Abstract
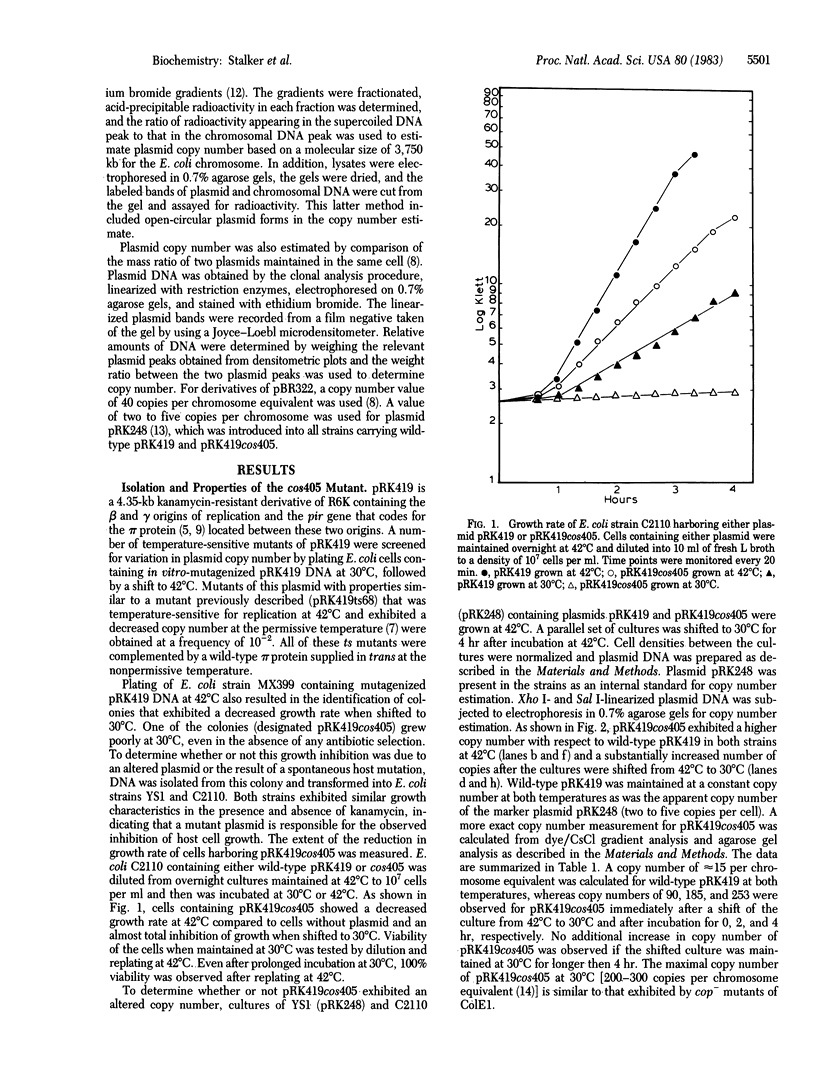
Plasmid pRK419, a derivative of the naturally occurring antibiotic resistance plasmid R6K, contains the pir gene that codes for the pi initiation protein and the beta and gamma replication origins of R6K. A mutation in plasmid pRK419, designated cos405, results in an elevated plasmid copy number in Escherichia coli growing at 42 degrees C and an even greater increase in copy number when the cells are shifted to 30 degrees C. This mutation was assigned to the structural gene for the pi protein on the basis of suppression of the mutant phenotype in E. coli when the wild-type pi protein is supplied in trans. Nucleotide sequence analysis of the cos405 mutant confirmed the pir gene location of the mutation and showed that this mutation results in a single amino acid substitution (glycine to aspartic acid) at the 81st position of the 305-amino acid pi protein. The properties of this mutant suggest that the pi protein plays a role in the negative control of the frequency of R6K initiation in addition to its requirement for the initiation of plasmid replication.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Germino J., Bastia D. The replication initiator protein of plasmid R6K tagged with beta-galactosidase shows sequence-specific DNA-binding. Cell. 1983 Jan;32(1):131–140. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90503-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inuzuka M., Helinski D. R. Requirement of a plasmid-encoded protein for replication in vitro of plasmid R6K. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Nov;75(11):5381–5385. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.11.5381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inuzuka N., Inuzuka M., Helinski D. R. Activity in vitro of three replication origins of the antibiotic resistance plasmid RSF1040. J Biol Chem. 1980 Dec 10;255(23):11071–11074. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn M., Kolter R., Thomas C., Figurski D., Meyer R., Remaut E., Helinski D. R. Plasmid cloning vehicles derived from plasmids ColE1, F, R6K, and RK2. Methods Enzymol. 1979;68:268–280. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)68019-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kellenberger-Gujer G., Podhajska A. J., Caro L. A cold sensitive dnaA mutant of E. coli which overinitiates chromosome replication at low temperature. Mol Gen Genet. 1978 Jun 1;162(1):9–16. doi: 10.1007/BF00333845. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolter R., Helinski D. R. Activity of the replication terminus of plasmid R6K in hybrid replicons in Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1978 Sep 25;124(3):425–441. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90180-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolter R., Helinski D. R. Construction of plasmid R6K derivatives in vitro: characterization of the R6K replication region. Plasmid. 1978 Sep;1(4):571–580. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(78)90014-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolter R., Inuzuka M., Helinski D. R. Trans-complementation-dependent replication of a low molecular weight origin fragment from plasmid R6K. Cell. 1978 Dec;15(4):1199–1208. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90046-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kontomichalou P., Mitani M., Clowes R. C. Circular R-factor molecules controlling penicillinase synthesis, replicating in Escherichia coli under either relaxed or stringent control. J Bacteriol. 1970 Oct;104(1):34–44. doi: 10.1128/jb.104.1.34-44.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muesing M., Tamm J., Shepard H. M., Polisky B. A single base-pair alteration is responsible for the DNA overproduction phenotype of a plasmid copy-number mutant. Cell. 1981 Apr;24(1):235–242. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90519-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noiman E. S. Phosphorylation of smooth muscle myosin light chains by cAMP-dependent protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1980 Dec 10;255(23):11067–11070. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shafferman A., Kolter R., Stalker D., Helinski D. R. Plasmid R6K DNA replication. III. Regulatory properties of the pi initiation protein. J Mol Biol. 1982 Oct 15;161(1):57–76. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90278-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stalker D. M., Kolter R., Helinski D. R. Plasmid R6K DNA replication. I. Complete nucleotide sequence of an autonomously replicating segment. J Mol Biol. 1982 Oct 15;161(1):33–43. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90276-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stougaard P., Molin S., Nordström K. RNAs involved in copy-number control and incompatibility of plasmid R1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Oct;78(10):6008–6012. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.10.6008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas C. M., Meyer R., Helinski D. R. Regions of broad-host-range plasmid RK2 which are essential for replication and maintenance. J Bacteriol. 1980 Jan;141(1):213–222. doi: 10.1128/jb.141.1.213-222.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uhlin B. E., Nordström K. A runaway-replication mutant of plasmid R1drd-19: temperature-dependent loss of copy number control. Mol Gen Genet. 1978 Oct 4;165(2):167–179. doi: 10.1007/BF00269904. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




