Abstract
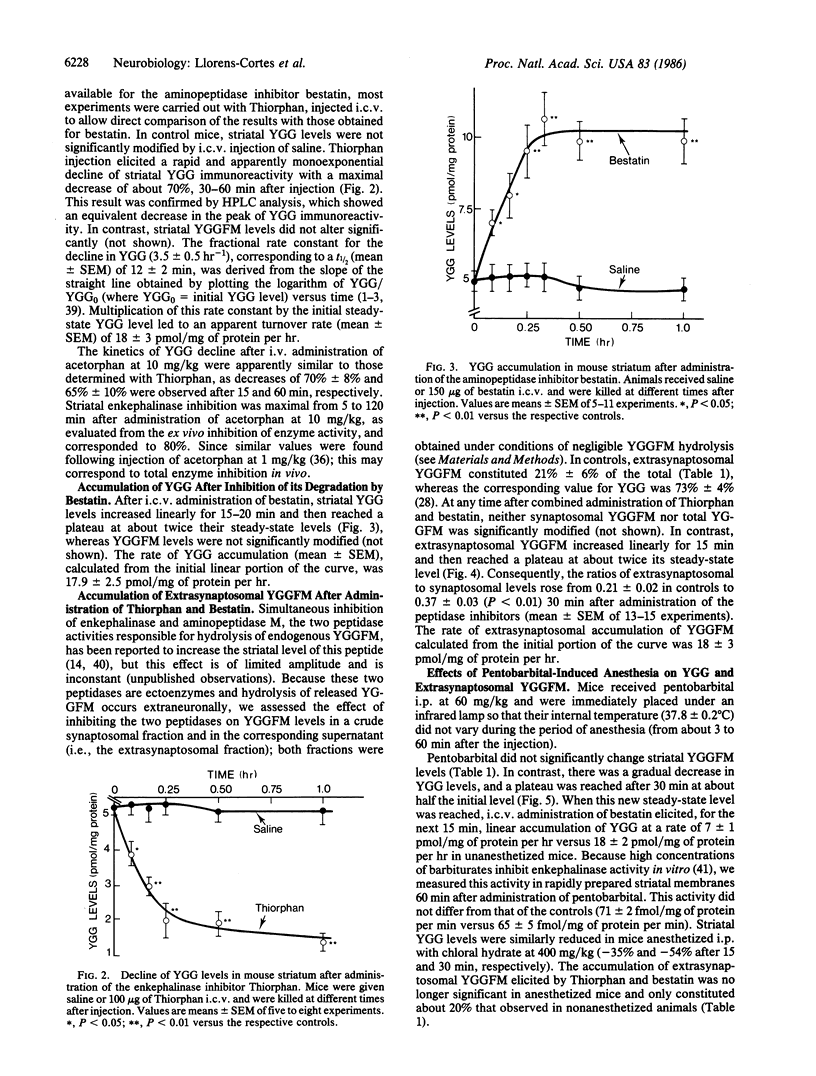
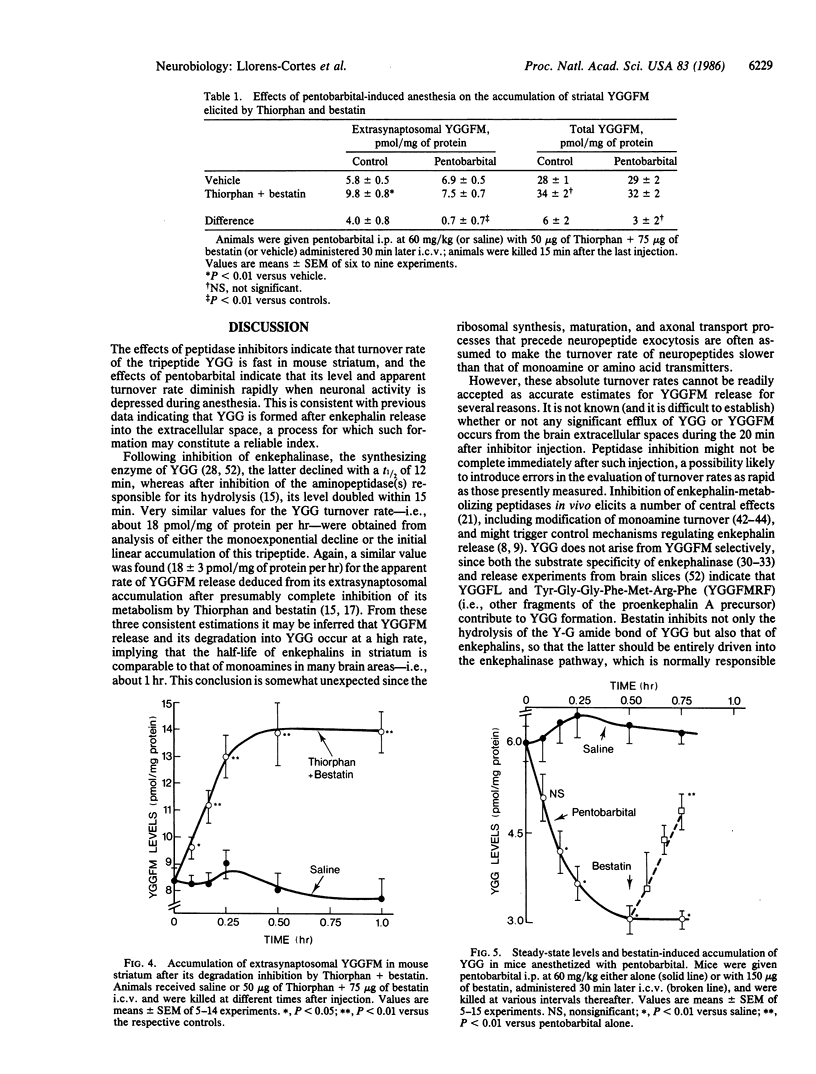
Tyr-Gly-Gly (YGG) was recently shown to be an extraneuronal metabolite of opioid peptides derived from proenkephalin A, formed in brain by the action of "enkephalinase" (membrane metalloendopeptidase, EC 3.4.24.11) and degraded by aminopeptidases. The dynamic state of YGG in mouse striatum was studied by evaluating the changes in its level elicited by inhibitors of these peptidases. Inhibition of YGG synthesis by Thiorphan or acetorphan reduced YGG levels with a t1/2 (mean +/- SEM) of 12 +/- 2 min, indicating an apparent turnover rate (mean +/- SEM) of 18 +/- 2 pmol/mg of protein per hr. An apparent turnover rate of 18 +/- 2 pmol/mg of protein per hr was derived from the rate of YGG accumulation elicited by the aminopeptidase inhibitor bestatin. In addition, accumulation of Tyr-Gly-Gly-Phe-Met (YGGFM) in an extrasynaptosomal fraction after blockade of its degradation by Thiorphan and bestatin occurred at a rate of 18 +/- 3 pmol/mg of protein per hr, which is likely to reflect the rate of enkephalin release in vivo. Hence, the three series of data suggest that striatal enkephalins rapidly turn over--e.g., with a t1/2 in the 1-hr range. Pentobarbital anesthesia reduced by about 60% the rate of YGG accumulation elicited by bestatin and the extrasynaptosomal YGGFM accumulation elicited by Thiorphan and bestatin. This suggests that the activity of striatal enkephalin neurons is depressed during anesthesia. Pentobarbital (and chloral hydrate) did not affect the steady-state level of YGGFM but rapidly reduced that of YGG. Hence, the steady-state levels of YGG seem a reliable index of changes in enkephalin release, and measuring levels of characteristic fragments might therefore provide a general means of evaluating neuropeptide release in vivo.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Algeri S., Altstein M., de Simone G. M., Guardabasso V. In vivo potentiation of [D-Ala2]Met-enkephalin amide central effects after administration of an enkephalinase inhibitor. Eur J Pharmacol. 1981 Sep 11;74(2-3):261–262. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(81)90541-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Almenoff J., Wilk S., Orlowski M. Membrane bound pituitary metalloendopeptidase: apparent identity to enkephalinase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1981 Sep 16;102(1):206–214. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(81)91508-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Altstein M., Mittman S., Vogel Z. The effect of barbiturates on the degradation of enkephalin by brain enzymes. Life Sci. 1981 Jan 12;28(2):185–191. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(81)90551-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brodie B. B., Costa E., Dlabac A., Neff N. H., Smookler H. H. Application of steady state kinetics to the estimation of synthesis rate and turnover time of tissue catecholamines. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1966 Dec;154(3):493–498. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlsson A. Measurements of monoamine synthesis and turnover with special reference to 5-hydroxytryptamine. Adv Biochem Psychopharmacol. 1974;10:75–81. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cesselin F., Soubrié P., Bourgoin S., Artaud F., Reisine T. D., Michelot R., Glowinski J., Hamon M. In vivo release of met-enkephalin in the cat brain. Neuroscience. 1981;6(3):301–313. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(81)90124-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaillet P., Marçais-Collado H., Costentin J., Yi C. C., De La Baume S., Schwartz J. C. Inhibition of enkephalin metabolism by, and antinociceptive activity of, bestatin, an aminopeptidase inhibitor. Eur J Pharmacol. 1983 Jan 21;86(3-4):329–336. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(83)90181-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou J., Tang J., Del Rio J., Yang H. Y., Costa E. Action of peptidase inhibitors on methionine5-enkephalin-arginine6-phenylalanine7 (YGGFMRF) and methionine5-enkephalin (YGGFM) metabolism and on electroacupuncture antinociception. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1984 Aug;230(2):349–352. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corrodi H., Fuxe K., Hökfelt T. The effect of some psychoactive drugs on central monoamine neurons. Eur J Pharmacol. 1967 Sep;1(5):363–368. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(67)90096-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corrodi H., Fuxe K., Hökfelt T. The effects of barbiturates on the activity of the catecholamine neurones in the rat brain. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1966 Aug;18(8):556–558. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1966.tb07932.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craves F. B., Law P. Y., Hunt C. A., Loh H. H. The metabolic disposition of radiolabeled enkephalins in vitro and in situ. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1978 Aug;206(2):492–506. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giros B., Gros C., Solhonne B., Schwartz J. C. Characterization of aminopeptidases responsible for inactivating endogenous (Met5)enkephalin in brain slices using peptidase inhibitors and anti-aminopeptidase M antibodies. Mol Pharmacol. 1986 Mar;29(3):281–287. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giros B., de la Baume S., Gros C., Schwartz J. C. Inhibition de la libération évoquée de (Met5)enképhaline de coupes de globus pallidus en présence de thiorphan et de bestatine. C R Seances Acad Sci III. 1983;297(13):609–612. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gros C., Giros B., Schwartz J. C. Identification of aminopeptidase M as an enkephalin-inactivating enzyme in rat cerebral membranes. Biochemistry. 1985 Apr 23;24(9):2179–2185. doi: 10.1021/bi00330a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gros C., Pradelles P., Rouget C., Bepoldin O., Dray F., Fournie-Zaluski M. C., Roques B. P., Pollard H., Llorens-Cortes C., Schwartz J. C. Radioimmunoassay of methionine- and leucine-enkephalins in regions of rat brain and comparison with endorphins estimated by a radioreceptor assay. J Neurochem. 1978 Jul;31(1):29–39. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1978.tb12429.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HALEY T. J., MCCORMICK W. G. Pharmacological effects produced by intracerebral injection of drugs in the conscious mouse. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1957 Mar;12(1):12–15. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1957.tb01354.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hersh L. B. Degradation of enkephalins: the search for an enkephalinase. Mol Cell Biochem. 1982 Aug 20;47(1):35–43. doi: 10.1007/BF00241564. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hersh L. B. Reaction of opioid peptides with neutral endopeptidase ("enkephalinase"). J Neurochem. 1984 Aug;43(2):487–493. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1984.tb00925.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hong J. S., Yoshikawa K., Kanamatsu T., Sabol S. L. Modulation of striatal enkephalinergic neurons by antipsychotic drugs. Fed Proc. 1985 Jun;44(9):2535–2539. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes J. Biogenesis, release and inactivation of enkephalins and dynorphins. Br Med Bull. 1983 Jan;39(1):17–24. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a071785. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jhamandas K., Yaksh T. L., Go V. L. Acute and chronic morphine modifies the in vivo release of methionine enkephalin-like immunoreactivity from the cat spinal cord and brain. Brain Res. 1984 Apr 9;297(1):91–103. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(84)90545-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lecomte J. M., Costentin J., Vlaiculescu A., Chaillet P., Marcais-Collado H., Llorens-Cortes C., Leboyer M., Schwartz J. C. Pharmacological properties of acetorphan, a parenterally active "enkephalinase" inhibitor. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1986 Jun;237(3):937–944. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lidbrink P., Corrodi H., Fuxe K., Olson L. Barbiturates and meprobamate: decreases in cathecholamine turnover of central dopamine and noradrenaline neuronal systems and the influence of immobilization stress. Brain Res. 1972 Oct 27;45(2):507–524. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(72)90479-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Llorens-Cortes C., Gros C., Schwartz J. C. Study of endogenous Tyr-Gly-Gly, a putative enkephalin metabolite, in mouse brain: validation of a radioimmunoassay, localisation and effects of peptidase inhibitors. Eur J Pharmacol. 1985 Dec 17;119(3):183–191. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(85)90294-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Llorens-Cortes C., Schwartz J. C. Changes in turnover of cerebral monoamines following inhibition of enkephalin metabolism by thiorphan and bestatin. Eur J Pharmacol. 1984 Sep 17;104(3-4):369–374. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(84)90415-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Llorens-Cortes C., Schwartz J. C., Gros C. Detection of the tripeptide Tyr-Gly-Gly, a putative enkephalin metabolite in brain, using a sensitive radioimmunoassay. FEBS Lett. 1985 Sep 23;189(2):325–328. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)81049-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Llorens C., Malfroy B., Schwartz J. C., Gacel G., Roques B. P., Roy J., Morgat J. L., Javoy-Agid F., Agid Y. Enkephalin dipeptidyl carboxypeptidase (enkephalinase) activity: selective radioassay, properties, and regional distribution in human brain. J Neurochem. 1982 Oct;39(4):1081–1089. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1982.tb11500.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malfroy B., Schwartz J. C. Enkephalinase from rat kidney. Purification, characterization, and study of substrate specificity. J Biol Chem. 1984 Dec 10;259(23):14365–14370. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malfroy B., Swerts J. P., Guyon A., Roques B. P., Schwartz J. C. High-affinity enkephalin-degrading peptidase in brain is increased after morphine. Nature. 1978 Nov 30;276(5687):523–526. doi: 10.1038/276523a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin W. R. Pharmacology of opioids. Pharmacol Rev. 1983 Dec;35(4):283–323. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollard H., Bischoff S., Schwartz J. C. Turnover of histamine in rat brain and its decrease under barbiturate anesthesia. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1974 Jul;190(1):88–99. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz J. C., Malfroy B., De La Baume S. Biological inactivation of enkephalins and the role of enkephalin-dipeptidyl-carboxypeptidase ("enkephalinase") as neuropeptidase. Life Sci. 1981 Oct 26;29(17):1715–1740. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(81)90182-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sosa R. P., McKnight A. T., Hughes J., Kosterlitz H. W. Incorporation of labelled amino acids into the enkephalins. FEBS Lett. 1977 Dec 1;84(1):195–198. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)81088-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tang F., Costa E., Schwartz J. P. Increase of proenkephalin mRNA and enkephalin content of rat striatum after daily injection of haloperidol for 2 to 3 weeks. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(12):3841–3844. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.12.3841. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogel Z., Altstein M. The adsorption of enkephalin to porous polystyrene beads: a simple assay for enkephalin hydrolysis. FEBS Lett. 1977 Aug 15;80(2):332–336. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)80469-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood P. L. Phasic enkephalinergic modulation of nigrostriatal dopamine metabolism: potentiation with enkephalinase inhibitors. Eur J Pharmacol. 1982 Aug 13;82(1-2):119–120. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(82)90566-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang H. Y., Hong J. S., Fratta W., Costa E. Rat brain enkephalins: distribution and biosynthesis. Adv Biochem Psychopharmacol. 1978;18:149–159. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang A. Z., Yang H. Y., Costa E. Nociception, enkephalin content and dipeptidyl carboxypeptidase activity in brain of mice treated with exopeptidase inhibitors. Neuropharmacology. 1982 Jul;21(7):625–630. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(82)90004-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de la Baume S., Yi C. C., Schwartz J. C., Chaillet P., Marcais-Collado H., Costentin J. Participation of both 'enkephalinase' and aminopeptidase activities in the metabolism of endogenous enkephalins. Neuroscience. 1983 Jan;8(1):143–151. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(83)90033-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


