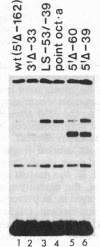
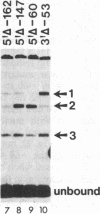
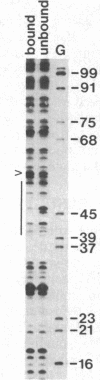
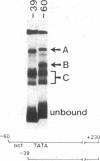
Abstract
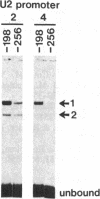
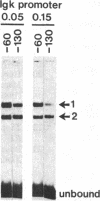
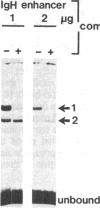
We have examined the interaction of factors in HeLa cell nuclear extracts with a human histone H2B gene (H2B) promoter. Protein-DNA mobility-shift and DNase I protection assays detected a factor(s) binding to a 15-base-pair consensus element that is essential for efficient H2B transcription in vitro. Part of this consensus sequence is the octanucleotide ATTTGCAT, which is apparently a functional component of several non-histone genes. A subset of these genes, including a human U2 small nuclear RNA (snRNA) gene promoter, a mouse immunoglobulin heavy chain enhancer, and a mouse light chain promoter, were shown to interact with the H2B consensus sequence-binding factor(s). These results suggest that a common factor or closely related factors may contribute to the regulation of these and other genes that share the octanucleotide sequence.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ares M., Jr, Mangin M., Weiner A. M. Orientation-dependent transcriptional activator upstream of a human U2 snRNA gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jul;5(7):1560–1570. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.7.1560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergman Y., Rice D., Grosschedl R., Baltimore D. Two regulatory elements for immunoglobulin kappa light chain gene expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(22):7041–7045. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.22.7041. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Busch H., Reddy R., Rothblum L., Choi Y. C. SnRNAs, SnRNPs, and RNA processing. Annu Rev Biochem. 1982;51:617–654. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.51.070182.003153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciliberto G., Buckland R., Cortese R., Philipson L. Transcription signals in embryonic Xenopus laevis U1 RNA genes. EMBO J. 1985 Jun;4(6):1537–1543. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03814.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ephrussi A., Church G. M., Tonegawa S., Gilbert W. B lineage--specific interactions of an immunoglobulin enhancer with cellular factors in vivo. Science. 1985 Jan 11;227(4683):134–140. doi: 10.1126/science.3917574. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falkner F. G., Zachau H. G. Correct transcription of an immunoglobulin kappa gene requires an upstream fragment containing conserved sequence elements. Nature. 1984 Jul 5;310(5972):71–74. doi: 10.1038/310071a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fried M., Crothers D. M. Equilibria and kinetics of lac repressor-operator interactions by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Dec 11;9(23):6505–6525. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.23.6505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garner M. M., Revzin A. A gel electrophoresis method for quantifying the binding of proteins to specific DNA regions: application to components of the Escherichia coli lactose operon regulatory system. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jul 10;9(13):3047–3060. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.13.3047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillies S. D., Morrison S. L., Oi V. T., Tonegawa S. A tissue-specific transcription enhancer element is located in the major intron of a rearranged immunoglobulin heavy chain gene. Cell. 1983 Jul;33(3):717–728. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90014-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heintz N., Roeder R. G. Transcription of human histone genes in extracts from synchronized HeLa cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 May;81(9):2713–2717. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.9.2713. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huet J., Cottrelle P., Cool M., Vignais M. L., Thiele D., Marck C., Buhler J. M., Sentenac A., Fromageot P. A general upstream binding factor for genes of the yeast translational apparatus. EMBO J. 1985 Dec 16;4(13A):3539–3547. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04114.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krol A., Lund E., Dahlberg J. E. The two embryonic U1 RNA genes of Xenopus laevis have both common and gene-specific transcription signals. EMBO J. 1985 Jun;4(6):1529–1535. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03813.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattaj I. W., Lienhard S., Jiricny J., De Robertis E. M. An enhancer-like sequence within the Xenopus U2 gene promoter facilitates the formation of stable transcription complexes. Nature. 1985 Jul 11;316(6024):163–167. doi: 10.1038/316163a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Möritz T., Edström J. E., Pongs O. Cloning of a gene localized and expressed at the ecdysteroid regulated puff 74EF in salivary glands of Drosophila larvae. EMBO J. 1984 Feb;3(2):289–295. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01798.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parslow T. G., Blair D. L., Murphy W. J., Granner D. K. Structure of the 5' ends of immunoglobulin genes: a novel conserved sequence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 May;81(9):2650–2654. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.9.2650. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry M., Thomsen G. H., Roeder R. G. Genomic organization and nucleotide sequence of two distinct histone gene clusters from Xenopus laevis. Identification of novel conserved upstream sequence elements. J Mol Biol. 1985 Oct 5;185(3):479–499. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90065-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh H., Sen R., Baltimore D., Sharp P. A. A nuclear factor that binds to a conserved sequence motif in transcriptional control elements of immunoglobulin genes. Nature. 1986 Jan 9;319(6049):154–158. doi: 10.1038/319154a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Topol J., Ruden D. M., Parker C. S. Sequences required for in vitro transcriptional activation of a Drosophila hsp 70 gene. Cell. 1985 Sep;42(2):527–537. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90110-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tso J. Y., Sun X. H., Wu R. Structure of two unlinked Drosophila melanogaster glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase genes. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jul 5;260(13):8220–8228. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westin G., Lund E., Murphy J. T., Pettersson U., Dahlberg J. E. Human U2 and U1 RNA genes use similar transcription signals. EMBO J. 1984 Dec 20;3(13):3295–3301. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02293.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhong R., Roeder R. G., Heintz N. The primary structure and expression of four cloned human histone genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Nov 11;11(21):7409–7425. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.21.7409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]