (pro-C4). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Apr;74(4):1707–1710. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.4.1707. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall R. E., Colten H. R. Genetic defect in biosynthesis of the precursor form of the fourth component of complement. Science. 1978 Jan 6;199(4324):69–70. doi: 10.1126/science.199.4324.69. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeffreys A. J., Flavell R. A. A physical map of the DNA regions flanking the rabbit beta-globin gene. Cell. 1977 Oct;12(2):429–439. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90119-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrach H., Diamond D., Wozney J. M., Boedtker H. RNA molecular weight determinations by gel electrophoresis under denaturing conditions, a critical reexamination. Biochemistry. 1977 Oct 18;16(21):4743–4751. doi: 10.1021/bi00640a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. A new method for sequencing DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):560–564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Neill G. J., Yang S. Y., Dupont B. Two HLA-linked loci controlling the fourth component of human complement. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Oct;75(10):5165–5169. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.10.5165. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker K. L., Roos M. H., Shreffler D. C. Structural characterization of the murine fourth component of complement and sex-limited protein and their precursors: evidence for two loci in the S region of the H-2 complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Nov;76(11):5853–5857. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.11.5853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker K. L., Shreffler D. C., Capra J. D. Partial amino acid sequences of the murine fourth component of complement (C4): demonstration of homology with human C4 and identification of the amino-terminal subunit in pro-C4. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):4275–4278. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.4275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. R., Jackson R. J. An efficient mRNA-dependent translation system from reticulocyte lysates. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Aug 1;67(1):247–256. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10656.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry R. P., La Torre J., Kelley D. E., Greenberg J. R. On the lability of poly(A) sequences during extraction of messenger RNA from polyribosomes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Mar 14;262(2):220–226. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(72)90236-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter R. R., Reid K. B. Activation of the complement system by antibody-antigen complexes: the classical pathway. Adv Protein Chem. 1979;33:1–71. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60458-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothenberg E., Boyse E. A. Synthesis and processing of molecules bearing thymus leukemia antigen. J Exp Med. 1979 Oct 1;150(4):777–791. doi: 10.1084/jem.150.4.777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreiber R. D., Müller-Eberhard H. J. Fourth component of human complement: description of a three polypeptide chain structure. J Exp Med. 1974 Nov 1;140(5):1324–1335. doi: 10.1084/jem.140.5.1324. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shreffler D C, Owen R D. A Serologically Detected Variant in Mouse Serum: Inheritance and Association with the Histocompatibility-2 Locus. Genetics. 1963 Jan;48(1):9–25. doi: 10.1093/genetics/48.1.9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl G. M., Stern M., Stark G. R. Efficient transfer of large DNA fragments from agarose gels to diazobenzyloxymethyl-paper and rapid hybridization by using dextran sulfate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):3683–3687. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.3683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woods D. E., Markham A. F., Ricker A. T., Goldberger G., Colten H. R. Isolation of cDNA clones for the human complement protein factor B, a class III major histocompatibility complex gene product. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Sep;79(18):5661–5665. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.18.5661. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]