Abstract
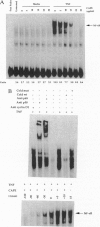
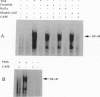
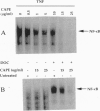
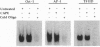
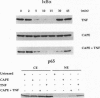
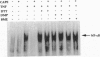
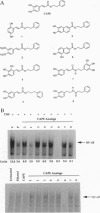
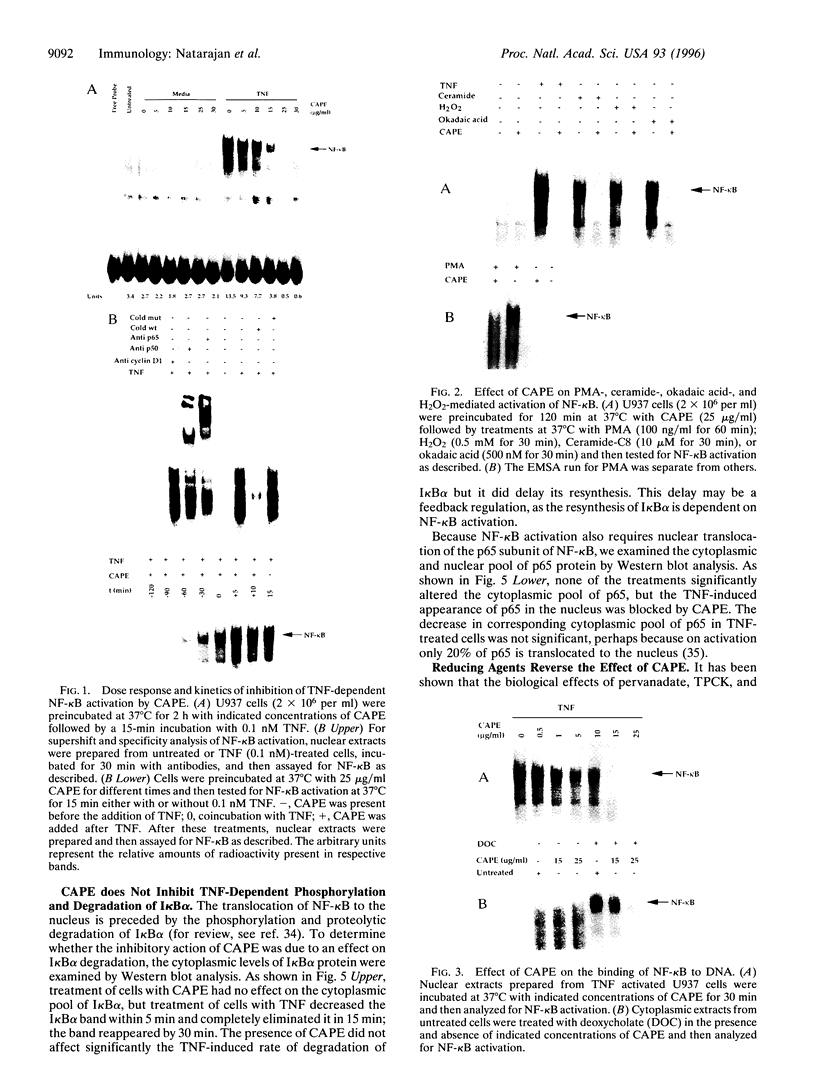
Caffeic acid phenethyl ester (CAPE), an active component of propolis from honeybee hives, is known to have antimitogenic, anticarcinogenic, antiinflammatory, and immunomodulatory properties. The molecular basis for these diverse properties is not known. Since the role of the nuclear factor NF-kappa B in these responses has been documented, we examined the effect of CAPE on this transcription factor. Our results show that the activation of NF-kappa B by tumor necrosis factor (TNF) is completely blocked by CAPE in a dose- and time-dependent manner. Besides TNF, CAPE also inhibited NF-kappa B activation induced by other inflammatory agents including phorbol ester, ceramide, hydrogen peroxide, and okadaic acid. Since the reducing agents reversed the inhibitory effect of CAPE, it suggests the role of critical sulfhydryl groups in NF-kappa B activation. CAPE prevented the translocation of the p65 subunit of NF-kappa B to the nucleus and had no significant effect on TNF-induced I kappa B alpha degradation, but did delay I kappa B alpha resynthesis. The effect of CAPE on inhibition of NF-kappa B binding to the DNA was specific, in as much as binding of other transcription factors including AP-1, Oct-1, and TFIID to their DNA were not affected. When various synthetic structural analogues of CAPE were examined, it was found that a bicyclic, rotationally constrained, 5,6-dihydroxy form was superactive, whereas 6,7-dihydroxy variant was least active. Thus, overall our results demonstrate that CAPE is a potent and a specific inhibitor of NF-kappa B activation and this may provide the molecular basis for its multiple immunomodulatory and antiinflammatory activities.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baeuerle P. A., Henkel T. Function and activation of NF-kappa B in the immune system. Annu Rev Immunol. 1994;12:141–179. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.12.040194.001041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baeuerle P. A. The inducible transcription activator NF-kappa B: regulation by distinct protein subunits. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Apr 16;1072(1):63–80. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(91)90007-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhimani R. S., Troll W., Grunberger D., Frenkel K. Inhibition of oxidative stress in HeLa cells by chemopreventive agents. Cancer Res. 1993 Oct 1;53(19):4528–4533. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke T. R., Jr, Fesen M. R., Mazumder A., Wang J., Carothers A. M., Grunberger D., Driscoll J., Kohn K., Pommier Y. Hydroxylated aromatic inhibitors of HIV-1 integrase. J Med Chem. 1995 Oct 13;38(21):4171–4178. doi: 10.1021/jm00021a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaturvedi M. M., LaPushin R., Aggarwal B. B. Tumor necrosis factor and lymphotoxin. Qualitative and quantitative differences in the mediation of early and late cellular response. J Biol Chem. 1994 May 20;269(20):14575–14583. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiao C., Carothers A. M., Grunberger D., Solomon G., Preston G. A., Barrett J. C. Apoptosis and altered redox state induced by caffeic acid phenethyl ester (CAPE) in transformed rat fibroblast cells. Cancer Res. 1995 Aug 15;55(16):3576–3583. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collart M. A., Baeuerle P., Vassalli P. Regulation of tumor necrosis factor alpha transcription in macrophages: involvement of four kappa B-like motifs and of constitutive and inducible forms of NF-kappa B. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Apr;10(4):1498–1506. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.4.1498. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eicher D. M., Tan T. H., Rice N. R., O'Shea J. J., Kennedy I. C. Expression of v-src in T cells correlates with nuclear expression of NF-kappa B. J Immunol. 1994 Mar 15;152(6):2710–2719. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fesen M. R., Kohn K. W., Leteurtre F., Pommier Y. Inhibitors of human immunodeficiency virus integrase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Mar 15;90(6):2399–2403. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.6.2399. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finco T. S., Beg A. A., Baldwin A. S., Jr Inducible phosphorylation of I kappa B alpha is not sufficient for its dissociation from NF-kappa B and is inhibited by protease inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Dec 6;91(25):11884–11888. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.25.11884. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frenkel K., Wei H., Bhimani R., Ye J., Zadunaisky J. A., Huang M. T., Ferraro T., Conney A. H., Grunberger D. Inhibition of tumor promoter-mediated processes in mouse skin and bovine lens by caffeic acid phenethyl ester. Cancer Res. 1993 Mar 15;53(6):1255–1261. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grilli M., Chiu J. J., Lenardo M. J. NF-kappa B and Rel: participants in a multiform transcriptional regulatory system. Int Rev Cytol. 1993;143:1–62. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)61873-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grunberger D., Banerjee R., Eisinger K., Oltz E. M., Efros L., Caldwell M., Estevez V., Nakanishi K. Preferential cytotoxicity on tumor cells by caffeic acid phenethyl ester isolated from propolis. Experientia. 1988 Mar 15;44(3):230–232. doi: 10.1007/BF01941717. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guarini L., Su Z. Z., Zucker S., Lin J., Grunberger D., Fisher P. B. Growth inhibition and modulation of antigenic phenotype in human melanoma and glioblastoma multiforme cells by caffeic acid phenethyl ester (CAPE) Cell Mol Biol. 1992 Aug;38(5):513–527. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hassanain H. H., Dai W., Gupta S. L. Enhanced gel mobility shift assay for DNA-binding factors. Anal Biochem. 1993 Aug 15;213(1):162–167. doi: 10.1006/abio.1993.1400. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hladoń B., Bylka W., Ellnain-Wojtaszek M., Skrzypczak L., Szafarek P., Chodera A., Kowalewski Z. In vitro studies on the cytostatic activity of propolis extracts. Arzneimittelforschung. 1980;30(11):1847–1848. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura Y., Okuda H., Okuda T., Hatano T., Agata I., Arichi S. Studies on the activities of tannins and related compounds from medicinal plants and drugs. VII. Effects of extracts of leaves of Artemisia species, and caffeic acid and chlorogenic acid on lipid metabolic injury in rats fed peroxidized oil. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo) 1985 May;33(5):2028–2034. doi: 10.1248/cpb.33.2028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laranjinha J., Vieira O., Madeira V., Almeida L. Two related phenolic antioxidants with opposite effects on vitamin E content in low density lipoproteins oxidized by ferrylmyoglobin: consumption vs regeneration. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1995 Nov 10;323(2):373–381. doi: 10.1006/abbi.1995.0057. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liou H. C., Baltimore D. Regulation of the NF-kappa B/rel transcription factor and I kappa B inhibitor system. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1993 Jun;5(3):477–487. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(93)90014-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahon T. M., O'Neill L. A. Studies into the effect of the tyrosine kinase inhibitor herbimycin A on NF-kappa B activation in T lymphocytes. Evidence for covalent modification of the p50 subunit. J Biol Chem. 1995 Dec 1;270(48):28557–28564. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.48.28557. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathias S., Dressler K. A., Kolesnick R. N. Characterization of a ceramide-activated protein kinase: stimulation by tumor necrosis factor alpha. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Nov 15;88(22):10009–10013. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.22.10009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meichle A., Schütze S., Hensel G., Brunsing D., Krönke M. Protein kinase C-independent activation of nuclear factor kappa B by tumor necrosis factor. J Biol Chem. 1990 May 15;265(14):8339–8343. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer M., Schreck R., Baeuerle P. A. H2O2 and antioxidants have opposite effects on activation of NF-kappa B and AP-1 in intact cells: AP-1 as secondary antioxidant-responsive factor. EMBO J. 1993 May;12(5):2005–2015. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05850.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nabel G., Baltimore D. An inducible transcription factor activates expression of human immunodeficiency virus in T cells. Nature. 1987 Apr 16;326(6114):711–713. doi: 10.1038/326711a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nolan G. P., Baltimore D. The inhibitory ankyrin and activator Rel proteins. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1992 Apr;2(2):211–220. doi: 10.1016/s0959-437x(05)80276-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao C. V., Desai D., Kaul B., Amin S., Reddy B. S. Effect of caffeic acid esters on carcinogen-induced mutagenicity and human colon adenocarcinoma cell growth. Chem Biol Interact. 1992 Nov 16;84(3):277–290. doi: 10.1016/0009-2797(92)90129-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao C. V., Desai D., Simi B., Kulkarni N., Amin S., Reddy B. S. Inhibitory effect of caffeic acid esters on azoxymethane-induced biochemical changes and aberrant crypt foci formation in rat colon. Cancer Res. 1993 Sep 15;53(18):4182–4188. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy S. A., Chaturvedi M. M., Darnay B. G., Chan H., Higuchi M., Aggarwal B. B. Reconstitution of nuclear factor kappa B activation induced by tumor necrosis factor requires membrane-associated components. Comparison with pathway activated by ceramide. J Biol Chem. 1994 Oct 14;269(41):25369–25372. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreck R., Meier B., Männel D. N., Dröge W., Baeuerle P. A. Dithiocarbamates as potent inhibitors of nuclear factor kappa B activation in intact cells. J Exp Med. 1992 May 1;175(5):1181–1194. doi: 10.1084/jem.175.5.1181. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreiber E., Matthias P., Müller M. M., Schaffner W. Rapid detection of octamer binding proteins with 'mini-extracts', prepared from a small number of cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Aug 11;17(15):6419–6419. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.15.6419. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulze-Osthoff K., Beyaert R., Vandevoorde V., Haegeman G., Fiers W. Depletion of the mitochondrial electron transport abrogates the cytotoxic and gene-inductive effects of TNF. EMBO J. 1993 Aug;12(8):3095–3104. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05978.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schütze S., Potthoff K., Machleidt T., Berkovic D., Wiegmann K., Krönke M. TNF activates NF-kappa B by phosphatidylcholine-specific phospholipase C-induced "acidic" sphingomyelin breakdown. Cell. 1992 Nov 27;71(5):765–776. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90553-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siebenlist U., Franzoso G., Brown K. Structure, regulation and function of NF-kappa B. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1994;10:405–455. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.10.110194.002201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh H., LeBowitz J. H., Baldwin A. S., Jr, Sharp P. A. Molecular cloning of an enhancer binding protein: isolation by screening of an expression library with a recognition site DNA. Cell. 1988 Feb 12;52(3):415–423. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)80034-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh S., Aggarwal B. B. Protein-tyrosine phosphatase inhibitors block tumor necrosis factor-dependent activation of the nuclear transcription factor NF-kappa B. J Biol Chem. 1995 May 5;270(18):10631–10639. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.18.10631. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staal F. J., Roederer M., Herzenberg L. A., Herzenberg L. A. Intracellular thiols regulate activation of nuclear factor kappa B and transcription of human immunodeficiency virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec;87(24):9943–9947. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.24.9943. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Su Z. Z., Grunberger D., Fisher P. B. Suppression of adenovirus type 5 E1A-mediated transformation and expression of the transformed phenotype by caffeic acid phenethyl ester (CAPE). Mol Carcinog. 1991;4(3):231–242. doi: 10.1002/mc.2940040310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Su Z. Z., Lin J., Grunberger D., Fisher P. B. Growth suppression and toxicity induced by caffeic acid phenethyl ester (CAPE) in type 5 adenovirus-transformed rat embryo cells correlate directly with transformation progression. Cancer Res. 1994 Apr 1;54(7):1865–1870. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sud'ina G. F., Mirzoeva O. K., Pushkareva M. A., Korshunova G. A., Sumbatyan N. V., Varfolomeev S. D. Caffeic acid phenethyl ester as a lipoxygenase inhibitor with antioxidant properties. FEBS Lett. 1993 Aug 23;329(1-2):21–24. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(93)80184-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thanos D., Maniatis T. NF-kappa B: a lesson in family values. Cell. 1995 Feb 24;80(4):529–532. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90506-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verma I. M., Stevenson J. K., Schwarz E. M., Van Antwerp D., Miyamoto S. Rel/NF-kappa B/I kappa B family: intimate tales of association and dissociation. Genes Dev. 1995 Nov 15;9(22):2723–2735. doi: 10.1101/gad.9.22.2723. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang Z., Costanzo M., Golde D. W., Kolesnick R. N. Tumor necrosis factor activation of the sphingomyelin pathway signals nuclear factor kappa B translocation in intact HL-60 cells. J Biol Chem. 1993 Sep 25;268(27):20520–20523. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zheng Z. S., Xue G. Z., Grunberger D., Prystowsky J. H. Caffeic acid phenethyl ester inhibits proliferation of human keratinocytes and interferes with the EGF regulation of ornithine decarboxylase. Oncol Res. 1995;7(9):445–452. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]