Abstract
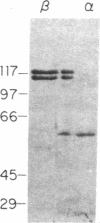
Exonuclease V (EC 3.1.11.5) of Escherichia coli, an enzyme with multiple activities promoting genetic recombination, has previously been shown to contain two polypeptides, the products of the recB and recC genes. We report here that the enzyme contains in addition a third polypeptide (alpha) with a molecular mass of about 58 kDa. The alpha polypeptide is not synthesized by a class of mutants (previously designated recB) lacking the nuclease activity of exonuclease V but retaining recombination proficiency. The gene, recD, coding for the alpha polypeptide is located near recB in the order thyA-recC-ptr-recB-recD-argA on the E. coli chromosome. The recB and recD genes appear to be governed by a common promoter to the left of recB; a weaker promoter appears to govern recD alone. In the light of these results we discuss the relation between the structure and function of the three polypeptides of exonuclease V, hereby alternatively designated RecBCD enzyme.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Belfort M., Maley G., Pedersen-Lane J., Maley F. Primary structure of the Escherichia coli thyA gene and its thymidylate synthase product. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Aug;80(16):4914–4918. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.16.4914. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bittner M., Vapnek D. Versatile cloning vectors derived from the runaway-replication plasmid pKN402. Gene. 1981 Dec;15(4):319–329. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(81)90175-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capaldo-Kimball F., Barbour S. D. Involvement of recombination genes in growth and viability of Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1971 Apr;106(1):204–212. doi: 10.1128/jb.106.1.204-212.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaudhury A. M., Smith G. R. A new class of Escherichia coli recBC mutants: implications for the role of RecBC enzyme in homologous recombination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(24):7850–7854. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.24.7850. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaudhury A. M., Smith G. R. Escherichia coli recBC deletion mutants. J Bacteriol. 1984 Nov;160(2):788–791. doi: 10.1128/jb.160.2.788-791.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland D. W., Fischer S. G., Kirschner M. W., Laemmli U. K. Peptide mapping by limited proteolysis in sodium dodecyl sulfate and analysis by gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1977 Feb 10;252(3):1102–1106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dykstra C. C., Palas K. M., Kushner S. R. Purification and characterization of exonuclease V from Escherichia coli K-12. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1984;49:463–467. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1984.049.01.052. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dykstra C. C., Prasher D., Kushner S. R. Physical and biochemical analysis of the cloned recB and recC genes of Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1984 Jan;157(1):21–27. doi: 10.1128/jb.157.1.21-27.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eichler D. C., Lehman I. R. On the role of ATP in phosphodiester bond hydrolysis catalyzed by the recBC deoxyribonuclease of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jan 25;252(2):499–503. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldmark P. J., Linn S. Purification and properties of the recBC DNase of Escherichia coli K-12. J Biol Chem. 1972 Mar 25;247(6):1849–1860. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guyer M. S. The gamma delta sequence of F is an insertion sequence. J Mol Biol. 1978 Dec 15;126(3):347–365. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90045-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henikoff S. Unidirectional digestion with exonuclease III creates targeted breakpoints for DNA sequencing. Gene. 1984 Jun;28(3):351–359. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90153-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hickson I. D., Emmerson P. T. Identification of the Escherichia coli recB and recC gene products. Nature. 1981 Dec 10;294(5841):578–580. doi: 10.1038/294578a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hickson I. D., Robson C. N., Atkinson K. E., Hutton L., Emmerson P. T. Reconstitution of RecBC DNase activity from purified Escherichia coli RecB and RecC proteins. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jan 25;260(2):1224–1229. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoekstra W. P., Storm P. K., Zuidweg E. M. Recombination in Escherichia coli. VI. Characterization of a recombination-deficient mutation with unusual properties. Mutat Res. 1974 Jun;23(3):319–326. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(74)90105-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lieberman R. P., Oishi M. The recBC deoxyribonuclease of Escherichia coli: isolation and characterization of the subunit proteins and reconstitution of the enzyme. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Dec;71(12):4816–4820. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.12.4816. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacKay V., Linn S. The mechanism of degradation of duplex deoxyribonucleic acid by the recBC enzyme of Escherichia coli K-12. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jul 10;249(13):4286–4294. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pahel G., Rothstein D. M., Magasanik B. Complex glnA-glnL-glnG operon of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1982 Apr;150(1):202–213. doi: 10.1128/jb.150.1.202-213.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ponticelli A. S., Schultz D. W., Taylor A. F., Smith G. R. Chi-dependent DNA strand cleavage by RecBC enzyme. Cell. 1985 May;41(1):145–151. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90069-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosamond J., Telander K. M., Linn S. Modulation of the action of the recBC enzyme of Escherichia coli K-12 by Ca2+. J Biol Chem. 1979 Sep 10;254(17):8646–8652. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sancar A., Wharton R. P., Seltzer S., Kacinski B. M., Clarke N. D., Rupp W. D. Identification of the uvrA gene product. J Mol Biol. 1981 May 5;148(1):45–62. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90234-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasaki M., Fujiyoshi T., Shimada K., Takagi Y. Fine structure of the recB and recC gene region of Escherichia coli. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Nov 30;109(2):414–422. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)91737-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultz D. W., Taylor A. F., Smith G. R. Escherichia coli RecBC pseudorevertants lacking chi recombinational hotspot activity. J Bacteriol. 1983 Aug;155(2):664–680. doi: 10.1128/jb.155.2.664-680.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith G. R., Amundsen S. K., Chaudhury A. M., Cheng K. C., Ponticelli A. S., Roberts C. M., Schultz D. W., Taylor A. F. Roles of RecBC enzyme and chi sites in homologous recombination. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1984;49:485–495. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1984.049.01.055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Storm P. K., Hoekstra W. P., de Haan P. G., Verhoef C. Genetic recombination in Escherichia coli. IV. Isolation and characterization of recombination-deficiency mutants of Escherichia coli K12. Mutat Res. 1971 Sep;13(1):9–17. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(71)90121-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor A. F., Schultz D. W., Ponticelli A. S., Smith G. R. RecBC enzyme nicking at Chi sites during DNA unwinding: location and orientation-dependence of the cutting. Cell. 1985 May;41(1):153–163. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90070-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor A. F., Smith G. R. Substrate specificity of the DNA unwinding activity of the RecBC enzyme of Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1985 Sep 20;185(2):431–443. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90414-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor A., Smith G. R. Unwinding and rewinding of DNA by the RecBC enzyme. Cell. 1980 Nov;22(2 Pt 2):447–457. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90355-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor W. E., Straus D. B., Grossman A. D., Burton Z. F., Gross C. A., Burgess R. R. Transcription from a heat-inducible promoter causes heat shock regulation of the sigma subunit of E. coli RNA polymerase. Cell. 1984 Sep;38(2):371–381. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90492-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umeno M., Sasaki M., Anai M., Takagi Y. Properties of the recB and recC gene products of Escherichia coli. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Nov 15;116(3):1144–1150. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(83)80262-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilcox K. W., Smith H. O. Mechanism of DNA degradation by the ATP-dependent DNase from Hemophilus influenzae Rd. J Biol Chem. 1976 Oct 10;251(19):6127–6134. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willetts N. S., Mount D. W. Genetic analysis of recombination-deficient mutants of Escherichia coli K-12 carrying rec mutations cotransducible with thyA. J Bacteriol. 1969 Nov;100(2):923–934. doi: 10.1128/jb.100.2.923-934.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van de Putte P., Zwenk H., Rörsch A. Properties of four mutants of Escherichia coli defective in genetic recombination. Mutat Res. 1966 Oct;3(5):381–392. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(66)90048-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]