Abstract
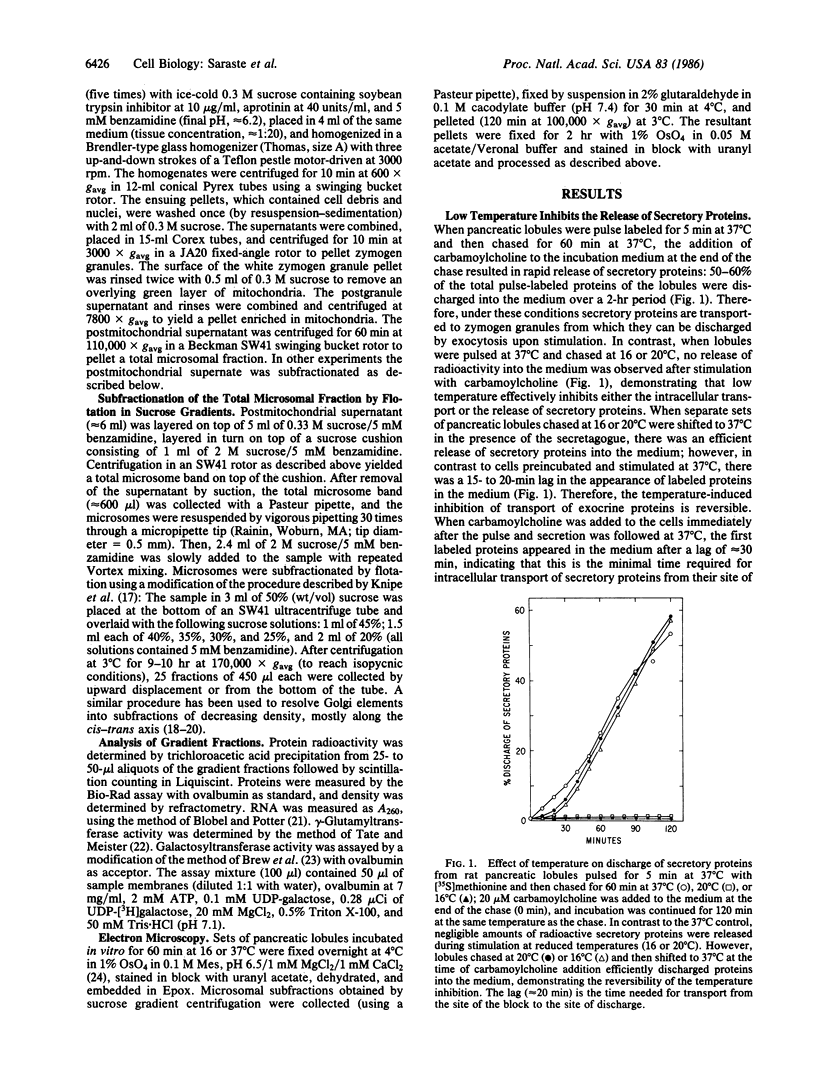
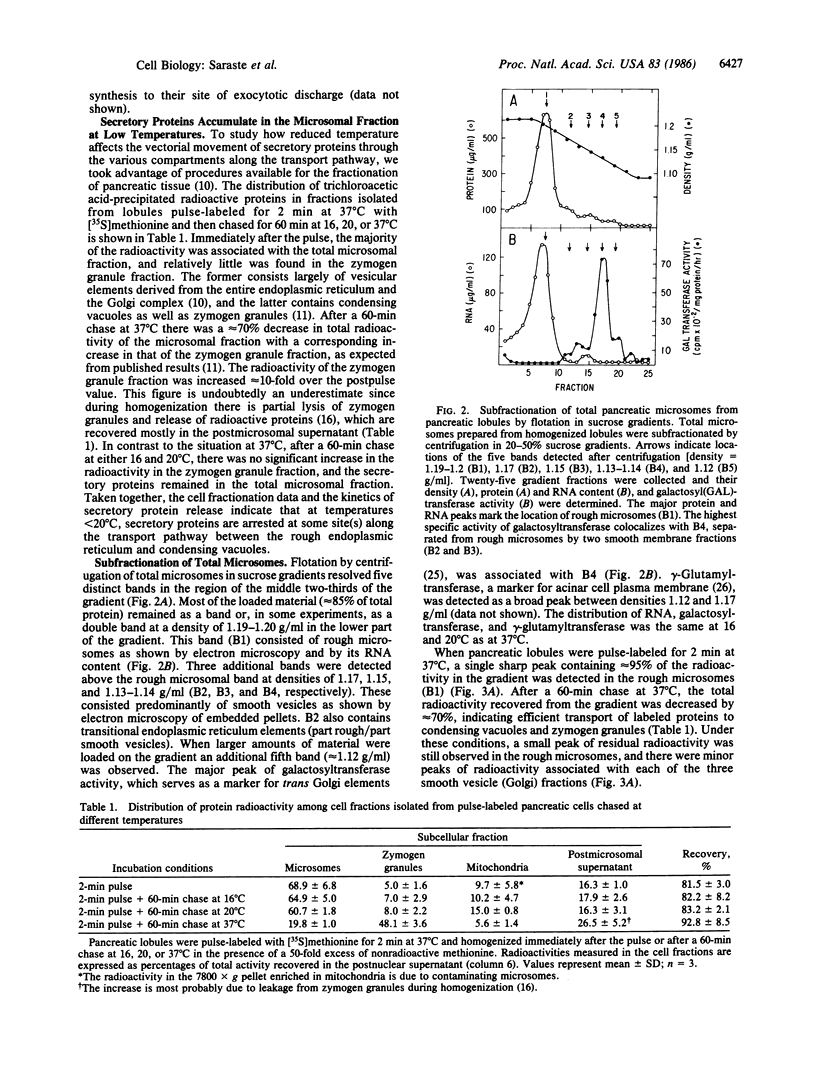
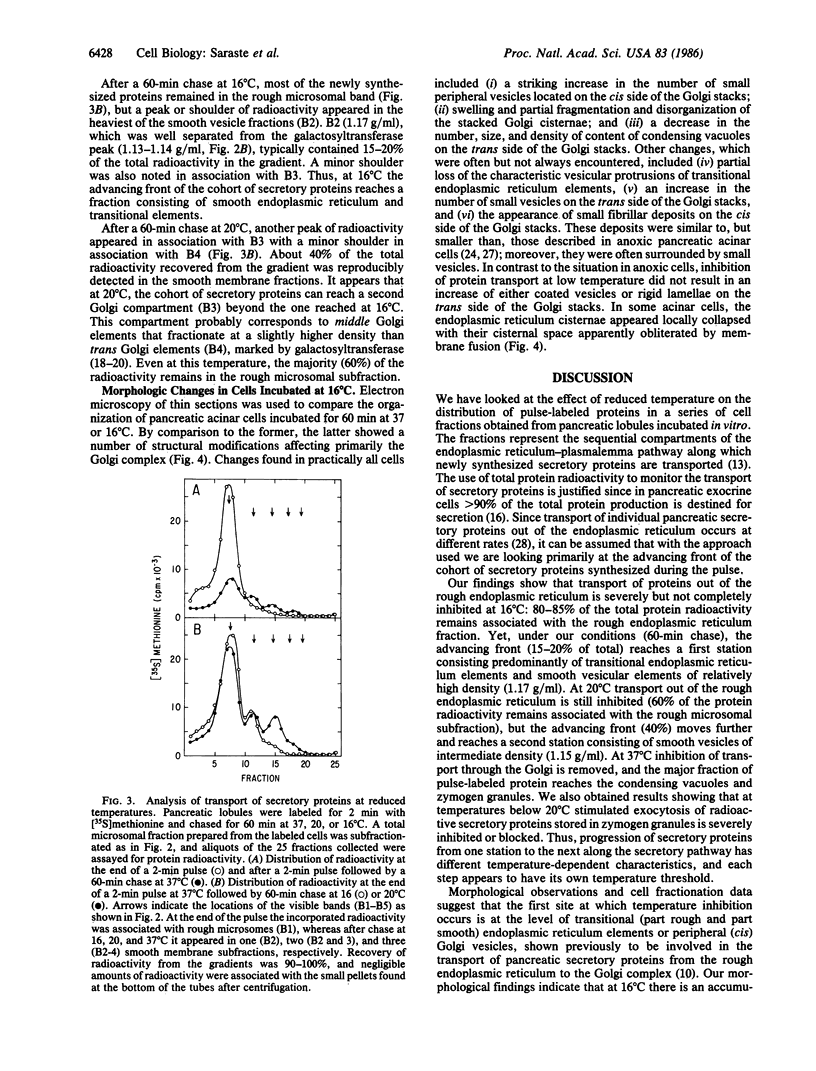
The effect of temperature on secretory protein transport was studied by cell fractionation of rat pancreatic lobules, pulse-labeled in vitro with [35S]methionine and chased for 60 min at 16, 20, or 37 degrees C. Chase at 37 degrees C allowed secretory proteins to reach a zymogen granule fraction, whereas chase at 16 or 20 degrees C led to their extensive retention in a total microsomal fraction. To pinpoint the sites of transport inhibition, total microsomes were subfractionated by flotation in a sucrose density gradient. Five bands were resolved, of which the heaviest or B1 (density = 1.20 g/ml) consisted primarily of rough microsomes. The lighter fractions, B2 (1.17 g/ml), B3 (1.15 g/ml), and B4 (1.14-1.13 g/ml), consisted primarily of smooth vesicles derived from Golgi elements. B4 had the highest specific activity for galactosyltransferase, a trans Golgi cisternal marker; B2, B3, and B4 are assumed to represent cis, middle, and trans Golgi subcompartments, respectively. At the end of a 2-min pulse, a single peak of labeled proteins colocalized with B1. During subsequent 60-min chases, labeled proteins advanced to B2 at 16 degrees C and to B3 at 20 degrees C. At 37 degrees C the radioactivity remaining in the total microsomal fraction was distributed among four peaks (B1-B4). The results indicate that transport from the endoplasmic reticulum to the Golgi complex is strongly inhibited below 20 degrees C. At 16 degrees C, the bulk of the cohort of labeled secretory proteins is still in the rough endoplasmic reticulum, but its advancing front reaches cis Golgi elements. At 20 degrees C, the front advances to a middle Golgi compartment, and at 37 degrees C most of the cohort (approximately 70%) reaches condensing vacuoles and zymogen granules. It is concluded that transport steps along the endoplasmic reticulum-plasmalemma pathway have distinct temperature requirements.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blobel G., Potter V. R. Distribution of radioactivity between the acid-soluble pool and the pools of RNA in the nuclear, nonsedimethable and ribosome fractions of rat liver after a single injection of lebaled orotic acid. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Aug 23;166(1):48–57. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(68)90489-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brew K., Shaper J. H., Olsen K. W., Trayer I. P., Hill R. L. Cross-linking of the components of lactose synthetase with dimethylpimelimidate. J Biol Chem. 1975 Feb 25;250(4):1434–1444. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castle J. D., Cameron R. S., Patterson P. L., Ma A. K. Identification of high molecular weight antigens structurally related to gamma-glutamyl transferase in epithelial tissues. J Membr Biol. 1985;87(1):13–26. doi: 10.1007/BF01870695. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn W. A., Hubbard A. L., Aronson N. N., Jr Low temperature selectively inhibits fusion between pinocytic vesicles and lysosomes during heterophagy of 125I-asialofetuin by the perfused rat liver. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jun 25;255(12):5971–5978. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunphy W. G., Fries E., Urbani L. J., Rothman J. E. Early and late functions associated with the Golgi apparatus reside in distinct compartments. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Dec;78(12):7453–7457. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.12.7453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunphy W. G., Rothman J. E. Compartmentation of asparagine-linked oligosaccharide processing in the Golgi apparatus. J Cell Biol. 1983 Jul;97(1):270–275. doi: 10.1083/jcb.97.1.270. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farquhar M. G. Progress in unraveling pathways of Golgi traffic. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1985;1:447–488. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.01.110185.002311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg D. E., Kornfeld S. Evidence for extensive subcellular organization of asparagine-linked oligosaccharide processing and lysosomal enzyme phosphorylation. J Biol Chem. 1983 Mar 10;258(5):3159–3165. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffiths G., Pfeiffer S., Simons K., Matlin K. Exit of newly synthesized membrane proteins from the trans cisterna of the Golgi complex to the plasma membrane. J Cell Biol. 1985 Sep;101(3):949–964. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.3.949. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jamieson J. D., Palade G. E. Intracellular transport of secretory proteins in the pancreatic exocrine cell. I. Role of the peripheral elements of the Golgi complex. J Cell Biol. 1967 Aug;34(2):577–596. doi: 10.1083/jcb.34.2.577. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jamieson J. D., Palade G. E. Intracellular transport of secretory proteins in the pancreatic exocrine cell. II. Transport to condensing vacuoles and zymogen granules. J Cell Biol. 1967 Aug;34(2):597–615. doi: 10.1083/jcb.34.2.597. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jamieson J. D., Palade G. E. Intracellular transport of secretory proteins in the pancreatic exocrine cell. IV. Metabolic requirements. J Cell Biol. 1968 Dec;39(3):589–603. doi: 10.1083/jcb.39.3.589. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knipe D. M., Baltimore D., Lodish H. F. Separate pathways of maturation of the major structural proteins of vesicular stomatitis virus. J Virol. 1977 Mar;21(3):1128–1139. doi: 10.1128/jvi.21.3.1128-1139.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lagunoff D., Wan H. Temperature dependence of mast cell histamine secretion. J Cell Biol. 1974 Jun;61(3):809–811. doi: 10.1083/jcb.61.3.809. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsh M., Bolzau E., Helenius A. Penetration of Semliki Forest virus from acidic prelysosomal vacuoles. Cell. 1983 Mar;32(3):931–940. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90078-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matlin K. S., Simons K. Reduced temperature prevents transfer of a membrane glycoprotein to the cell surface but does not prevent terminal glycosylation. Cell. 1983 Aug;34(1):233–243. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90154-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merisko E. M., Farquhar M. G., Palade G. E. Redistribution of clathrin heavy and light chains in anoxic pancreatic acinar cells. Pancreas. 1986;1(2):110–123. doi: 10.1097/00006676-198603000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merisko E. M., Fletcher M., Palade G. E. The reorganization of the Golgi complex in anoxic pancreatic acinar cells. Pancreas. 1986;1(2):95–109. doi: 10.1097/00006676-198603000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palade G. Intracellular aspects of the process of protein synthesis. Science. 1975 Aug 1;189(4200):347–358. doi: 10.1126/science.1096303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth J., Berger E. G. Immunocytochemical localization of galactosyltransferase in HeLa cells: codistribution with thiamine pyrophosphatase in trans-Golgi cisternae. J Cell Biol. 1982 Apr;93(1):223–229. doi: 10.1083/jcb.93.1.223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rotundo R. L., Fambrough D. M. Secretion of acetylcholinesterase: relation to acetylcholine receptor metabolism. Cell. 1980 Nov;22(2 Pt 2):595–602. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90369-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandvig K., Olsnes S. Effect of temperature on the uptake, excretion and degradation of abrin and ricin by HeLa cells. Exp Cell Res. 1979 Jun;121(1):15–25. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(79)90439-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saraste J., Hedman K. Intracellular vesicles involved in the transport of Semliki Forest virus membrane proteins to the cell surface. EMBO J. 1983;2(11):2001–2006. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01691.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saraste J., Kuismanen E. Pre- and post-Golgi vacuoles operate in the transport of Semliki Forest virus membrane glycoproteins to the cell surface. Cell. 1984 Sep;38(2):535–549. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90508-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheele G. A., Palade G. E. Studies on the guinea pig pancreas. Parallel discharge of exocrine enzyme activities. J Biol Chem. 1975 Apr 10;250(7):2660–2670. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheele G. A., Palade G. E., Tartakoff A. M. Cell fractionation studies on the guinea pig pancreas. Redistribution of exocrine proteins during tissue homogenization. J Cell Biol. 1978 Jul;78(1):110–130. doi: 10.1083/jcb.78.1.110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheele G. Pancreatic lobules in the in vitro study of pancreatic acinar cell function. Methods Enzymol. 1983;98:17–28. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)98135-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheele G., Tartakoff A. Exit of nonglycosylated secretory proteins from the rough endoplasmic reticulum is asynchronous in the exocrine pancreas. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jan 25;260(2):926–931. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tate S. S., Meister A. Interaction of gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase with amino acids, dipeptides, and derivatives and analogs of glutathione. J Biol Chem. 1974 Dec 10;249(23):7593–7602. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



