Abstract
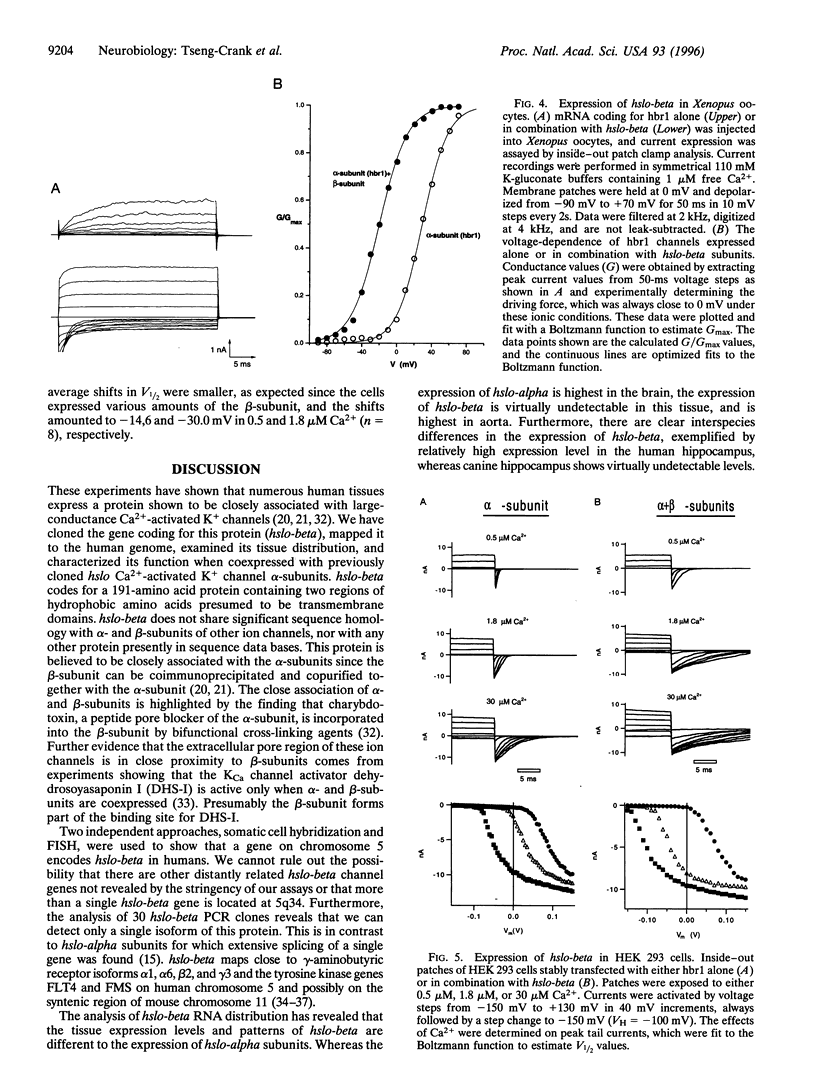
We have cloned and expressed a Ca(2+)-activated K+ channel beta-subunit from human brain. The open reading frame encodes a 191-amino acid protein possessing significant homology to a previously described subunit cloned from bovine muscle. The gene for this subunit is located on chromosome 5 at band q34 (hslo-beta). There is no evidence for alternative RNA splicing of this gene product. hslo-beta mRNA is abundantly expressed in smooth muscle, but expression levels are low in most other tissues, including brain. Brain subregions in which beta-subunit mRNA expression is relatively high are the hippocampus and corpus callosum. The coexpression of hslo-beta mRNA together with hslo-alpha subunits in either Xenopus oocytes or stably transfected HEK 293 cells give rise to Ca(2+)-activated potassium currents with a much increased calcium and/or voltage sensitivity. These data indicate that the beta-subunit shows a tissue distribution different to that of the alpha-subunit, and in many tissues there may be no association of alpha-subunits with beta-subunits. These beta-subunits can play a functional role in the regulation of neuronal excitability by tuning the Ca2+ and/or the voltage dependence of alpha-subunits.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adelman J. P., Shen K. Z., Kavanaugh M. P., Warren R. A., Wu Y. N., Lagrutta A., Bond C. T., North R. A. Calcium-activated potassium channels expressed from cloned complementary DNAs. Neuron. 1992 Aug;9(2):209–216. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90160-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atkinson N. S., Robertson G. A., Ganetzky B. A component of calcium-activated potassium channels encoded by the Drosophila slo locus. Science. 1991 Aug 2;253(5019):551–555. doi: 10.1126/science.1857984. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bielefeldt K., Jackson M. B. Phosphorylation and dephosphorylation modulate a Ca(2+)-activated K+ channel in rat peptidergic nerve terminals. J Physiol. 1994 Mar 1;475(2):241–254. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1994.sp020065. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butler A., Tsunoda S., McCobb D. P., Wei A., Salkoff L. mSlo, a complex mouse gene encoding "maxi" calcium-activated potassium channels. Science. 1993 Jul 9;261(5118):221–224. doi: 10.1126/science.7687074. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christie M. J., North R. A., Osborne P. B., Douglass J., Adelman J. P. Heteropolymeric potassium channels expressed in Xenopus oocytes from cloned subunits. Neuron. 1990 Mar;4(3):405–411. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90052-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung S. K., Reinhart P. H., Martin B. L., Brautigan D., Levitan I. B. Protein kinase activity closely associated with a reconstituted calcium-activated potassium channel. Science. 1991 Aug 2;253(5019):560–562. doi: 10.1126/science.1857986. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiChiara T. J., Reinhart P. H. Distinct effects of Ca2+ and voltage on the activation and deactivation of cloned Ca(2+)-activated K+ channels. J Physiol. 1995 Dec 1;489(Pt 2):403–418. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1995.sp021061. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galland F., Karamysheva A., Mattei M. G., Rosnet O., Marchetto S., Birnbaum D. Chromosomal localization of FLT4, a novel receptor-type tyrosine kinase gene. Genomics. 1992 Jun;13(2):475–478. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(92)90277-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galland F., Karamysheva A., Mattei M. G., Rosnet O., Marchetto S., Birnbaum D. Chromosomal localization of FLT4, a novel receptor-type tyrosine kinase gene. Genomics. 1992 Jun;13(2):475–478. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(92)90277-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia-Calvo M., Knaus H. G., McManus O. B., Giangiacomo K. M., Kaczorowski G. J., Garcia M. L. Purification and reconstitution of the high-conductance, calcium-activated potassium channel from tracheal smooth muscle. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jan 7;269(1):676–682. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gola M., Crest M. Colocalization of active KCa channels and Ca2+ channels within Ca2+ domains in helix neurons. Neuron. 1993 Apr;10(4):689–699. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(93)90170-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamill O. P., Marty A., Neher E., Sakmann B., Sigworth F. J. Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflugers Arch. 1981 Aug;391(2):85–100. doi: 10.1007/BF00656997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hicks A. A., Bailey M. E., Riley B. P., Kamphuis W., Siciliano M. J., Johnson K. J., Darlison M. G. Further evidence for clustering of human GABAA receptor subunit genes: localization of the alpha 6-subunit gene (GABRA6) to distal chromosome 5q by linkage analysis. Genomics. 1994 Mar 15;20(2):285–288. doi: 10.1006/geno.1994.1167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isacoff E. Y., Jan Y. N., Jan L. Y. Evidence for the formation of heteromultimeric potassium channels in Xenopus oocytes. Nature. 1990 Jun 7;345(6275):530–534. doi: 10.1038/345530a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isom L. L., De Jongh K. S., Catterall W. A. Auxiliary subunits of voltage-gated ion channels. Neuron. 1994 Jun;12(6):1183–1194. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(94)90436-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knaus H. G., Folander K., Garcia-Calvo M., Garcia M. L., Kaczorowski G. J., Smith M., Swanson R. Primary sequence and immunological characterization of beta-subunit of high conductance Ca(2+)-activated K+ channel from smooth muscle. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jun 24;269(25):17274–17278. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knaus H. G., Garcia-Calvo M., Kaczorowski G. J., Garcia M. L. Subunit composition of the high conductance calcium-activated potassium channel from smooth muscle, a representative of the mSlo and slowpoke family of potassium channels. J Biol Chem. 1994 Feb 11;269(6):3921–3924. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Latorre R., Oberhauser A., Labarca P., Alvarez O. Varieties of calcium-activated potassium channels. Annu Rev Physiol. 1989;51:385–399. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.51.030189.002125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maletic-Savatic M., Lenn N. J., Trimmer J. S. Differential spatiotemporal expression of K+ channel polypeptides in rat hippocampal neurons developing in situ and in vitro. J Neurosci. 1995 May;15(5 Pt 2):3840–3851. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.15-05-03840.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marty A., Neher E. Potassium channels in cultured bovine adrenal chromaffin cells. J Physiol. 1985 Oct;367:117–141. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015817. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maruyama Y., Petersen O. H., Flanagan P., Pearson G. T. Quantification of Ca2+-activated K+ channels under hormonal control in pig pancreas acinar cells. Nature. 1983 Sep 15;305(5931):228–232. doi: 10.1038/305228a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCormack K., Lin J. W., Iverson L. E., Rudy B. Shaker K+ channel subunits from heteromultimeric channels with novel functional properties. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Sep 28;171(3):1361–1371. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)90836-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McManus O. B. Calcium-activated potassium channels: regulation by calcium. J Bioenerg Biomembr. 1991 Aug;23(4):537–560. doi: 10.1007/BF00785810. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McManus O. B., Helms L. M., Pallanck L., Ganetzky B., Swanson R., Leonard R. J. Functional role of the beta subunit of high conductance calcium-activated potassium channels. Neuron. 1995 Mar;14(3):645–650. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(95)90321-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McManus O. B., Helms L. M., Pallanck L., Ganetzky B., Swanson R., Leonard R. J. Functional role of the beta subunit of high conductance calcium-activated potassium channels. Neuron. 1995 Mar;14(3):645–650. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(95)90321-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McPhalen C. A., Strynadka N. C., James M. N. Calcium-binding sites in proteins: a structural perspective. Adv Protein Chem. 1991;42:77–144. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60535-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miledi R. A calcium-dependent transient outward current in Xenopus laevis oocytes. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1982 Jul 22;215(1201):491–497. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1982.0056. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moczydlowski E., Latorre R. Gating kinetics of Ca2+-activated K+ channels from rat muscle incorporated into planar lipid bilayers. Evidence for two voltage-dependent Ca2+ binding reactions. J Gen Physiol. 1983 Oct;82(4):511–542. doi: 10.1085/jgp.82.4.511. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morales M. J., Castellino R. C., Crews A. L., Rasmusson R. L., Strauss H. C. A novel beta subunit increases rate of inactivation of specific voltage-gated potassium channel alpha subunits. J Biol Chem. 1995 Mar 17;270(11):6272–6277. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.11.6272. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierce J. C., Sternberg N., Sauer B. A mouse genomic library in the bacteriophage P1 cloning system: organization and characterization. Mamm Genome. 1992;3(10):550–558. doi: 10.1007/BF00350620. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pérez G., Lagrutta A., Adelman J. P., Toro L. Reconstitution of expressed KCa channels from Xenopus oocytes to lipid bilayers. Biophys J. 1994 Apr;66(4):1022–1027. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(94)80883-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinhart P. H., Chung S., Levitan I. B. A family of calcium-dependent potassium channels from rat brain. Neuron. 1989 Jan;2(1):1031–1041. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(89)90227-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinhart P. H., Chung S., Martin B. L., Brautigan D. L., Levitan I. B. Modulation of calcium-activated potassium channels from rat brain by protein kinase A and phosphatase 2A. J Neurosci. 1991 Jun;11(6):1627–1635. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.11-06-01627.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinhart P. H., Levitan I. B. Kinase and phosphatase activities intimately associated with a reconstituted calcium-dependent potassium channel. J Neurosci. 1995 Jun;15(6):4572–4579. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.15-06-04572.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinhart P. H., Taylor W. M., Bygrave F. L. The contribution of both extracellular and intracellular calcium to the action of alpha-adrenergic agonists in perfused rat liver. Biochem J. 1984 May 15;220(1):35–42. doi: 10.1042/bj2200035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rettig J., Heinemann S. H., Wunder F., Lorra C., Parcej D. N., Dolly J. O., Pongs O. Inactivation properties of voltage-gated K+ channels altered by presence of beta-subunit. Nature. 1994 May 26;369(6478):289–294. doi: 10.1038/369289a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhodes K. J., Keilbaugh S. A., Barrezueta N. X., Lopez K. L., Trimmer J. S. Association and colocalization of K+ channel alpha- and beta-subunit polypeptides in rat brain. J Neurosci. 1995 Jul;15(7 Pt 2):5360–5371. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.15-07-05360.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts W. M., Jacobs R. A., Hudspeth A. J. Colocalization of ion channels involved in frequency selectivity and synaptic transmission at presynaptic active zones of hair cells. J Neurosci. 1990 Nov;10(11):3664–3684. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.10-11-03664.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robitaille R., Charlton M. P. Presynaptic calcium signals and transmitter release are modulated by calcium-activated potassium channels. J Neurosci. 1992 Jan;12(1):297–305. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.12-01-00297.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robitaille R., Garcia M. L., Kaczorowski G. J., Charlton M. P. Functional colocalization of calcium and calcium-gated potassium channels in control of transmitter release. Neuron. 1993 Oct;11(4):645–655. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(93)90076-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tseng-Crank J., Foster C. D., Krause J. D., Mertz R., Godinot N., DiChiara T. J., Reinhart P. H. Cloning, expression, and distribution of functionally distinct Ca(2+)-activated K+ channel isoforms from human brain. Neuron. 1994 Dec;13(6):1315–1330. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(94)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wisgirda M. E., Dryer S. E. Functional dependence of Ca(2+)-activated K+ current on L- and N-type Ca2+ channels: differences between chicken sympathetic and parasympathetic neurons suggest different regulatory mechanisms. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Mar 29;91(7):2858–2862. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.7.2858. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]