Abstract
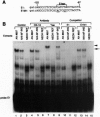
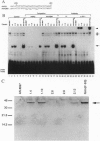
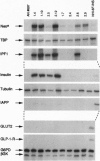
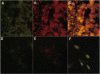
Insulin promoter factor 1 (IPF1), a member of the homeodomain protein family, serves an early role in pancreas formation, as evidenced by the lack of pancreas formation in mice carrying a targeted disruption of the IPF1 gene [Jonsson, J., Carlsson, L., Edlund, T. & Edlund, H. (1994) Nature (London) 371, 606-609]. In adults, IPF1 expression is restricted to the beta-cells in the islets of Langerhans. We report here that IPF1 induces expression of a subset of beta-cell-specific genes (insulin and islet amyloid polypeptide) when ectopically expressed in clones of transformed pancreatic islet alpha-cells. In contrast, expression of IPF1 in rat embryo fibroblasts factor failed to induce insulin and islet amyloid polypeptide expression. This is most likely due to the lack of at least one other essential insulin gene transcription factor, the basic helix-loop-helix protein Beta 2/NeuroD, which is expressed in both alpha- and beta-cells. We conclude that IPF1 is a potent transcriptional activator of endogenous insulin genes in non-beta islet cells, which suggests an important role of IPF1 in beta-cell maturation.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aronheim A., Ohlsson H., Park C. W., Edlund T., Walker M. D. Distribution and characterization of helix-loop-helix enhancer-binding proteins from pancreatic beta cells and lymphocytes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Jul 25;19(14):3893–3899. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.14.3893. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blume N., Skouv J., Larsson L. I., Holst J. J., Madsen O. D. Potent inhibitory effects of transplantable rat glucagonomas and insulinomas on the respective endogenous islet cells are associated with pancreatic apoptosis. J Clin Invest. 1995 Nov;96(5):2227–2235. doi: 10.1172/JCI118278. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cordle S. R., Henderson E., Masuoka H., Weil P. A., Stein R. Pancreatic beta-cell-type-specific transcription of the insulin gene is mediated by basic helix-loop-helix DNA-binding proteins. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Mar;11(3):1734–1738. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.3.1734. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crowe D. T., Tsai M. J. Mutagenesis of the rat insulin II 5'-flanking region defines sequences important for expression in HIT cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Apr;9(4):1784–1789. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.4.1784. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- German M. S., Blanar M. A., Nelson C., Moss L. G., Rutter W. J. Two related helix-loop-helix proteins participate in separate cell-specific complexes that bind the insulin enhancer. Mol Endocrinol. 1991 Feb;5(2):292–299. doi: 10.1210/mend-5-2-292. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- German M. S., Moss L. G., Wang J., Rutter W. J. The insulin and islet amyloid polypeptide genes contain similar cell-specific promoter elements that bind identical beta-cell nuclear complexes. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Apr;12(4):1777–1788. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.4.1777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- German M. S., Wang J., Chadwick R. B., Rutter W. J. Synergistic activation of the insulin gene by a LIM-homeo domain protein and a basic helix-loop-helix protein: building a functional insulin minienhancer complex. Genes Dev. 1992 Nov;6(11):2165–2176. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.11.2165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- German M., Ashcroft S., Docherty K., Edlund H., Edlund T., Goodison S., Imura H., Kennedy G., Madsen O., Melloul D. The insulin gene promoter. A simplified nomenclature. Diabetes. 1995 Aug;44(8):1002–1004. doi: 10.2337/diab.44.8.1002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guz Y., Montminy M. R., Stein R., Leonard J., Gamer L. W., Wright C. V., Teitelman G. Expression of murine STF-1, a putative insulin gene transcription factor, in beta cells of pancreas, duodenal epithelium and pancreatic exocrine and endocrine progenitors during ontogeny. Development. 1995 Jan;121(1):11–18. doi: 10.1242/dev.121.1.11. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heimberg H., De Vos A., Moens K., Quartier E., Bouwens L., Pipeleers D., Van Schaftingen E., Madsen O., Schuit F. The glucose sensor protein glucokinase is expressed in glucagon-producing alpha-cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1996 Jul 9;93(14):7036–7041. doi: 10.1073/pnas.93.14.7036. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs Y., Vierra C., Nelson C. E2A expression, nuclear localization, and in vivo formation of DNA- and non-DNA-binding species during B-cell development. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Dec;13(12):7321–7333. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.12.7321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jonsson J., Carlsson L., Edlund T., Edlund H. Insulin-promoter-factor 1 is required for pancreas development in mice. Nature. 1994 Oct 13;371(6498):606–609. doi: 10.1038/371606a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karlsson O., Edlund T., Moss J. B., Rutter W. J., Walker M. D. A mutational analysis of the insulin gene transcription control region: expression in beta cells is dependent on two related sequences within the enhancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(24):8819–8823. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.24.8819. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee J. E., Hollenberg S. M., Snider L., Turner D. L., Lipnick N., Weintraub H. Conversion of Xenopus ectoderm into neurons by NeuroD, a basic helix-loop-helix protein. Science. 1995 May 12;268(5212):836–844. doi: 10.1126/science.7754368. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leonard J., Peers B., Johnson T., Ferreri K., Lee S., Montminy M. R. Characterization of somatostatin transactivating factor-1, a novel homeobox factor that stimulates somatostatin expression in pancreatic islet cells. Mol Endocrinol. 1993 Oct;7(10):1275–1283. doi: 10.1210/mend.7.10.7505393. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madsen O. D., Andersen L. C., Michelsen B., Owerbach D., Larsson L. I., Lernmark A., Steiner D. F. Tissue-specific expression of transfected human insulin genes in pluripotent clonal rat insulinoma lines induced during passage in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(18):6652–6656. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.18.6652. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madsen O. D., Karlsen C., Nielsen E., Lund K., Kofod H., Welinder B., Rehfeld J. F., Larsson L. I., Steiner D. F., Holst J. J. The dissociation of tumor-induced weight loss from hypoglycemia in a transplantable pluripotent rat islet tumor results in the segregation of stable alpha- and beta-cell tumor phenotypes. Endocrinology. 1993 Nov;133(5):2022–2030. doi: 10.1210/endo.133.5.8404649. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madsen O. D., Larsson L. I., Rehfeld J. F., Schwartz T. W., Lernmark A., Labrecque A. D., Steiner D. F. Cloned cell lines from a transplantable islet cell tumor are heterogeneous and express cholecystokinin in addition to islet hormones. J Cell Biol. 1986 Nov;103(5):2025–2034. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.5.2025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller C. P., McGehee R. E., Jr, Habener J. F. IDX-1: a new homeodomain transcription factor expressed in rat pancreatic islets and duodenum that transactivates the somatostatin gene. EMBO J. 1994 Mar 1;13(5):1145–1156. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06363.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moens K., Heimberg H., Flamez D., Huypens P., Quartier E., Ling Z., Pipeleers D., Gremlich S., Thorens B., Schuit F. Expression and functional activity of glucagon, glucagon-like peptide I, and glucose-dependent insulinotropic peptide receptors in rat pancreatic islet cells. Diabetes. 1996 Feb;45(2):257–261. doi: 10.2337/diab.45.2.257. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Møller C. J., Christgau S., Williamson M. R., Madsen O. D., Niu Z. P., Bock E., Baekkeskov S. Differential expression of neural cell adhesion molecule and cadherins in pancreatic islets, glucagonomas, and insulinomas. Mol Endocrinol. 1992 Aug;6(8):1332–1342. doi: 10.1210/mend.6.8.1406710. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naya F. J., Stellrecht C. M., Tsai M. J. Tissue-specific regulation of the insulin gene by a novel basic helix-loop-helix transcription factor. Genes Dev. 1995 Apr 15;9(8):1009–1019. doi: 10.1101/gad.9.8.1009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Offield M. F., Jetton T. L., Labosky P. A., Ray M., Stein R. W., Magnuson M. A., Hogan B. L., Wright C. V. PDX-1 is required for pancreatic outgrowth and differentiation of the rostral duodenum. Development. 1996 Mar;122(3):983–995. doi: 10.1242/dev.122.3.983. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohlsson H., Karlsson K., Edlund T. IPF1, a homeodomain-containing transactivator of the insulin gene. EMBO J. 1993 Nov;12(11):4251–4259. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb06109.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohlsson H., Karlsson O., Edlund T. A beta-cell-specific protein binds to the two major regulatory sequences of the insulin gene enhancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(12):4228–4231. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.12.4228. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohlsson H., Thor S., Edlund T. Novel insulin promoter- and enhancer-binding proteins that discriminate between pancreatic alpha- and beta-cells. Mol Endocrinol. 1991 Jul;5(7):897–904. doi: 10.1210/mend-5-7-897. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park C. W., Walker M. D. Subunit structure of cell-specific E box-binding proteins analyzed by quantitation of electrophoretic mobility shift. J Biol Chem. 1992 Aug 5;267(22):15642–15649. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peers B., Leonard J., Sharma S., Teitelman G., Montminy M. R. Insulin expression in pancreatic islet cells relies on cooperative interactions between the helix loop helix factor E47 and the homeobox factor STF-1. Mol Endocrinol. 1994 Dec;8(12):1798–1806. doi: 10.1210/mend.8.12.7708065. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petersen H. V., Serup P., Leonard J., Michelsen B. K., Madsen O. D. Transcriptional regulation of the human insulin gene is dependent on the homeodomain protein STF1/IPF1 acting through the CT boxes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Oct 25;91(22):10465–10469. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.22.10465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peyton M., Moss L. G., Tsai M. J. Two distinct class A helix-loop-helix transcription factors, E2A and BETA1, form separate DNA binding complexes on the insulin gene E box. J Biol Chem. 1994 Oct 14;269(41):25936–25941. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson G. L., Peshavaria M., Henderson E., Shieh S. Y., Tsai M. J., Teitelman G., Stein R. Expression of the trans-active factors that stimulate insulin control element-mediated activity appear to precede insulin gene transcription. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jan 28;269(4):2452–2460. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schøller J. Construction of novel eukaryotic transfection-vector, pJNL-1. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jan 25;16(2):769–769. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.2.769. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
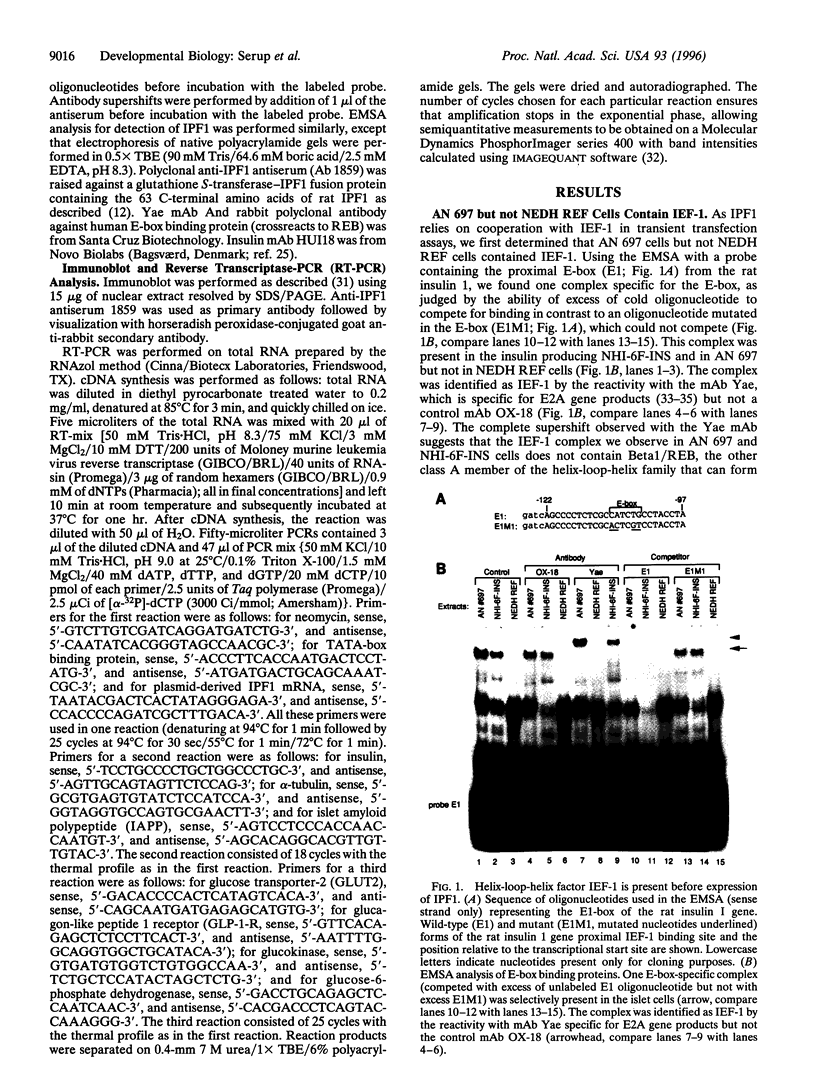
- Serup P., Petersen H. V., Pedersen E. E., Edlund H., Leonard J., Petersen J. S., Larsson L. I., Madsen O. D. The homeodomain protein IPF-1/STF-1 is expressed in a subset of islet cells and promotes rat insulin 1 gene expression dependent on an intact E1 helix-loop-helix factor binding site. Biochem J. 1995 Sep 15;310(Pt 3):997–1003. doi: 10.1042/bj3100997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serup P., Schøller J. Transfected rat islet tumour cells express mouse major histocompatibility complex class I antigens functionally. Applicable as "pseudo-syngeneic" targets in the multiple low-dose streptozotocin diabetes model. Diabetologia. 1989 Jul;32(7):409–415. doi: 10.1007/BF00271259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharma A., Stein R. Glucose-induced transcription of the insulin gene is mediated by factors required for beta-cell-type-specific expression. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Feb;14(2):871–879. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.2.871. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shelton K. D., Franklin A. J., Khoor A., Beechem J., Magnuson M. A. Multiple elements in the upstream glucokinase promoter contribute to transcription in insulinoma cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Oct;12(10):4578–4589. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.10.4578. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shieh S. Y., Tsai M. J. Cell-specific and ubiquitous factors are responsible for the enhancer activity of the rat insulin II gene. J Biol Chem. 1991 Sep 5;266(25):16708–16714. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
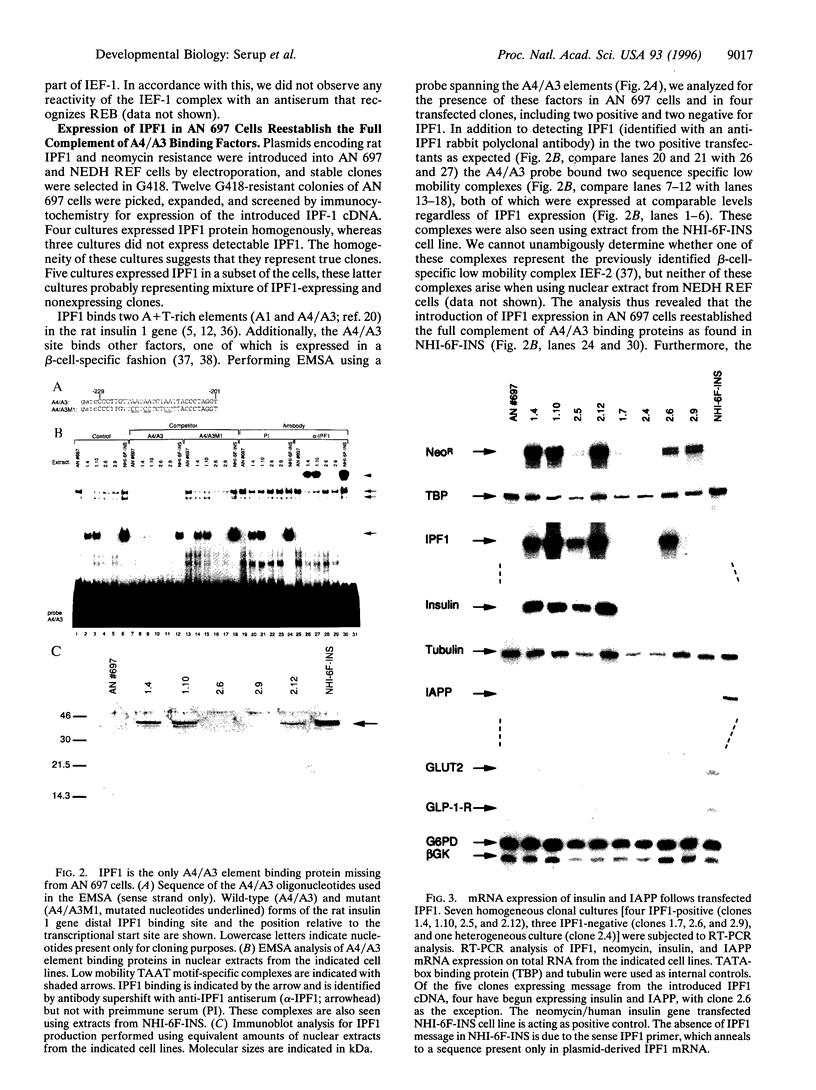
- TODARO G. J., GREEN H. Quantitative studies of the growth of mouse embryo cells in culture and their development into established lines. J Cell Biol. 1963 May;17:299–313. doi: 10.1083/jcb.17.2.299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vierra C. A., Jacobs Y., Ly L., Nelson C. Patterns of Pan expression and role of Pan proteins in endocrine cell type-specific complex formation. Mol Endocrinol. 1994 Feb;8(2):197–209. doi: 10.1210/mend.8.2.8170476. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vierra C. A., Nelson C. The Pan basic helix-loop-helix proteins are required for insulin gene expression. Mol Endocrinol. 1995 Jan;9(1):64–71. doi: 10.1210/mend.9.1.7760851. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vierra C. A., Xin X. Q., Jacobs Y. T., Campbell J. M., Shen L. P., Rutter W. J., Nelson C. Purification of E. coli-synthesized Pan proteins and development of a Pan-specific monoclonal antibody. Hybridoma. 1994 Jun;13(3):191–197. doi: 10.1089/hyb.1994.13.191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]