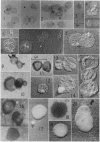
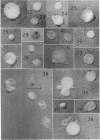
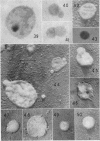
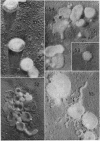
Full text
PDF







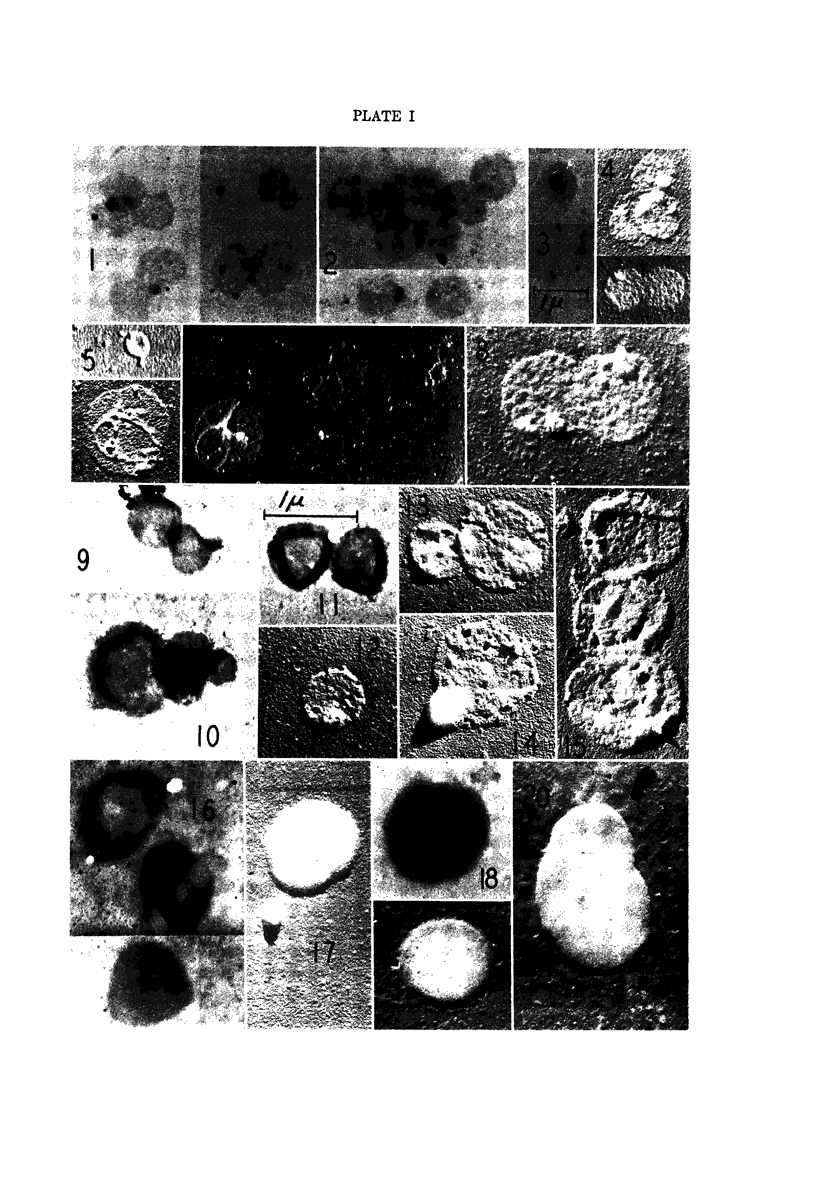

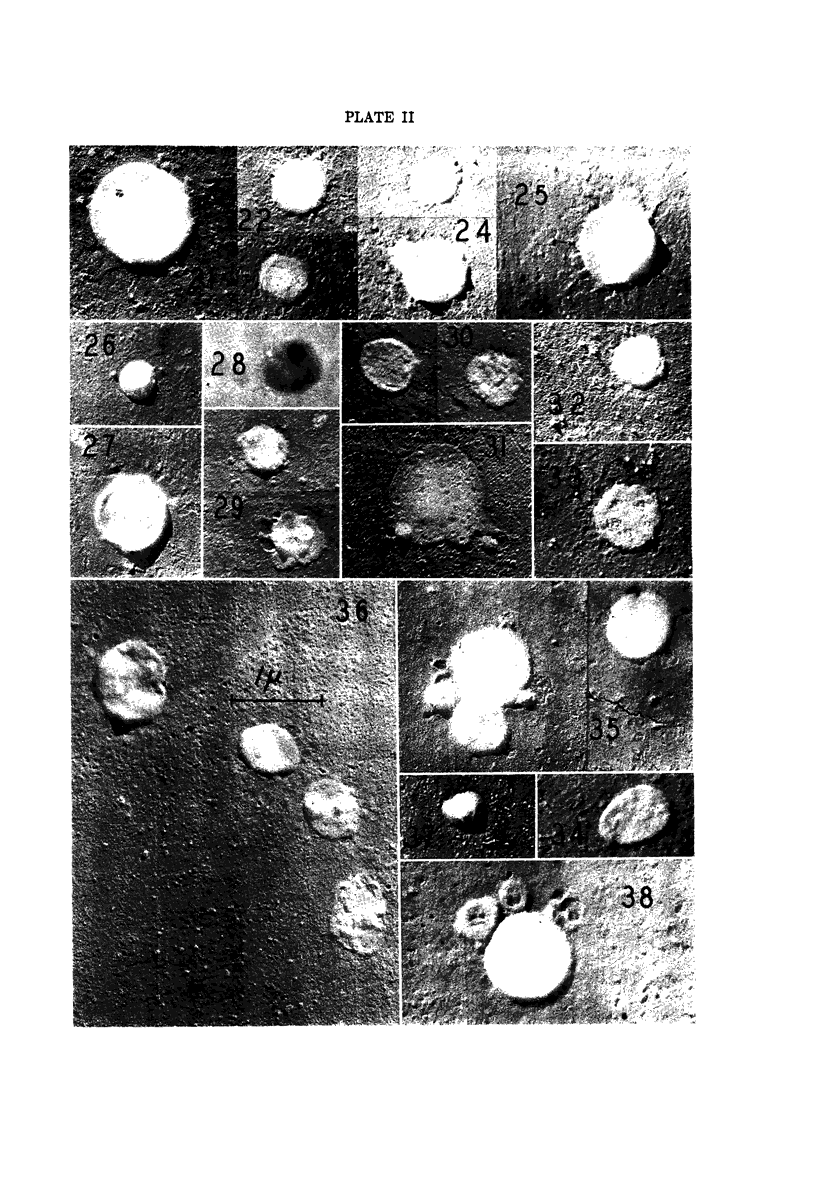

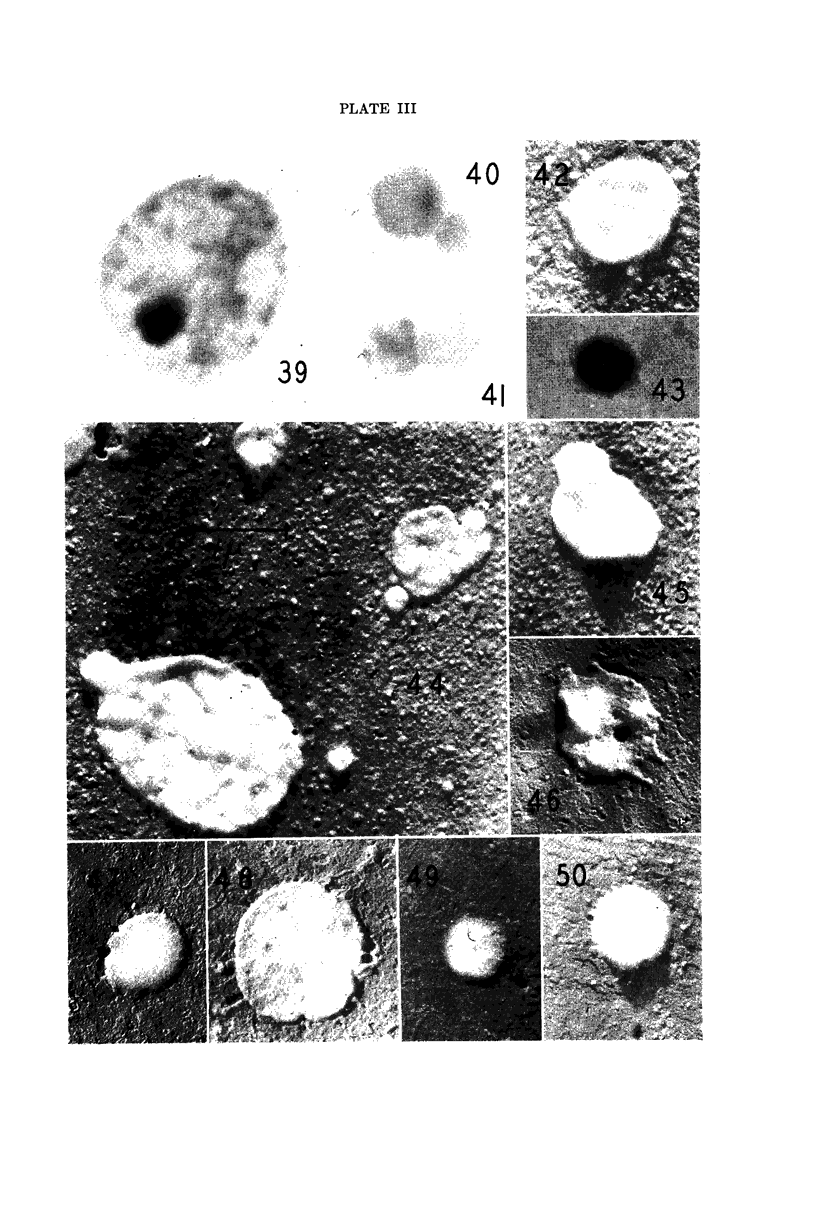

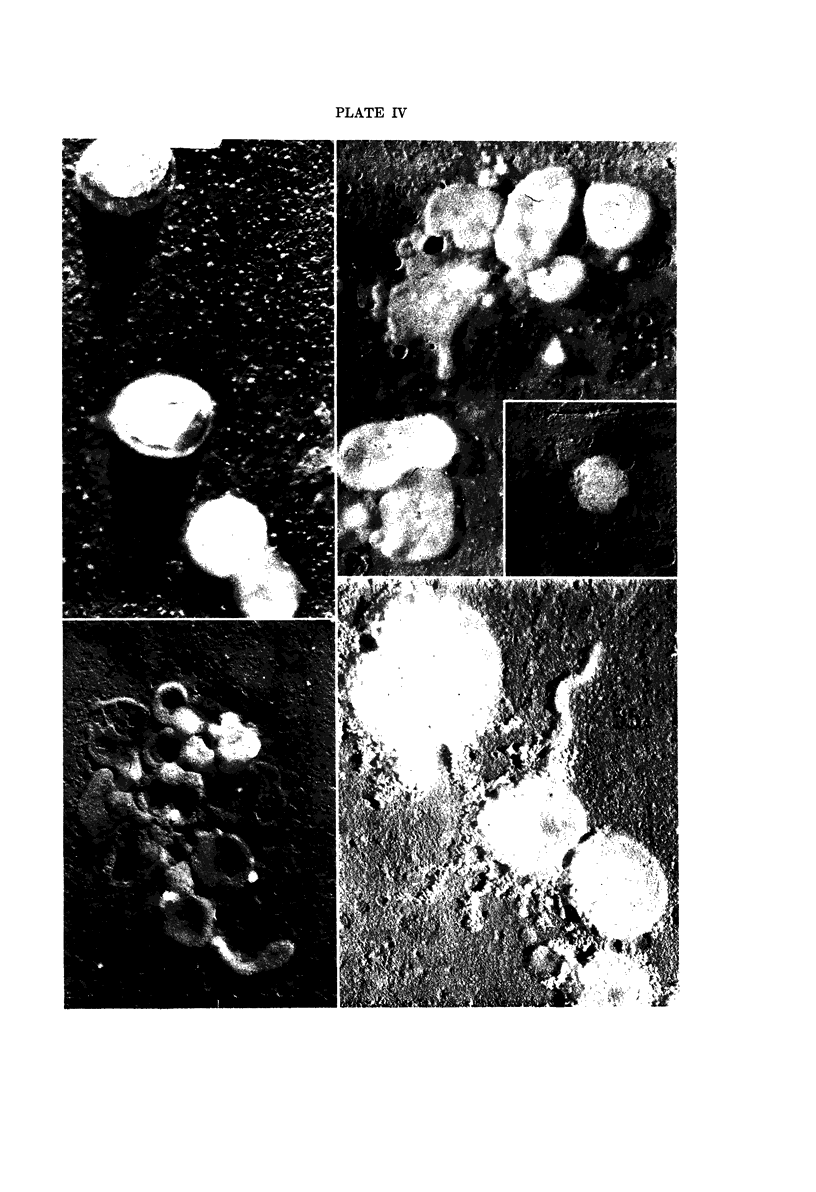

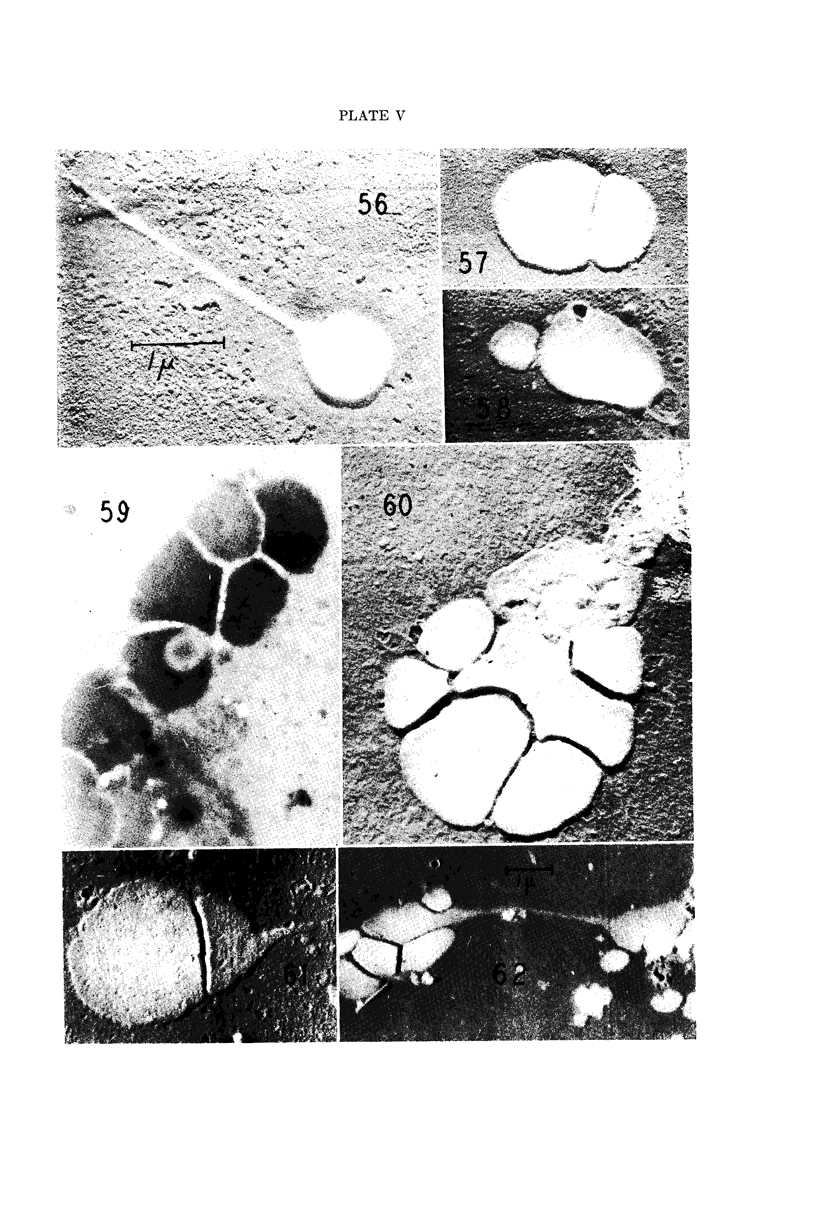

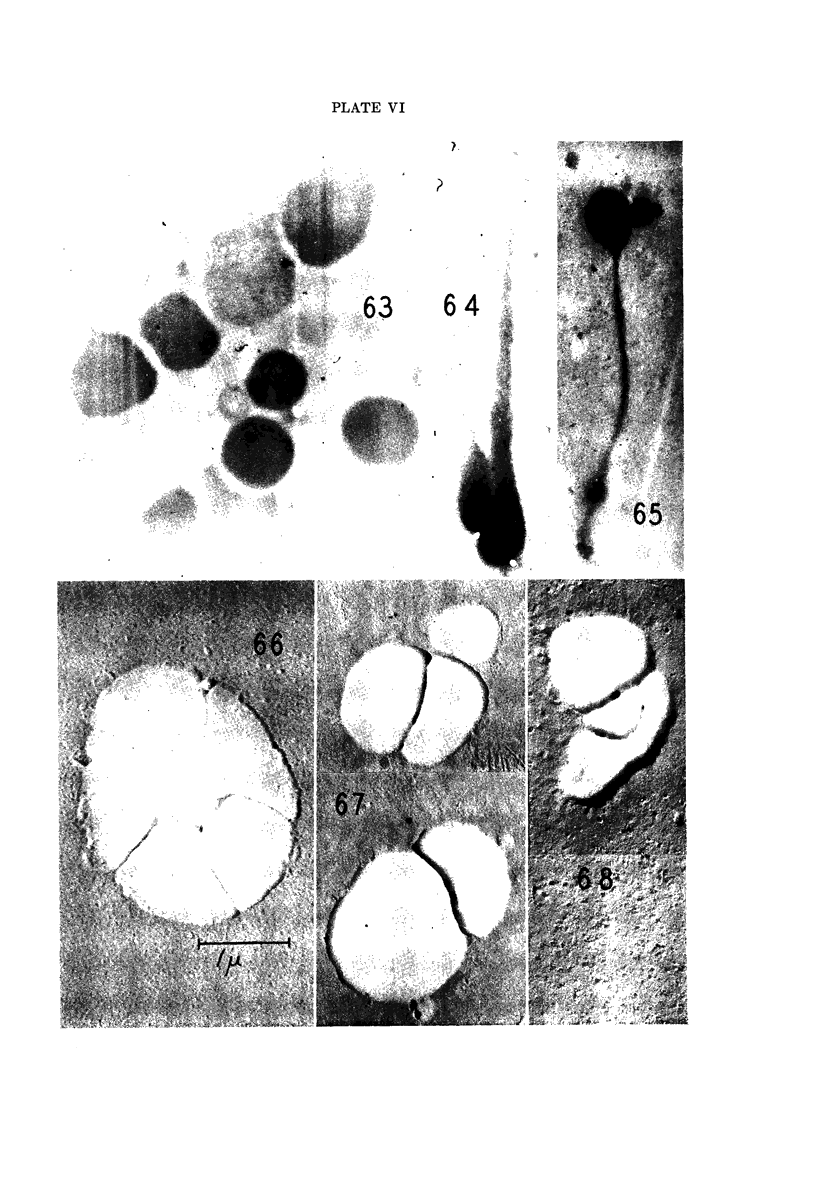

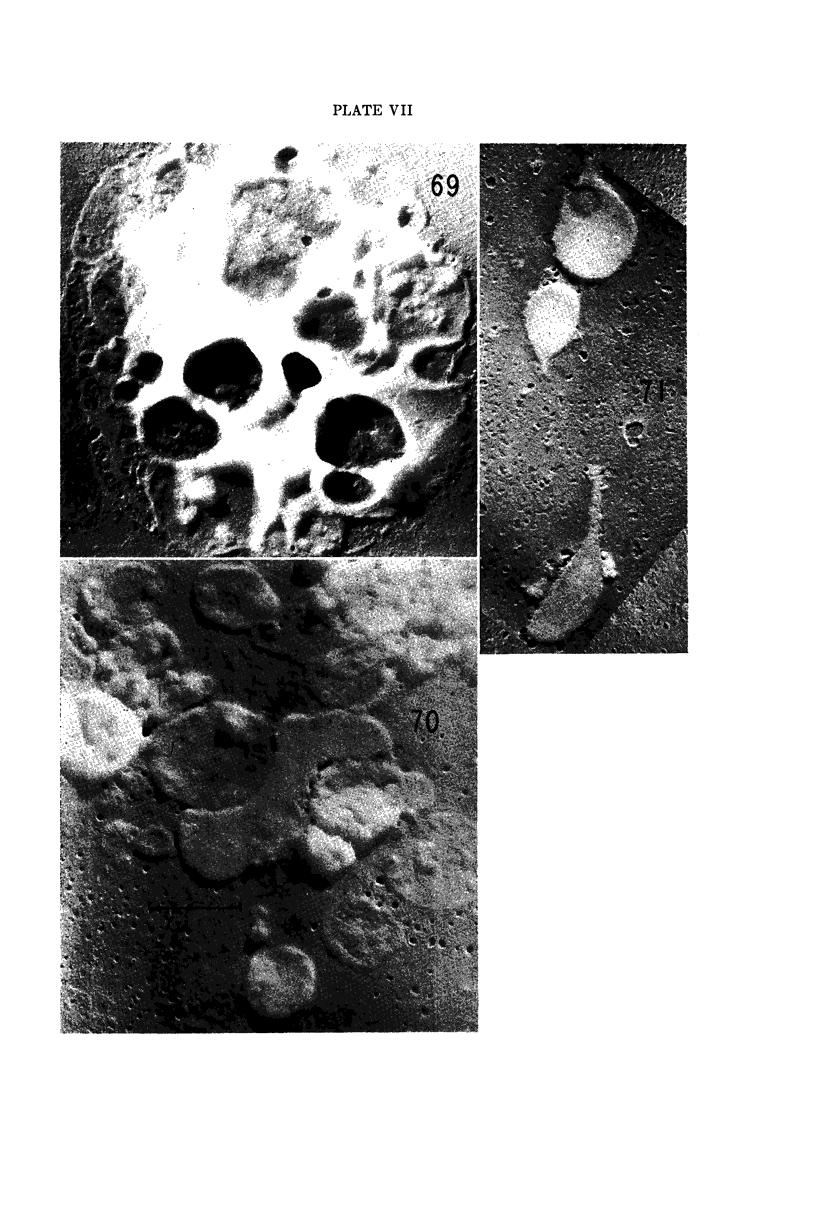
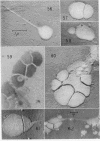
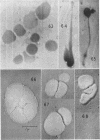
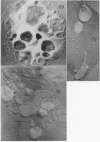
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- DIENES L. Electron micrographs made from L forms of Proteus and two human strains of pleuropneumonia-like organisms. J Bacteriol. 1953 Sep;66(3):280–286. doi: 10.1128/jb.66.3.280-286.1953. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EDWARD D. G. F. An investigation of the biological properties of organisms of the pleuropneumonia group, with suggestions regarding the identification of strains. J Gen Microbiol. 1950 Sep;4(3):311–329. doi: 10.1099/00221287-4-3-311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EDWARD D. G. The pleuropneumonia group of organisms: a review, together with some new observations. J Gen Microbiol. 1954 Feb;10(1):27–64. doi: 10.1099/00221287-10-1-27. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FREUNDT E. A. Morphological and biochemical investigations of human pleuropneumonia-like organisms (Micromyces). Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1954;34(2):127–144. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1954.tb00810.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FREUNDT E. A. Morphological studies of the peripneumonia organism (Micromyces peripneumoniae bovis). Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1952;31(4):508–529. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1952.tb00220.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FREUNDT E. A. The nature of the large bodies in the peripneumonia organism (Micromyces peripneumoniae bovis). Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1952;31(4):560–573. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KELLER R., MORTON H. E. The growth of pleuropneumonia-like organisms of human origin: cultivation in the developing chick embryo and an in vitro growth cycle. J Bacteriol. 1954 Feb;67(2):129–134. doi: 10.1128/jb.67.2.129-134.1954. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KELLER R., SMITH P. F., MORTON H. E. Susceptibility of pleuropneumonia-like organisms from human genital tract to the action of soaps. J Gen Microbiol. 1952 Nov;7(3-4):313–319. doi: 10.1099/00221287-7-3-4-313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LECCE J. G., MORTON H. E. Metabolic studies on three strains of Pleuropneumonia-like organisms isolated from man. J Bacteriol. 1954 Jan;67(1):62–68. doi: 10.1128/jb.67.1.62-68.1954. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MORTON H. E., SMITH P. F., LEBERMAN P. R. Investigation of the cultivation of pleuropneumonia-like organisms from man. Am J Syph Gonorrhea Vener Dis. 1951 Jul;35(4):361–369. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMITH P. F., MORTON H. E. The separation and characterization of the growth factor in serum and ascitic fluid which is required by certain pleuropneumonia-like organisms. J Bacteriol. 1951 Apr;61(4):395–405. doi: 10.1128/jb.61.4.395-405.1951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith W. E., Hillier J., Mudd S. Electron Micrograph Studies of Two Strains of Pleuropneumonia-like (L) Organisms of Human Derivation. J Bacteriol. 1948 Nov;56(5):589–601. doi: 10.1128/jb.56.5.589-601.1948. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss L. J. Electron Micrographs of Pleuropneumonia-like Organisms. J Bacteriol. 1944 Jun;47(6):523–527. doi: 10.1128/jb.47.6.523-527.1944. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]