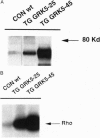
Abstract
Transgenic mice were generated with cardiac-specific overexpression of the G protein-coupled receptor kinase-5 (GRK5), a serine/threonine kinase most abundantly expressed in the heart compared with other tissues. Animals overexpressing GRK5 showed marked beta-adrenergic receptor desensitization in both the anesthetized and conscious state compared with nontransgenic control mice, while the contractile response to angiotensin II receptor stimulation was unchanged. In contrast, the angiotensin II-induced rise in contractility was significantly attenuated in transgenic mice overexpressing the beta-adrenergic receptor kinase-1, another member of the GRK family. These data suggest that myocardial overexpression of GRK5 results in selective uncoupling of G protein-coupled receptors and demonstrate that receptor specificity of the GRKs may be important in determining the physiological phenotype.
Full text
PDF

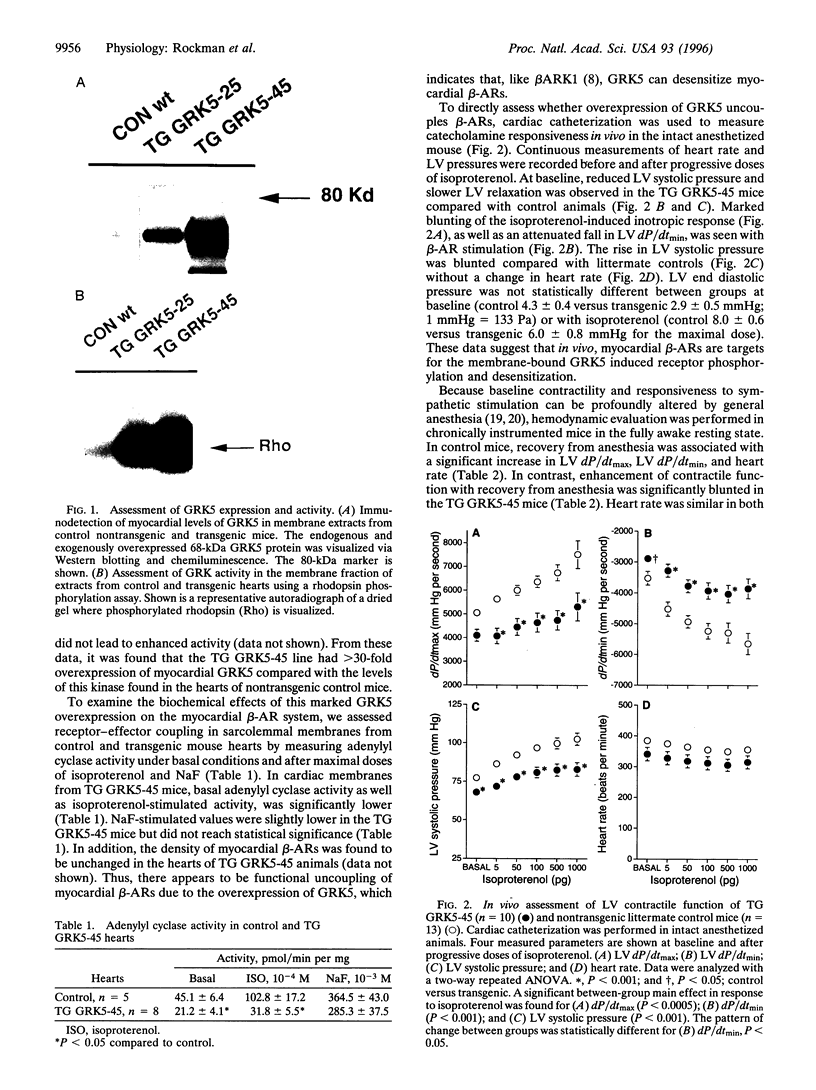
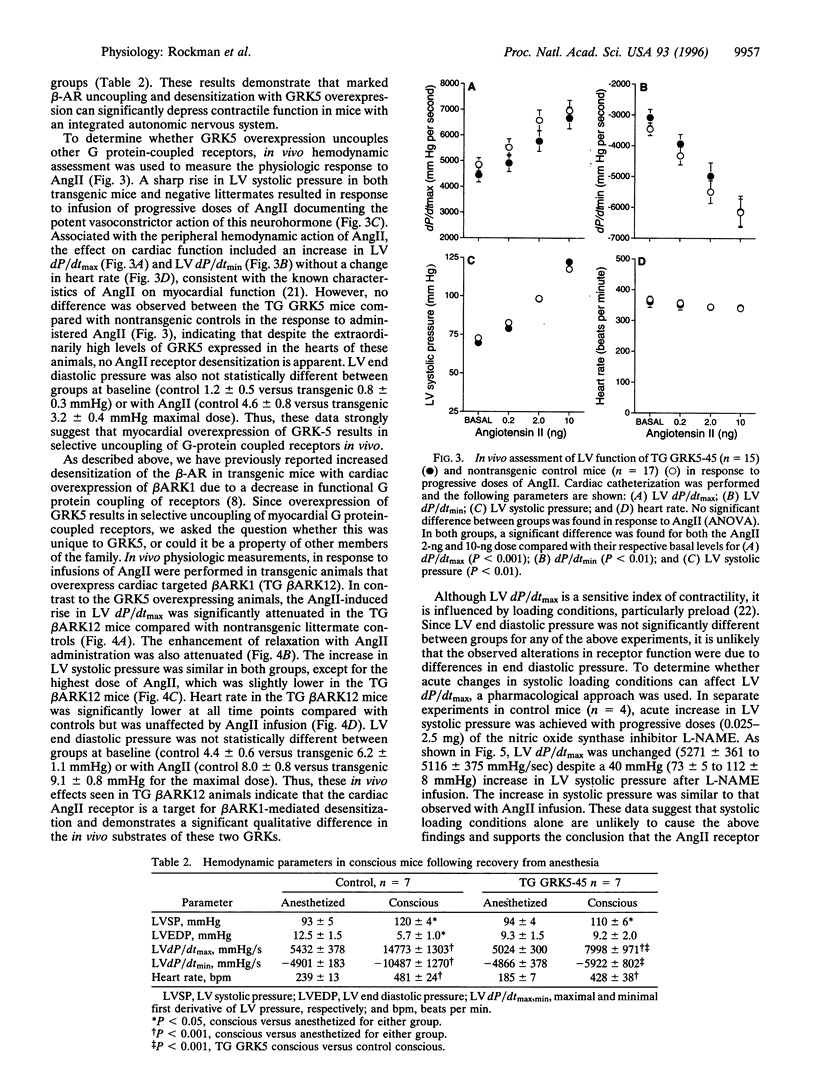
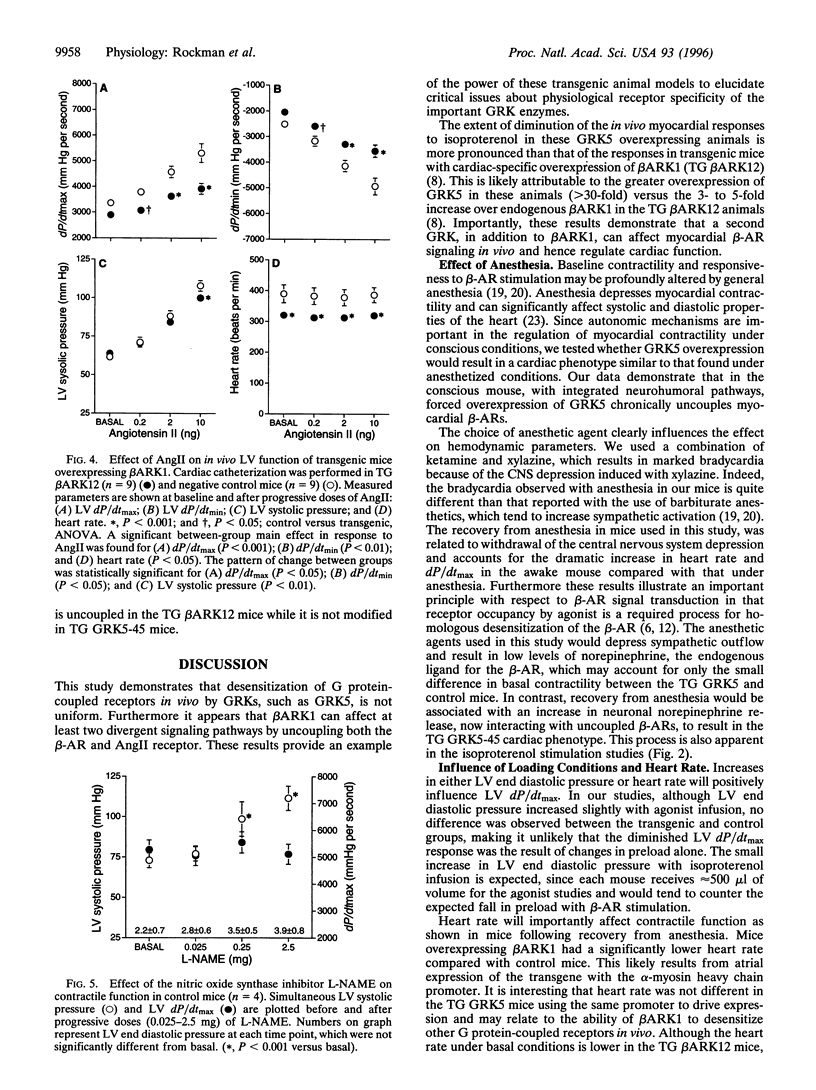

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bernstein K. E., Berk B. C. The biology of angiotensin II receptors. Am J Kidney Dis. 1993 Nov;22(5):745–754. doi: 10.1016/s0272-6386(12)80441-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bristow M. R., Ginsburg R., Minobe W., Cubicciotti R. S., Sageman W. S., Lurie K., Billingham M. E., Harrison D. C., Stinson E. B. Decreased catecholamine sensitivity and beta-adrenergic-receptor density in failing human hearts. N Engl J Med. 1982 Jul 22;307(4):205–211. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198207223070401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freedman N. J., Liggett S. B., Drachman D. E., Pei G., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. Phosphorylation and desensitization of the human beta 1-adrenergic receptor. Involvement of G protein-coupled receptor kinases and cAMP-dependent protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1995 Jul 28;270(30):17953–17961. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.30.17953. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujii A. M., Vatner S. F. Autonomic mechanisms regulating myocardial contractility in conscious animals. Pharmacol Ther. 1985;29(2):221–238. doi: 10.1016/0163-7258(85)90030-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilman A. G. G proteins: transducers of receptor-generated signals. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:615–649. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.003151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hausdorff W. P., Bouvier M., O'Dowd B. F., Irons G. P., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. Phosphorylation sites on two domains of the beta 2-adrenergic receptor are involved in distinct pathways of receptor desensitization. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jul 25;264(21):12657–12665. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ihara T., Shannon R. P., Komamura K., Pasipoularides A., Patrick T., Shen Y. T., Vatner S. F. Effects of anaesthesia and recent surgery on diastolic function. Cardiovasc Res. 1994 Mar;28(3):325–336. doi: 10.1093/cvr/28.3.325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikenouchi H., Barry W. H., Bridge J. H., Weinberg E. O., Apstein C. S., Lorell B. H. Effects of angiotensin II on intracellular Ca2+ and pH in isolated beating rabbit hearts and myocytes loaded with the indicator indo-1. J Physiol. 1994 Oct 15;480(Pt 2):203–215. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1994.sp020353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inglese J., Freedman N. J., Koch W. J., Lefkowitz R. J. Structure and mechanism of the G protein-coupled receptor kinases. J Biol Chem. 1993 Nov 15;268(32):23735–23738. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khairallah P. A. Action of angiotensin on adrenergic nerve endings: inhibition of norepinephrine uptake. Fed Proc. 1972 Jul-Aug;31(4):1351–1357. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch W. J., Inglese J., Stone W. C., Lefkowitz R. J. The binding site for the beta gamma subunits of heterotrimeric G proteins on the beta-adrenergic receptor kinase. J Biol Chem. 1993 Apr 15;268(11):8256–8260. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch W. J., Rockman H. A., Samama P., Hamilton R. A., Bond R. A., Milano C. A., Lefkowitz R. J. Cardiac function in mice overexpressing the beta-adrenergic receptor kinase or a beta ARK inhibitor. Science. 1995 Jun 2;268(5215):1350–1353. doi: 10.1126/science.7761854. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lefkowitz R. J. G protein-coupled receptor kinases. Cell. 1993 Aug 13;74(3):409–412. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)80042-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahler F., Ross J., Jr, O'Rourke R. A., Covell J. W. Effects of changes in preload, afterload and inotropic state on ejection and isovolumic phase measures of contractility in the conscious dog. Am J Cardiol. 1975 May;35(5):626–634. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(75)90048-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohnishi J., Ishido M., Shibata T., Inagami T., Murakami K., Miyazaki H. The rat angiotensin II AT1A receptor couples with three different signal transduction pathways. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 Jul 31;186(2):1094–1101. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(92)90859-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oppermann M., Freedman N. J., Alexander R. W., Lefkowitz R. J. Phosphorylation of the type 1A angiotensin II receptor by G protein-coupled receptor kinases and protein kinase C. J Biol Chem. 1996 May 31;271(22):13266–13272. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.22.13266. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ping P., Gelzer-Bell R., Roth D. A., Kiel D., Insel P. A., Hammond H. K. Reduced beta-adrenergic receptor activation decreases G-protein expression and beta-adrenergic receptor kinase activity in porcine heart. J Clin Invest. 1995 Mar;95(3):1271–1280. doi: 10.1172/JCI117777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pitcher J. A., Inglese J., Higgins J. B., Arriza J. L., Casey P. J., Kim C., Benovic J. L., Kwatra M. M., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. Role of beta gamma subunits of G proteins in targeting the beta-adrenergic receptor kinase to membrane-bound receptors. Science. 1992 Aug 28;257(5074):1264–1267. doi: 10.1126/science.1325672. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Premont R. T., Koch W. J., Inglese J., Lefkowitz R. J. Identification, purification, and characterization of GRK5, a member of the family of G protein-coupled receptor kinases. J Biol Chem. 1994 Mar 4;269(9):6832–6841. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramkumar V., Kwatra M., Benovic J. L., Stiles G. L., Stilesa G. L. Functional consequences of A1 adenosine-receptor phosphorylation by the beta-adrenergic receptor kinase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1993 Oct 7;1179(1):89–97. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(93)90075-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rockman H. A., Hamilton R. A., Jones L. R., Milano C. A., Mao L., Lefkowitz R. J. Enhanced myocardial relaxation in vivo in transgenic mice overexpressing the beta2-adrenergic receptor is associated with reduced phospholamban protein. J Clin Invest. 1996 Apr 1;97(7):1618–1623. doi: 10.1172/JCI118587. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rockman H. A., Wachhorst S. P., Mao L., Ross J., Jr ANG II receptor blockade prevents ventricular hypertrophy and ANF gene expression with pressure overload in mice. Am J Physiol. 1994 Jun;266(6 Pt 2):H2468–H2475. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1994.266.6.H2468. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Subramaniam A., Jones W. K., Gulick J., Wert S., Neumann J., Robbins J. Tissue-specific regulation of the alpha-myosin heavy chain gene promoter in transgenic mice. J Biol Chem. 1991 Dec 25;266(36):24613–24620. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vatner S. F., Braunwald E. Cardiovascular control mechanisms in the conscious state. N Engl J Med. 1975 Nov 6;293(19):970–976. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197511062931906. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]