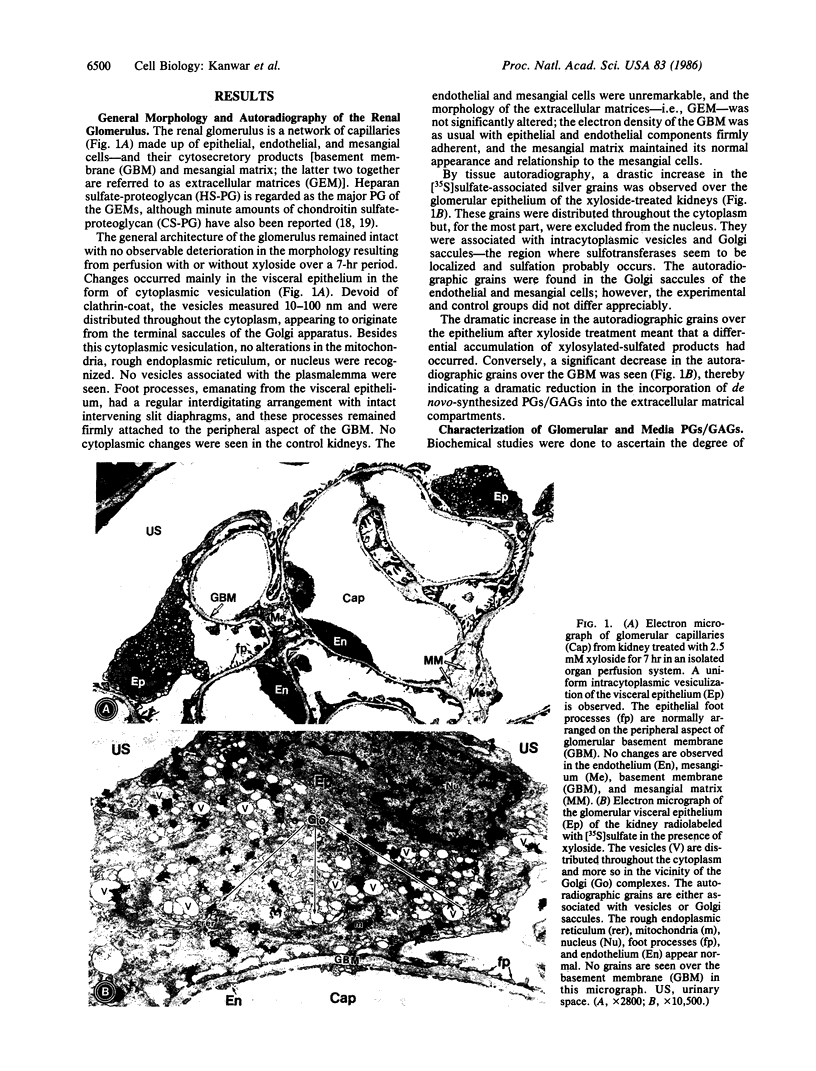
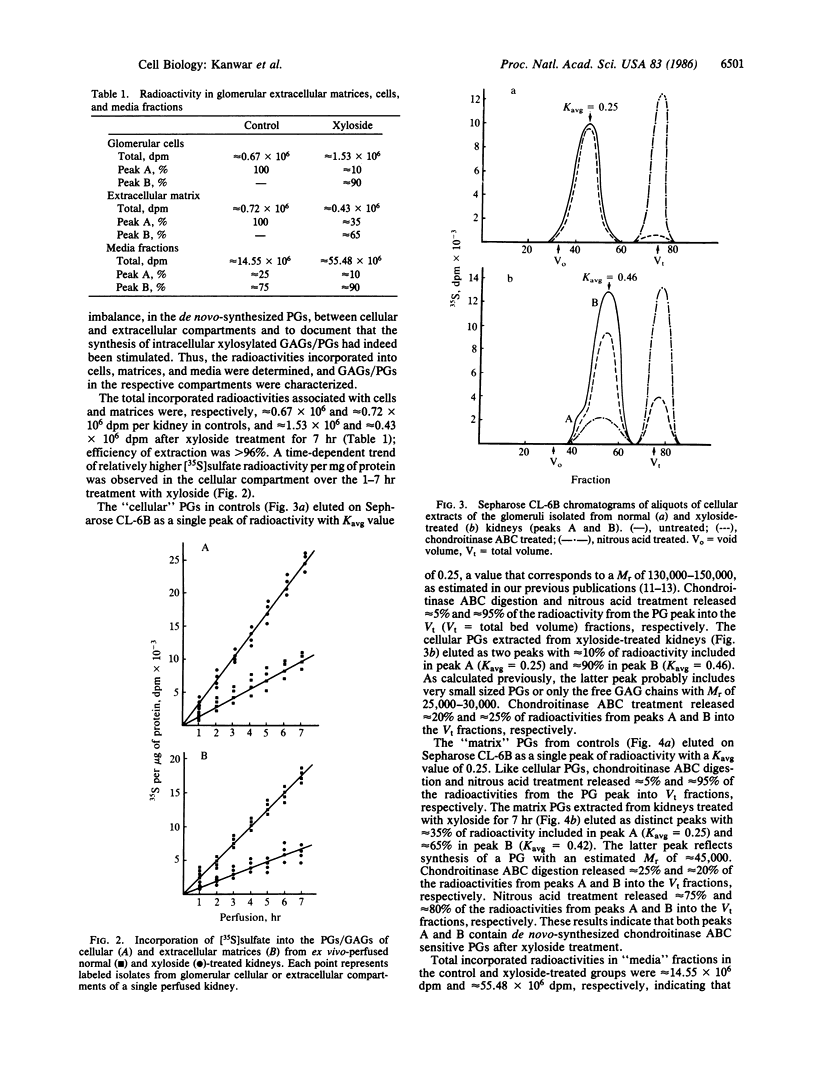
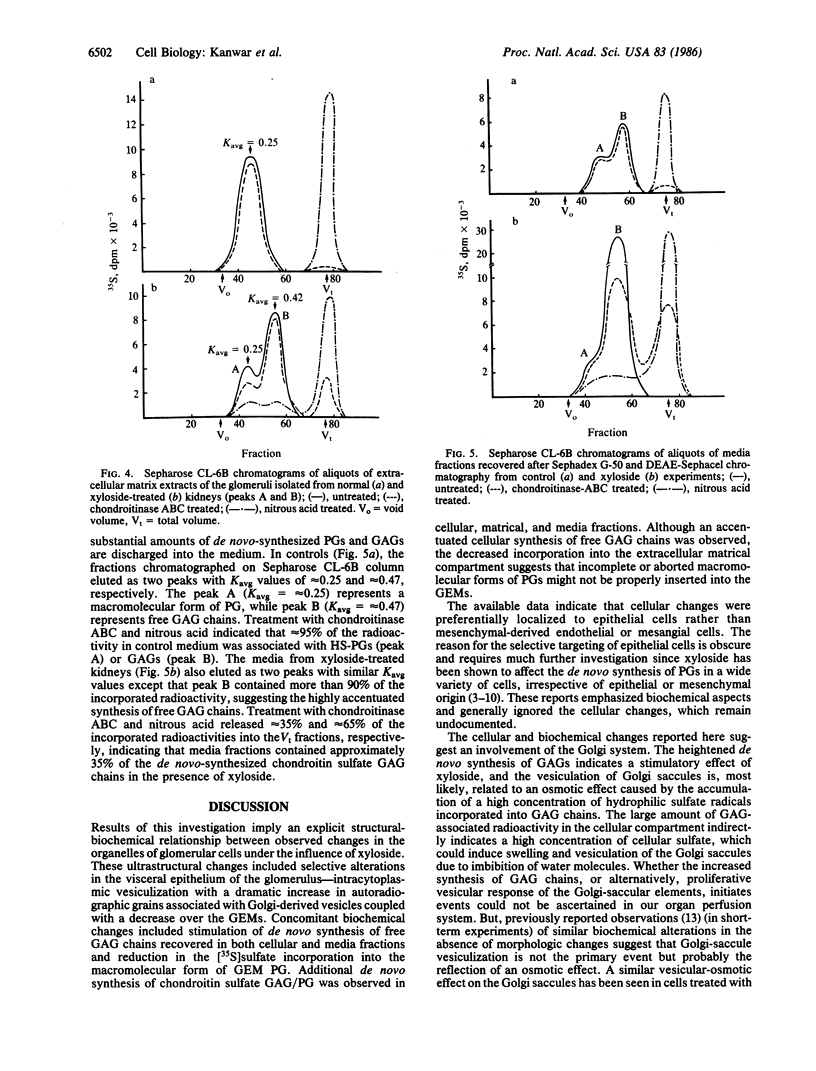
Abstract
The effect of p-nitrophenyl beta-D-xylopyranoside on the Golgi apparatus and proteoglycans (PG) of the renal glomerulus was investigated in an isolated kidney organ perfusion system and monitored by utilizing [35S]sulfate as the PG precursor. By electron microscopy, a selective intracytoplasmic vesiculization of Golgi apparatus of visceral epithelium was observed in the beta-xyloside-treated kidneys. Electron microscopic autoradiography revealed most grains localized to the intracytoplasmic Golgi-derived vesicles, while very few grains were associated with the extracellular matrix membranes. Biochemically, a 2.3-fold increase in cellular matrix and a reduction by a factor of 1.7 in extracellular matrix of [35S]sulfate incorporation was observed. Besides a larger macromolecular form (Kavg = 0.25; Mr = 130,000), lower molecular weight PGs were recovered in the cellular (Kavg = 0.46, Mr = 30,000) and matrical (Kavg = 0.42, Mr = 45,000) compartments after xyloside treatment. The xyloside treatment increased the incorporated radioactivity, mostly included in free glycosaminoglycans and small PGs, in the media fraction by 3.8-fold. These data indicate that xyloside induces a dramatic imbalance in the de novo-synthesized PGs of cellular and extracellular compartments and that cellular accumulation of xylosylated (sulfated) PGs selectively alters the Golgi apparatus of the glomerular epithelial cell, the cell that actively synthesizes PGs.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Border W. A., Ward H. J., Kamil E. S., Cohen A. H. Induction of membranous nephropathy in rabbits by administration of an exogenous cationic antigen. J Clin Invest. 1982 Feb;69(2):451–461. doi: 10.1172/JCI110469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang Y., Yanagishita M., Hascall V. C., Wight T. N. Proteoglycans synthesized by smooth muscle cells derived from monkey (Macaca nemestrina) aorta. J Biol Chem. 1983 May 10;258(9):5679–5688. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallo G. R., Caulin-Glaser T., Emancipator S. N., Lamm M. E. Nephritogenicity and differential distribution of glomerular immune complexes related to immunogen charge. Lab Invest. 1983 Mar;48(3):353–362. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallo G. R., Caulin-Glaser T., Lamm M. E. Charge of circulating immune complexes as a factor in glomerular basement membrane localization in mice. J Clin Invest. 1981 May;67(5):1305–1313. doi: 10.1172/JCI110159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinegård D., Hascall V. C. Characterization of chondroitin sulfate isolated from trypsin-chymotrypsin digests of cartilage proteoglycans. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1974 Nov;165(1):427–441. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(74)90182-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston L. S., Keller J. M. The effect of beta-xylosides on heparan sulfate synthesis by SV40-transformed Swiss mouse 3T3 cells. J Biol Chem. 1979 Apr 25;254(8):2575–2578. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanwar Y. S., Carone F. A. Reversible changes of tubular cell and basement membrane in drug-induced renal cystic disease. Kidney Int. 1984 Jul;26(1):35–43. doi: 10.1038/ki.1984.131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanwar Y. S., Farquhar M. G. Isolation of glycosaminoglycans (heparan sulfate) from glomerular basement membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4493–4497. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4493. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanwar Y. S., Farquhar M. G. Presence of heparan sulfate in the glomerular basement membrane. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Mar;76(3):1303–1307. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.3.1303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanwar Y. S., Hascall V. C., Jakubowski M. L., Gibbons J. T. Effect of beta-D-xyloside on the glomerular proteoglycans. I. Biochemical studies. J Cell Biol. 1984 Aug;99(2):715–722. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.2.715. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanwar Y. S., Linker A., Farquhar M. G. Increased permeability of the glomerular basement membrane to ferritin after removal of glycosaminoglycans (heparan sulfate) by enzyme digestion. J Cell Biol. 1980 Aug;86(2):688–693. doi: 10.1083/jcb.86.2.688. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanwar Y. S., Rosenzweig L. J. Clogging of the glomerular basement membrane. J Cell Biol. 1982 May;93(2):489–494. doi: 10.1083/jcb.93.2.489. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanwar Y. S., Rosenzweig L. J., Linker A., Jakubowski M. L. Decreased de novo synthesis of glomerular proteoglycans in diabetes: biochemical and autoradiographic evidence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Apr;80(8):2272–2275. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.8.2272. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanwar Y. S., Veis A., Kimura J. H., Jakubowski M. L. Characterization of heparan sulfate-proteoglycan of glomerular basement membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Feb;81(3):762–766. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.3.762. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura J. H., Hardingham T. E., Hascall V. C. Assembly of newly synthesized proteoglycan and link protein into aggregates in cultures of chondrosarcoma chondrocytes. J Biol Chem. 1980 Aug 10;255(15):7134–7143. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lohmander L. S., Hascall V. C., Caplan A. I. Effects of 4-methyl umbelliferyl-beta-D-xylopyranoside on chondrogenesis and proteoglycan synthesis in chick limb bud mesenchymal cell cultures. J Biol Chem. 1979 Oct 25;254(20):10551–10561. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okayama M., Kimata K., Suzuki S. The influence of p-nitrophenyl beta-d-xyloside on the synthesis of proteochondroitin sulfate by slices of embryonic chick cartilage. J Biochem. 1973 Nov;74(5):1069–1073. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rennke H. G., Cotran R. S., Venkatachalam M. A. Role of molecular charge in glomerular permeability. Tracer studies with cationized ferritins. J Cell Biol. 1975 Dec;67(3):638–646. doi: 10.1083/jcb.67.3.638. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz N. B., Galligani L., Ho P. L., Dorfman A. Stimulation of synthesis of free chondroitin sulfate chains by beta-D-xylosides in cultured cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Oct;71(10):4047–4051. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.10.4047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spooncer E., Gallagher J. T., Krizsa F., Dexter T. M. Regulation of haemopoiesis in long-term bone marrow cultures. IV. Glycosaminoglycan synthesis and the stimulation of haemopoiesis by beta-D-xylosides. J Cell Biol. 1983 Feb;96(2):510–514. doi: 10.1083/jcb.96.2.510. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens R. L., Austen K. F. Effect of p-nitrophenyl-beta-D-xyloside on proteoglycan and glycosaminoglycan biosynthesis in rat serosal mast cell cultures. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jan 10;257(1):253–259. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sudhakaran P. R., Sinn W., von Figura K. Initiation of altered heparan sulphate on beta-D-xyloside in rat hepatocytes. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1981 Jan;362(1):39–46. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1981.362.1.39. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tartakoff A. M., Vassalli P. Plasma cell immunoglobulin secretion: arrest is accompanied by alterations of the golgi complex. J Exp Med. 1977 Nov 1;146(5):1332–1345. doi: 10.1084/jem.146.5.1332. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tartakoff A., Vassalli P., Détraz M. Comparative studies of intracellular transport of secretory proteins. J Cell Biol. 1978 Dec;79(3):694–707. doi: 10.1083/jcb.79.3.694. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson H. A., Spooner B. S. Proteoglycan and glycosaminoglycan synthesis in embryonic mouse salivary glands: effects of beta-D-xyloside, an inhibitor of branching morphogenesis. J Cell Biol. 1983 May;96(5):1443–1450. doi: 10.1083/jcb.96.5.1443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venkatachalam M. A., Rennke H. G. The structural and molecular basis of glomerular filtration. Circ Res. 1978 Sep;43(3):337–347. doi: 10.1161/01.res.43.3.337. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasteson A. A method for the determination of the molecular weight and molecular-weight distribution of chondroitin sulphate. J Chromatogr. 1971 Jul 8;59(1):87–97. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(01)80009-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young R. W. The role of the Golgi complex in sulfate metabolism. J Cell Biol. 1973 Apr;57(1):175–189. doi: 10.1083/jcb.57.1.175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]