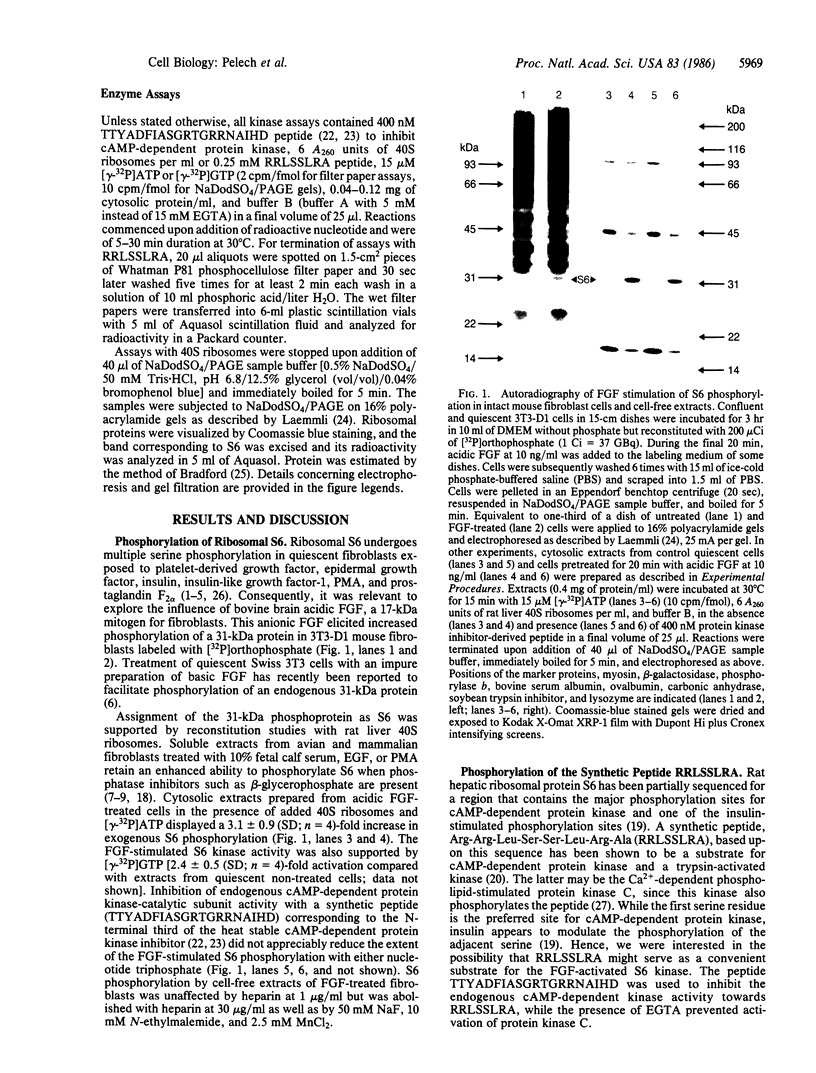
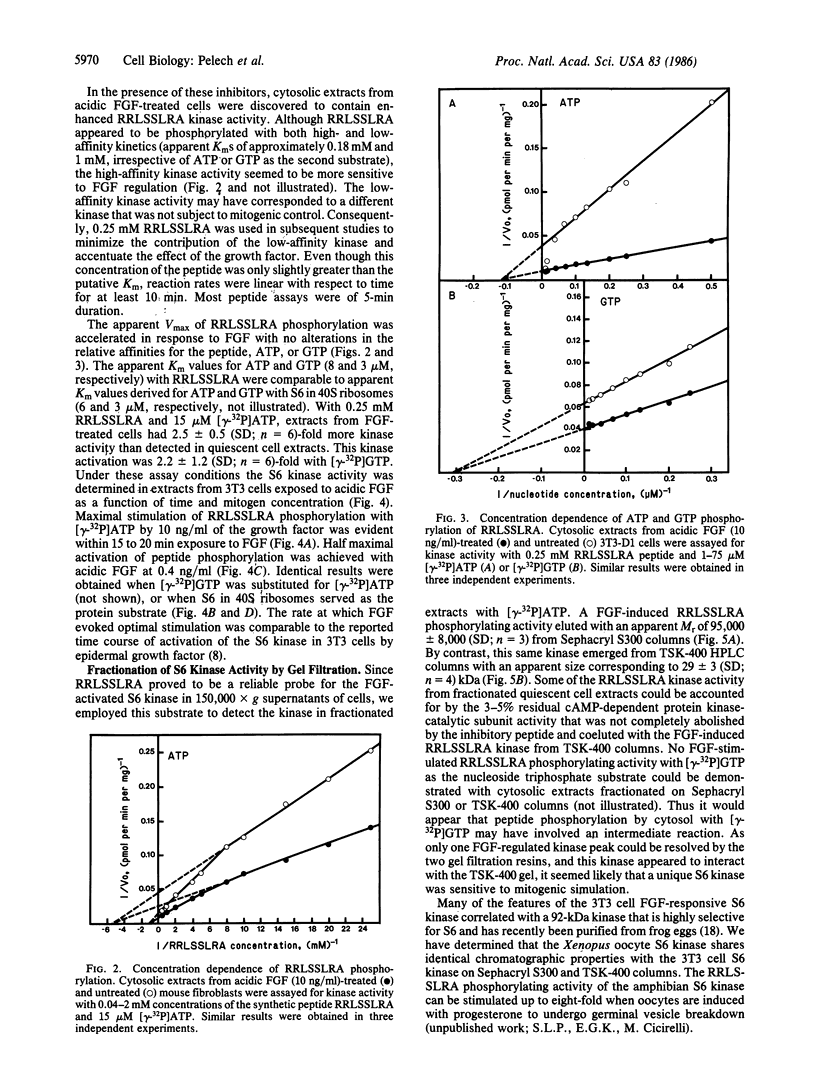
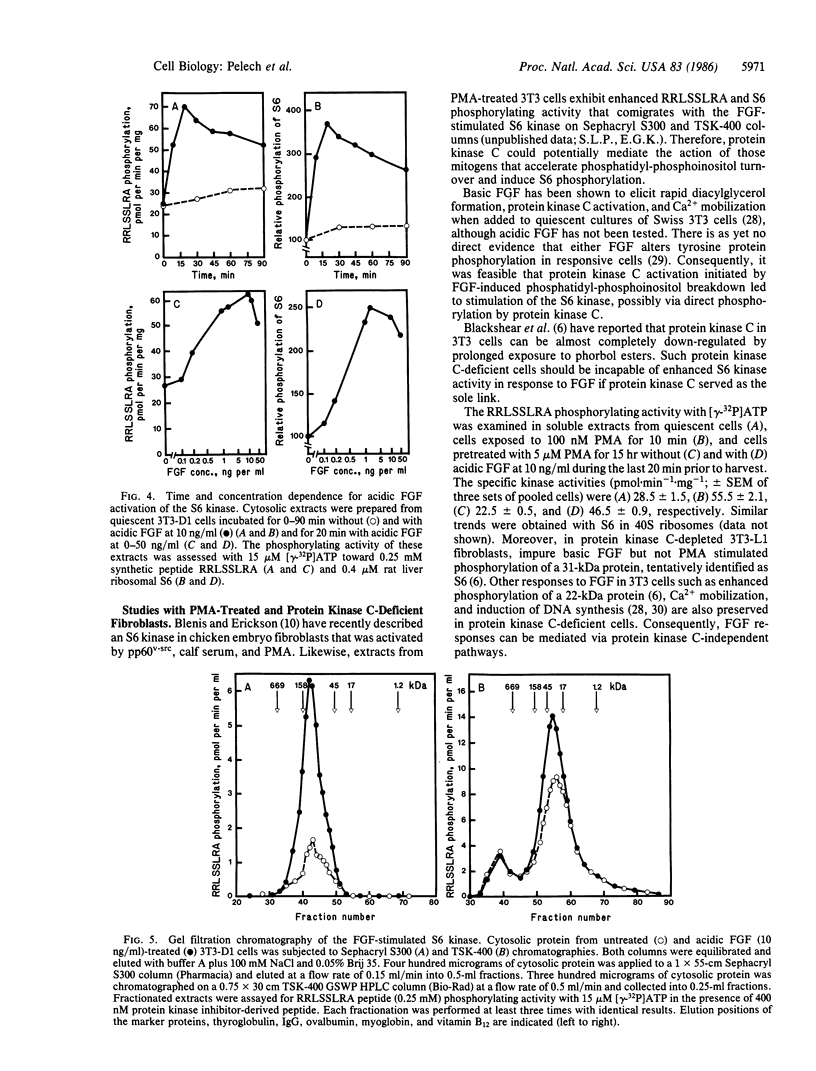
Abstract
Exposure of quiescent cultures of Swiss 3T3-D1 cells to bovine brain acidic fibroblast growth factor (FGF) enhanced phosphorylation of a 31-kDa protein tentatively identified as 40S ribosomal subunit S6 (S6). Soluble extracts from FGF-treated as compared with quiescent fibroblasts exhibited up to 3-fold higher kinase activity towards S6 in exogenously added rat liver 40S ribosomes and a synthetic peptide, RRLSSLRA. This peptide was patterned after a phosphorylation site sequence in S6 and was phosphorylated with an apparent Km corresponding to 0.18 mM. Optimal activation of the S6 kinase with pure mitogen at 10 ng/ml occurred within 15 to 20 min exposure to FGF. Half-maximal stimulation of the FGF-induced S6 kinase was attained with FGF at 0.4 ng/ml. The S6 kinase in crude extracts utilized both [gamma-32P]ATP (apparent Km congruent to 6-8 microM) and [gamma-32P]GTP (apparent Km congruent to 3 microM), but the ability to utilize GTP was lost after partial purification of the kinase. The FGF-stimulated kinase had an apparent Mr of about 95,000 as determined by chromatography on Sephacryl S300 but appeared to be retarded on TSK 400 HPLC columns, since it eluted with an apparent Mr of 29,000. Treatment of Swiss 3T3 cells with the tumor promoter phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA) activated the FGF-stimulated S6 kinase. However, protein kinase C was not required to mediate the FGF activation of the S6 kinase, as FGF still evoked a two-fold activation of the S6 kinase in phorbol ester-pretreated, protein kinase C-depleted cells.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blackshear P. J., Witters L. A., Girard P. R., Kuo J. F., Quamo S. N. Growth factor-stimulated protein phosphorylation in 3T3-L1 cells. Evidence for protein kinase C-dependent and -independent pathways. J Biol Chem. 1985 Oct 25;260(24):13304–13315. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blenis J., Erikson R. L. Regulation of a ribosomal protein S6 kinase activity by the Rous sarcoma virus transforming protein, serum, or phorbol ester. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Nov;82(22):7621–7625. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.22.7621. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blenis J., Spivack J. G., Erikson R. L. Phorbol ester, serum, and rous sarcoma virus transforming gene product induce similar phosphorylations of ribosomal protein S6. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Oct;81(20):6408–6412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.20.6408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonato M. C., da Silva A. M., Maia J. C., Juliani M. H. Phosphorylation of ribosomal protein S6 in the aquatic fungus Blastocladiella emersonii. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Nov 2;144(3):597–606. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb08507.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng H. C., Kemp B. E., Pearson R. B., Smith A. J., Misconi L., Van Patten S. M., Walsh D. A. A potent synthetic peptide inhibitor of the cAMP-dependent protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jan 25;261(3):989–992. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cobb M. H., Rosen O. M. Description of a protein kinase derived from insulin-treated 3T3-L1 cells that catalyzes the phosphorylation of ribosomal protein S6 and casein. J Biol Chem. 1983 Oct 25;258(20):12472–12481. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donahue M. J., Masaracchia R. A. Phosphorylation of ribosomal protein S6 at multiple sites by a cyclic AMP-independent protein kinase from lymphoid cells. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jan 10;259(1):435–440. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erikson E., Maller J. L. Purification and characterization of a protein kinase from Xenopus eggs highly specific for ribosomal protein S6. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jan 5;261(1):350–355. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrari S., Marchiori F., Borin G., Pinna L. A. Distinct structural requirements of Ca2+/phospholipid-dependent protein kinase (protein kinase C) and cAMP-dependent protein kinase as evidenced by synthetic peptide substrates. FEBS Lett. 1985 May 6;184(1):72–77. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80656-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabrielli B., Wettenhall R. E., Kemp B. E., Quinn M., Bizonova L. Phosphorylation of ribosomal protein S6 and a peptide analogue of S6 by a protease-activated kinase isolated from rat liver. FEBS Lett. 1984 Oct 1;175(2):219–226. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(84)80740-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haselbacher G. K., Humbel R. E., Thomas G. Insulin-like growth factor: insulin or serum increase phosphorylation of ribosomal protein S6 during transition of stationary chick embryo fibroblasts into early G1 phase of the cell cycle. FEBS Lett. 1979 Apr 1;100(1):185–190. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)81160-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuret J., Schulman H. Purification and characterization of a Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase from rat brain. Biochemistry. 1984 Nov 6;23(23):5495–5504. doi: 10.1021/bi00318a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawen A., Martini O. H. A chick embryo fibroblast protein kinase recognizing ribosomal protein S6. Activity increase after serum stimulation. FEBS Lett. 1985 Jun 17;185(2):272–276. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80921-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin-Pérez J., Siegmann M., Thomas G. EGF, PGF2 alpha and insulin induce the phosphorylation of identical S6 peptides in swiss mouse 3T3 cells: effect of cAMP on early sites of phosphorylation. Cell. 1984 Feb;36(2):287–294. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90222-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neufeld G., Gospodarowicz D. The identification and partial characterization of the fibroblast growth factor receptor of baby hamster kidney cells. J Biol Chem. 1985 Nov 5;260(25):13860–13868. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishimura J., Deuel T. F. Platelet-derived growth factor stimulates the phosphorylation of ribosomal protein S6. FEBS Lett. 1983 May 30;156(1):130–134. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(83)80263-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novak-Hofer I., Thomas G. An activated S6 kinase in extracts from serum- and epidermal growth factor-stimulated Swiss 3T3 cells. J Biol Chem. 1984 May 10;259(9):5995–6000. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novak-Hofer I., Thomas G. Epidermal growth factor-mediated activation of an S6 kinase in Swiss mouse 3T3 cells. J Biol Chem. 1985 Aug 25;260(18):10314–10319. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olwin B. B., Hauschka S. D. Identification of the fibroblast growth factor receptor of Swiss 3T3 cells and mouse skeletal muscle myoblasts. Biochemistry. 1986 Jun 17;25(12):3487–3492. doi: 10.1021/bi00360a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker P. J., Katan M., Waterfield M. D., Leader D. P. The phosphorylation of eukaryotic ribosomal protein S6 by protein kinase C. Eur J Biochem. 1985 May 2;148(3):579–586. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb08879.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott J. D., Glaccum M. B., Fischer E. H., Krebs E. G. Primary-structure requirements for inhibition by the heat-stable inhibitor of the cAMP-dependent protein kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(6):1613–1616. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.6.1613. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabarini D., Heinrich J., Rosen O. M. Activation of S6 kinase activity in 3T3-L1 cells by insulin and phorbol ester. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(13):4369–4373. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.13.4369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeyama Y., Kaibuchi K., Ohyanagi H., Saitoh Y., Takai Y. Enhancement of growth factor-induced DNA synthesis by colon tumor-promoting bile acids in Swiss 3T3 cells. Their different mode of action from that of phorbol esters. FEBS Lett. 1985 Dec 2;193(2):153–158. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80141-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trevillyan J. M., Kulkarni R. K., Byus C. V. Tumor-promoting phorbol esters stimulate the phosphorylation of ribosomal protein S6 in quiescent Reuber H35 hepatoma cells. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jan 25;259(2):897–902. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuda T., Kaibuchi K., Kawahara Y., Fukuzaki H., Takai Y. Induction of protein kinase C activation and Ca2+ mobilization by fibroblast growth factor in Swiss 3T3 cells. FEBS Lett. 1985 Oct 28;191(2):205–210. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80009-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wettenhall R. E., Chesterman C. N., Walker T., Morgan F. J. Phosphorylation sites for ribosomal S6 protein kinases in mouse 3T3 fibroblasts stimulated with platelet-derived growth factor. FEBS Lett. 1983 Oct 3;162(1):171–176. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(83)81072-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wettenhall R. E., Morgan F. J. Phosphorylation of hepatic ribosomal protein S6 on 80 and 40 S ribosomes. Primary structure of S6 in the region of the major phosphorylation sites for cAMP-dependent protein kinases. J Biol Chem. 1984 Feb 25;259(4):2084–2091. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- del Grande R. W., Traugh J. A. Phosphorylation of 40-S ribosomal subunits by cAMP-dependent, cGMP-dependent and protease-activated protein kinases. Eur J Biochem. 1982 Apr 1;123(2):421–428. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb19785.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]