Abstract
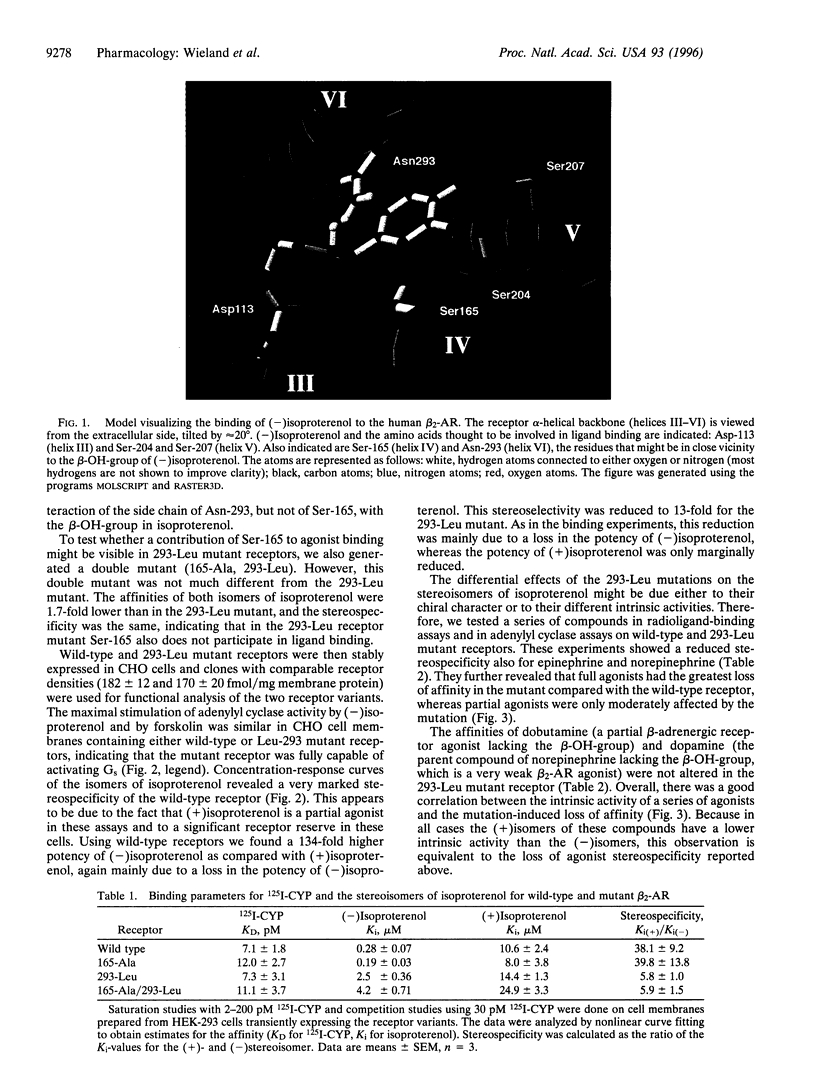
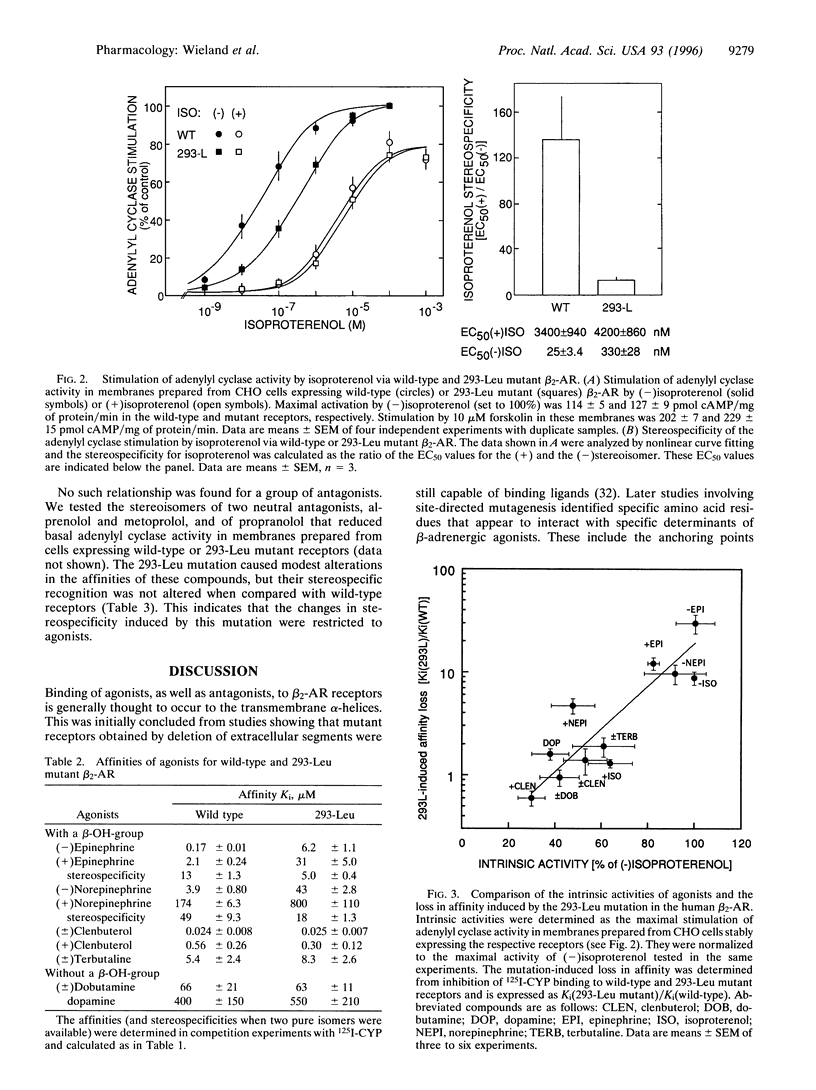
To investigate the molecular mechanism for stereospecific binding of agonists to beta 2-adrenergic receptors we used receptor models to identify potential binding sites for the beta-OH-group of the ligand, which defines the chiral center. Ser-165, located in transmembrane helix IV, and Asn-293, situated in the upper half of transmembrane helix VI, were identified as potential binding sites. Mutation of Ser-165 to Ala did not change the binding of either isoproterenol isomer as revealed after transient expression in human embryonic kidney (HEK)-293 cells. In contrast, a receptor mutant in which Asn-293 was replaced by Leu showed substantial loss of stereospecific isoproterenol binding. Adenylyl cyclase stimulation by this mutant after stable expression in CHO cells confirmed the substantial loss of stereospecificity for isoproterenol. In a series of agonists the loss of affinity in the Leu-293 mutant receptor was strongly correlated with the intrinsic activity of the compounds. Full agonists showed a 10-30-fold affinity loss, whereas partial agonists had almost the same affinity for both receptors. Stereospecific recognition of antagonists was unaltered in the Leu-293 mutant receptor. These data indicate a relationship between stereospecificity and intrinsic activity of agonists and suggest that Asn-293 is important for both properties of the agonist-receptor interaction.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baldwin J. M. The probable arrangement of the helices in G protein-coupled receptors. EMBO J. 1993 Apr;12(4):1693–1703. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05814.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen C., Okayama H. High-efficiency transformation of mammalian cells by plasmid DNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Aug;7(8):2745–2752. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.8.2745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cotecchia S., Schwinn D. A., Randall R. R., Lefkowitz R. J., Caron M. G., Kobilka B. K. Molecular cloning and expression of the cDNA for the hamster alpha 1-adrenergic receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Oct;85(19):7159–7163. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.19.7159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Lean A., Hancock A. A., Lefkowitz R. J. Validation and statistical analysis of a computer modeling method for quantitative analysis of radioligand binding data for mixtures of pharmacological receptor subtypes. Mol Pharmacol. 1982 Jan;21(1):5–16. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixon R. A., Sigal I. S., Rands E., Register R. B., Candelore M. R., Blake A. D., Strader C. D. Ligand binding to the beta-adrenergic receptor involves its rhodopsin-like core. Nature. 1987 Mar 5;326(6108):73–77. doi: 10.1038/326073a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dohlman H. G., Bouvier M., Benovic J. L., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. The multiple membrane spanning topography of the beta 2-adrenergic receptor. Localization of the sites of binding, glycosylation, and regulatory phosphorylation by limited proteolysis. J Biol Chem. 1987 Oct 15;262(29):14282–14288. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Findlay J., Eliopoulos E. Three-dimensional modelling of G protein-linked receptors. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1990 Dec;11(12):492–499. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(90)90050-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freund S., Ungerer M., Lohse M. J. A1 adenosine receptors expressed in CHO-cells couple to adenylyl cyclase and to phospholipase C. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1994 Jul;350(1):49–56. doi: 10.1007/BF00180010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerskowitch V. P., Girdlestone D., Jenkinson D. H. Receptors on the agenda: a symposium to honour Sir James Black. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1994 Oct;15(10):355–361. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(94)90153-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green S. A., Cole G., Jacinto M., Innis M., Liggett S. B. A polymorphism of the human beta 2-adrenergic receptor within the fourth transmembrane domain alters ligand binding and functional properties of the receptor. J Biol Chem. 1993 Nov 5;268(31):23116–23121. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson R., Baldwin J. M., Ceska T. A., Zemlin F., Beckmann E., Downing K. H. Model for the structure of bacteriorhodopsin based on high-resolution electron cryo-microscopy. J Mol Biol. 1990 Jun 20;213(4):899–929. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80271-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hibert M. F., Trumpp-Kallmeyer S., Hoflack J., Bruinvels A. This is not a G protein-coupled receptor. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1993 Jan;14(1):7–12. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(93)90106-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- IJzerman A. P., Bultsma T., Timmerman H., Zaagsma J. The relation between ionization and affinity of beta-adrenoceptor ligands. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1984 Oct;327(4):293–298. doi: 10.1007/BF00506239. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- IJzerman A. P., Van Galen P. J., Jacobson K. A. Molecular modeling of adenosine receptors. I. The ligand binding site on the A1 receptor. Drug Des Discov. 1992;9(1):49–67. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kjelsberg M. A., Cotecchia S., Ostrowski J., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. Constitutive activation of the alpha 1B-adrenergic receptor by all amino acid substitutions at a single site. Evidence for a region which constrains receptor activation. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jan 25;267(3):1430–1433. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobilka B. K., Dixon R. A., Frielle T., Dohlman H. G., Bolanowski M. A., Sigal I. S., Yang-Feng T. L., Francke U., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. cDNA for the human beta 2-adrenergic receptor: a protein with multiple membrane-spanning domains and encoded by a gene whose chromosomal location is shared with that of the receptor for platelet-derived growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jan;84(1):46–50. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.1.46. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobilka B. K., Kobilka T. S., Daniel K., Regan J. W., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. Chimeric alpha 2-,beta 2-adrenergic receptors: delineation of domains involved in effector coupling and ligand binding specificity. Science. 1988 Jun 3;240(4857):1310–1316. doi: 10.1126/science.2836950. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobilka B. K., Matsui H., Kobilka T. S., Yang-Feng T. L., Francke U., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J., Regan J. W. Cloning, sequencing, and expression of the gene coding for the human platelet alpha 2-adrenergic receptor. Science. 1987 Oct 30;238(4827):650–656. doi: 10.1126/science.2823383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):488–492. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewell X. Q. A model of the adrenergic beta-2 receptor and binding sites for agonist and antagonist. Drug Des Discov. 1992;9(1):29–48. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lohse M. J., Benovic J. L., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. Multiple pathways of rapid beta 2-adrenergic receptor desensitization. Delineation with specific inhibitors. J Biol Chem. 1990 Feb 25;265(6):3202–3211. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lohse M. J., Klotz K. N., Schwabe U. Agonist photoaffinity labeling of A1 adenosine receptors: persistent activation reveals spare receptors. Mol Pharmacol. 1986 Oct;30(4):403–409. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lohse M. J., Lenschow V., Schwabe U. Two affinity states of Ri adenosine receptors in brain membranes. Analysis of guanine nucleotide and temperature effects on radioligand binding. Mol Pharmacol. 1984 Jul;26(1):1–9. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lohse M. J. Stable overexpression of human beta 2-adrenergic receptors in mammalian cells. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1992 Apr;345(4):444–451. doi: 10.1007/BF00176623. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Münch G., Dees C., Hekman M., Palm D. Multisite contacts involved in coupling of the beta-adrenergic receptor with the stimulatory guanine-nucleotide-binding regulatory protein. Structural and functional studies by beta-receptor-site-specific synthetic peptides. Eur J Biochem. 1991 Jun 1;198(2):357–364. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1991.tb16023.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okamoto T., Murayama Y., Hayashi Y., Inagaki M., Ogata E., Nishimoto I. Identification of a Gs activator region of the beta 2-adrenergic receptor that is autoregulated via protein kinase A-dependent phosphorylation. Cell. 1991 Nov 15;67(4):723–730. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90067-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pardo L., Ballesteros J. A., Osman R., Weinstein H. On the use of the transmembrane domain of bacteriorhodopsin as a template for modeling the three-dimensional structure of guanine nucleotide-binding regulatory protein-coupled receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 May 1;89(9):4009–4012. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.9.4009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pippig S., Andexinger S., Daniel K., Puzicha M., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J., Lohse M. J. Overexpression of beta-arrestin and beta-adrenergic receptor kinase augment desensitization of beta 2-adrenergic receptors. J Biol Chem. 1993 Feb 15;268(5):3201–3208. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Regan J. W., Kobilka T. S., Yang-Feng T. L., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J., Kobilka B. K. Cloning and expression of a human kidney cDNA for an alpha 2-adrenergic receptor subtype. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(17):6301–6305. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.17.6301. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savarese T. M., Fraser C. M. In vitro mutagenesis and the search for structure-function relationships among G protein-coupled receptors. Biochem J. 1992 Apr 1;283(Pt 1):1–19. doi: 10.1042/bj2830001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schertler G. F., Villa C., Henderson R. Projection structure of rhodopsin. Nature. 1993 Apr 22;362(6422):770–772. doi: 10.1038/362770a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soppa J. Two hypotheses--one answer. Sequence comparison does not support an evolutionary link between halobacterial retinal proteins including bacteriorhodopsin and eukaryotic G-protein-coupled receptors. FEBS Lett. 1994 Mar 28;342(1):7–11. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(94)80573-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strader C. D., Candelore M. R., Hill W. S., Sigal I. S., Dixon R. A. Identification of two serine residues involved in agonist activation of the beta-adrenergic receptor. J Biol Chem. 1989 Aug 15;264(23):13572–13578. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strader C. D., Sigal I. S., Candelore M. R., Rands E., Hill W. S., Dixon R. A. Conserved aspartic acid residues 79 and 113 of the beta-adrenergic receptor have different roles in receptor function. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jul 25;263(21):10267–10271. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strader C. D., Sigal I. S., Dixon R. A. Structural basis of beta-adrenergic receptor function. FASEB J. 1989 May;3(7):1825–1832. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.3.7.2541037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strader C. D., Sigal I. S., Register R. B., Candelore M. R., Rands E., Dixon R. A. Identification of residues required for ligand binding to the beta-adrenergic receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(13):4384–4388. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.13.4384. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trumpp-Kallmeyer S., Hoflack J., Bruinvels A., Hibert M. Modeling of G-protein-coupled receptors: application to dopamine, adrenaline, serotonin, acetylcholine, and mammalian opsin receptors. J Med Chem. 1992 Sep 18;35(19):3448–3462. doi: 10.1021/jm00097a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walseth T. F., Johnson R. A. The enzymatic preparation of [alpha-(32)P]nucleoside triphosphates, cyclic [32P] AMP, and cyclic [32P] GMP. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Mar 28;562(1):11–31. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(79)90122-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang H., Lipfert L., Malbon C. C., Bahouth S. Site-directed anti-peptide antibodies define the topography of the beta-adrenergic receptor. J Biol Chem. 1989 Aug 25;264(24):14424–14431. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang D., Weinstein H. Polarity conserved positions in transmembrane domains of G-protein coupled receptors and bacteriorhodopsin. FEBS Lett. 1994 Jan 10;337(2):207–212. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(94)80274-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




