Abstract
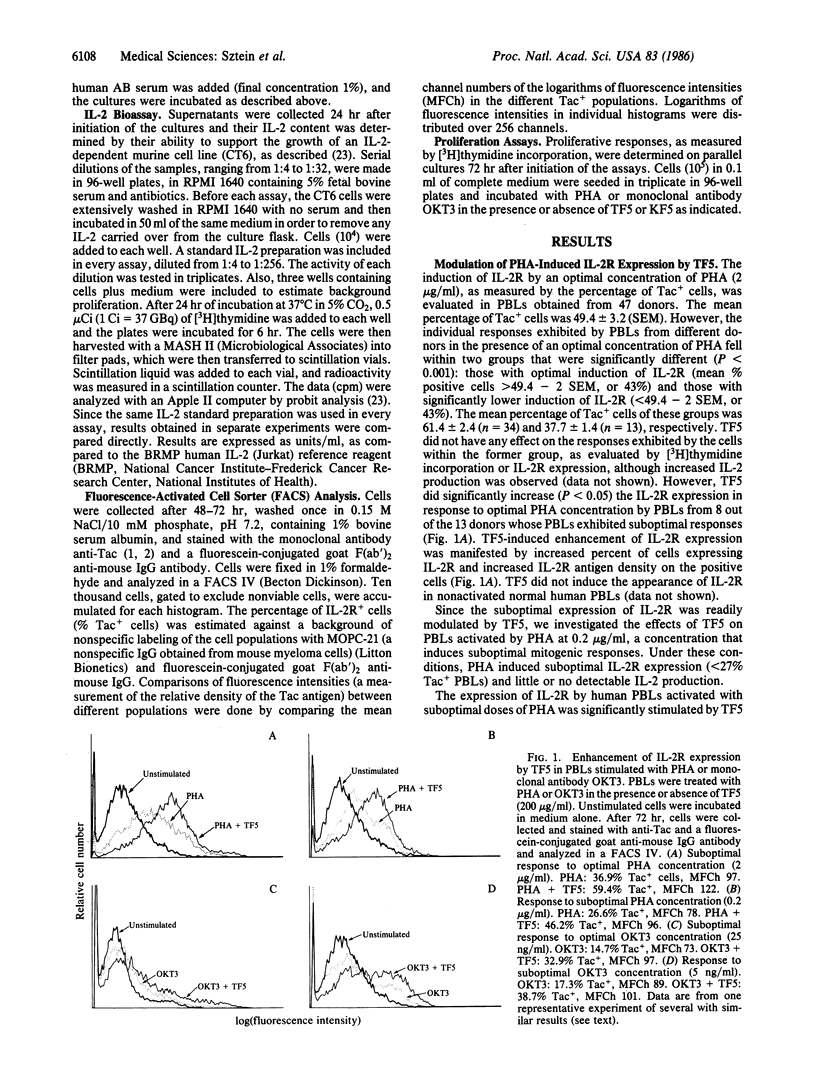
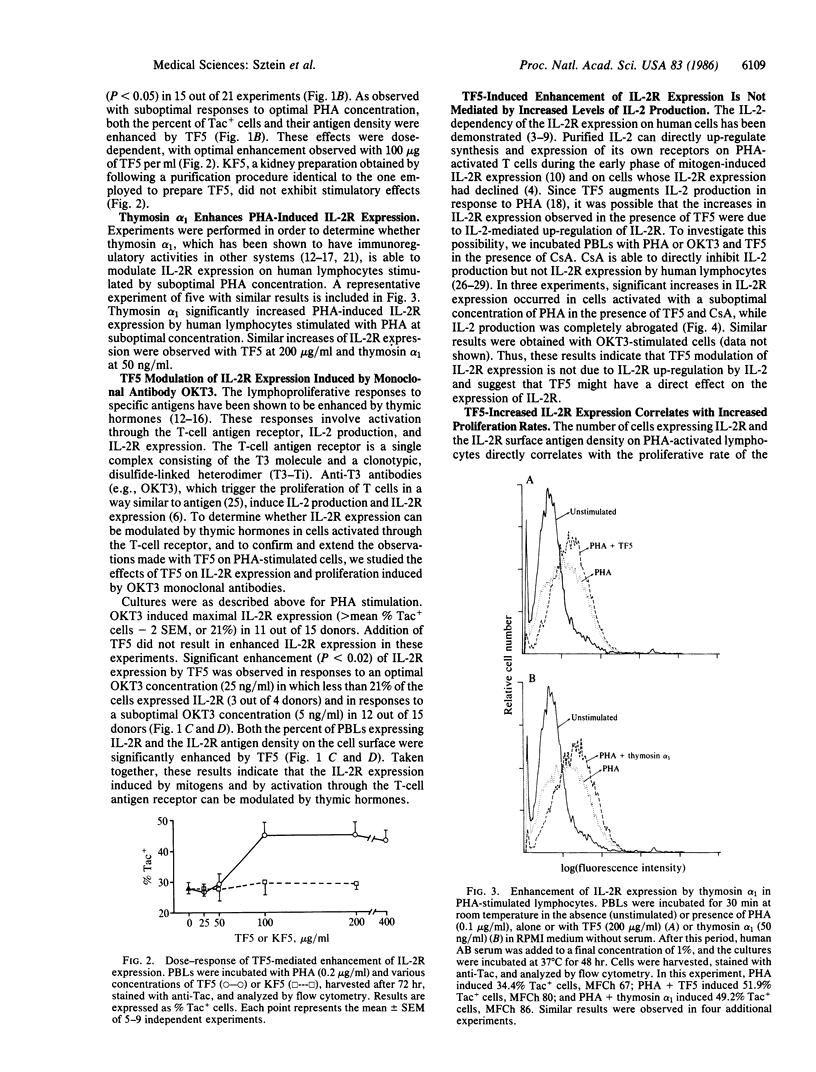
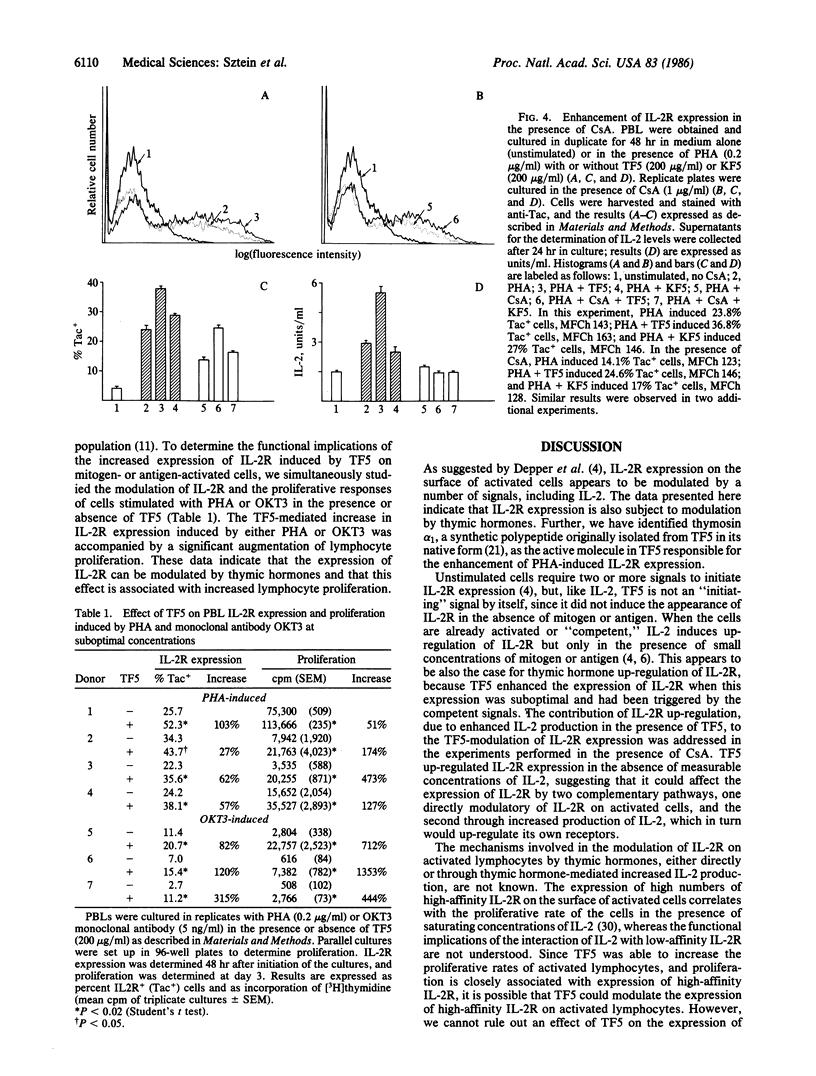
The expression of interleukin 2 receptors (IL-2R) is a critical step leading to normal lymphocyte proliferation. Since thymosin fraction 5 (TF5), a thymic hormone preparation, enhances lymphoproliferative responses of human cells, we examined the effects of TF5 on the expression of IL-2R on mitogen-stimulated human lymphocytes. TF5 significantly increased the percentage and antigen density of cells expressing IL-2R after stimulation with an optimal concentration of phytohemagglutinin (PHA) when the cells from the same donor exhibited suboptimal responses to PHA alone. The same effect was observed with a suboptimal PHA concentration and with OKT3 monoclonal antibody stimulation. Thymosin alpha 1, a synthetic polypeptide originally isolated in its native form from TF5, was also able to increase IL-2R expression in response to PHA, suggesting that it is the active species in TF5. The enhancement of IL-2R expression was paralleled by increased proliferative responses. Increased IL-2R expression appears to be the direct effect of thymic hormones, since abrogation of interleukin 2 production by cyclosporin A did not affect TF5-mediated enhancement of PHA-induced IL-2R expression. These results point to a physiological role of thymic hormones in the maintenance of normal levels of IL-2R expression. This immunoregulatory activity of thymic hormones might be relevant in the treatment of conditions where there is decreased IL-2R expression, such as the acquired immune-deficiency syndrome, or in the restoration of normal IL-2R expression to lymphocytes from aged individuals.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baxevanis C. N., Perez S., Kokkinopoulos D., Papamichail M. The biological effect of three thymosin fraction 5 polypeptides in the murine mixed lymphocyte reaction. Immunology. 1985 Apr;54(4):723–730. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantrell D. A., Smith K. A. Transient expression of interleukin 2 receptors. Consequences for T cell growth. J Exp Med. 1983 Dec 1;158(6):1895–1911. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.6.1895. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Depper J. M., Leonard W. J., Drogula C., Krönke M., Waldmann T. A., Greene W. C. Interleukin 2 (IL-2) augments transcription of the IL-2 receptor gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(12):4230–4234. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.12.4230. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elliott J. F., Lin Y., Mizel S. B., Bleackley R. C., Harnish D. G., Paetkau V. Induction of interleukin 2 messenger RNA inhibited by cyclosporin A. Science. 1984 Dec 21;226(4681):1439–1441. doi: 10.1126/science.6334364. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillis S., Ferm M. M., Ou W., Smith K. A. T cell growth factor: parameters of production and a quantitative microassay for activity. J Immunol. 1978 Jun;120(6):2027–2032. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hooper J. A., McDaniel M. C., Thurman G. B., Cohen G. H., Schulof R. S., Goldstein A. L. Purification and properties of bovine thymosin. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1975 Feb 28;249:125–144. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1975.tb29063.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang K. Y., Kind P. D., Jagoda E. M., Goldstein A. L. Thymosin treatment modulates production of interferon. J Interferon Res. 1981;1(3):411–420. doi: 10.1089/jir.1981.1.411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katzen D., Chu E., Terhost C., Leung D. Y., Gesner M., Miller R. A., Geha R. S. Mechanisms of human T cell response to mitogens: IL 2 induces IL 2 receptor expression and proliferation but not IL 2 synthesis in PHA-stimulated T cells. J Immunol. 1985 Sep;135(3):1840–1845. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaye J., Gillis S., Mizel S. B., Shevach E. M., Malek T. R., Dinarello C. A., Lachman L. B., Janeway C. A., Jr Growth of a cloned helper T cell line induced by a monoclonal antibody specific for the antigen receptor: interleukin 1 is required for the expression of receptors for interleukin 2. J Immunol. 1984 Sep;133(3):1339–1345. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kermani-Arab V., Salehmoghaddam S., Danovitch G., Hirji K., Rezai A. Mediation of the antiproliferative effect of cyclosporine on human lymphocytes by blockade of interleukin 2 biosynthesis. Transplantation. 1985 Apr;39(4):439–442. doi: 10.1097/00007890-198504000-00019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krönke M., Leonard W. J., Depper J. M., Arya S. K., Wong-Staal F., Gallo R. C., Waldmann T. A., Greene W. C. Cyclosporin A inhibits T-cell growth factor gene expression at the level of mRNA transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Aug;81(16):5214–5218. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.16.5214. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipkowitz S., Greene W. C., Rubin A. L., Novogrodsky A., Stenzel K. H. Expression of receptors for interleukin 2: Role in the commitment of T lymphocytes to proliferate. J Immunol. 1984 Jan;132(1):31–37. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Makinodan T., James S. J., Inamizu T., Chang M. P. Immunologic basis for susceptibility to infection in the aged. Gerontology. 1984;30(5):279–289. doi: 10.1159/000212647. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malek T. R., Chan C., Glimcher L. H., Germain R. N., Shevach E. M. Influence of accessory cell and T cell surface antigens on mitogen-induced IL 2 receptor expression. J Immunol. 1985 Sep;135(3):1826–1833. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meltzer M. S., Oppenheim J. J. Bidirectional amplification of macrophage-lymphocyte interactions: enhanced lymphocyte activation factor production by activated adherent mouse peritoneal cells. J Immunol. 1977 Jan;118(1):77–82. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meuer S. C., Hussey R. E., Cantrell D. A., Hodgdon J. C., Schlossman S. F., Smith K. A., Reinherz E. L. Triggering of the T3-Ti antigen-receptor complex results in clonal T-cell proliferation through an interleukin 2-dependent autocrine pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Mar;81(5):1509–1513. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.5.1509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prince H. E., Kermani-Arab V., Fahey J. L. Depressed interleukin 2 receptor expression in acquired immune deficiency and lymphadenopathy syndromes. J Immunol. 1984 Sep;133(3):1313–1317. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reem G. H., Yeh N. H. Interleukin 2 regulates expression of its receptor and synthesis of gamma interferon by human T lymphocytes. Science. 1984 Jul 27;225(4660):429–430. doi: 10.1126/science.6429853. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeves W. G., Zamkoff K. W., Poiesz B. J., Paolozzi F. P., Tomar R. H., Moore J. L., Ruscetti F. W. T cell growth factor required for optimal induction of T cell growth factor receptor expression in phytohemagglutinin-stimulated T cells. J Biol Response Mod. 1985 Feb;4(1):83–95. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robb R. J., Greene W. C., Rusk C. M. Low and high affinity cellular receptors for interleukin 2. Implications for the level of Tac antigen. J Exp Med. 1984 Oct 1;160(4):1126–1146. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.4.1126. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulof R. S. Thymic peptide hormones: basic properties and clinical applications in cancer. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 1985;3(4):309–376. doi: 10.1016/s1040-8428(85)80035-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shoham J., Eshel I. Thymic hormonal activity on human peripheral blood lymphocytes, in vitro. IV. Proliferative response to allogeneic tumor cells in healthy adults and cancer patients. Int J Immunopharmacol. 1983;5(6):515–522. doi: 10.1016/0192-0561(83)90044-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith K. A., Cantrell D. A. Interleukin 2 regulates its own receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(3):864–868. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.3.864. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sztein M. B., Goldstein A. L. Thymic hormones--a clinical update. Springer Semin Immunopathol. 1986;9(1):1–18. doi: 10.1007/BF00201901. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talmadge J. E., Benedict K. L., Uithoven K. A., Lenz B. F. The effect of experimental conditions on the assessment of T cell immunomodulation by biological response modifiers (thymosin fraction five). Immunopharmacology. 1984 Feb;7(1):17–26. doi: 10.1016/0162-3109(84)90004-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uchiyama T., Nelson D. L., Fleisher T. A., Waldmann T. A. A monoclonal antibody (anti-Tac) reactive with activated and functionally mature human T cells. II. Expression of Tac antigen on activated cytotoxic killer T cells, suppressor cells, and on one of two types of helper T cells. J Immunol. 1981 Apr;126(4):1398–1403. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umiel T., Pecht M., Trainin N. THF, a thymic hormone, promotes interleukin-2 production in intact and thymus-deprived mice. J Biol Response Mod. 1984 Aug;3(4):423–434. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welte K., Andreeff M., Platzer E., Holloway K., Rubin B. Y., Moore M. A., Mertelsmann R. Interleukin 2 regulates the expression of Tac antigen on peripheral blood T lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1984 Nov 1;160(5):1390–1403. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.5.1390. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zatz M. M., Goldstein A. L. Mechanism of action of thymosin. I. Thymosin fraction 5 increases lymphokine production by mature murine T cells responding in a mixed lymphocyte reaction. J Immunol. 1985 Feb;134(2):1032–1038. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zatz M. M., Oliver J., Samuels C., Skotnicki A. B., Sztein M. B., Goldstein A. L. Thymosin increases production of T-cell growth factor by normal human peripheral blood lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 May;81(9):2882–2885. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.9.2882. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zatz M. M., Oliver J., Sztein M. B., Skotnicki A. B., Goldstein A. L. Comparison of the effects of thymosin and other thymic factors on modulation of interleukin-2 production. J Biol Response Mod. 1985 Aug;4(4):365–376. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


