Abstract
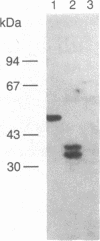
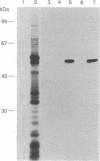
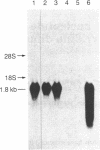
We previously purified a 48-kDa protein (p48) that specifically reacts with an antiserum directed against the 12 carboxyl-terminal amino acids of the c-myc gene product. Using an antiserum directed against the purified p48, we have cloned a cDNA from a human expression library. This cDNA hybrid-selects an mRNA that translates to a 48-kDa protein that specifically reacts with anti-p48 serum. We have isolated a full-length cDNA that encodes p48 and spans 1755 bases. The coding region is 1299 bases long; 94 bases are 5' noncoding and 359 bases are 3' noncoding. The cDNA encodes a 433 amino acid protein that is 67% homologous to yeast enolase and 94% homologous to the rat non-neuronal enolase. The purified protein has been shown to have enolase activity and has been identified to be of the alpha type by isoenzyme analysis. The transcriptional regulation of enolase expression in response to mitogenic stimulation of peripheral blood lymphocytes and in response to heat shock is also discussed.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baranowski T., Wolna E. Enolase from human muscle. Methods Enzymol. 1975;42:335–338. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(75)42137-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berger S. L., Birkenmeier C. S. Inhibition of intractable nucleases with ribonucleoside--vanadyl complexes: isolation of messenger ribonucleic acid from resting lymphocytes. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 13;18(23):5143–5149. doi: 10.1021/bi00590a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen S. H., Giblett E. R. Enolase: human tissue distribution and evidence for three different loci. Ann Hum Genet. 1976 Jan;39(3):277–280. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1976.tb00131.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chin C. C., Brewer J. M., Wold F. The amino acid sequence of yeast enolase. J Biol Chem. 1981 Feb 10;256(3):1377–1384. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courtney M., Buchwalder A., Tessier L. H., Jaye M., Benavente A., Balland A., Kohli V., Lathe R., Tolstoshev P., Lecocq J. P. High-level production of biologically active human alpha 1-antitrypsin in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Feb;81(3):669–673. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.3.669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Croce C. M., Isobe M., Palumbo A., Puck J., Ming J., Tweardy D., Erikson J., Davis M., Rovera G. Gene for alpha-chain of human T-cell receptor: location on chromosome 14 region involved in T-cell neoplasms. Science. 1985 Mar 1;227(4690):1044–1047. doi: 10.1126/science.3919442. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giallongo A., Appella E., Ricciardi R., Rovera G., Croce C. M. Identification of the c-myc oncogene product in normal and malignant B cells. Science. 1983 Oct 28;222(4622):430–432. doi: 10.1126/science.6604943. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giallongo A., Feo S., Showe L. C., Croce C. M. Isolation and partial characterization of a 48-kDa protein which is induced in normal lymphocytes upon mitogenic stimulation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Feb 13;134(3):1238–1244. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)90383-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grunstein M., Hogness D. S. Colony hybridization: a method for the isolation of cloned DNAs that contain a specific gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Oct;72(10):3961–3965. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.10.3961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helfman D. M., Feramisco J. R., Fiddes J. C., Thomas G. P., Hughes S. H. Identification of clones that encode chicken tropomyosin by direct immunological screening of a cDNA expression library. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(1):31–35. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.1.31. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henikoff S. Unidirectional digestion with exonuclease III creates targeted breakpoints for DNA sequencing. Gene. 1984 Jun;28(3):351–359. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90153-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matrisian L. M., Rautmann G., Magun B. E., Breathnach R. Epidermal growth factor or serum stimulation of rat fibroblasts induces an elevation in mRNA levels for lactate dehydrogenase and other glycolytic enzymes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Feb 11;13(3):711–726. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.3.711. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nigg E. A., Walter G., Singer S. J. On the nature of crossreactions observed with antibodies directed to defined epitopes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Oct;79(19):5939–5943. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.19.5939. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Persson H., Hennighausen L., Taub R., DeGrado W., Leder P. Antibodies to human c-myc oncogene product: evidence of an evolutionarily conserved protein induced during cell proliferation. Science. 1984 Aug 17;225(4663):687–693. doi: 10.1126/science.6431612. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakimura K., Kushiya E., Obinata M., Takahashi Y. Molecular cloning and the nucleotide sequence of cDNA to mRNA for non-neuronal enolase (alpha alpha enolase) of rat brain and liver. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Jun 25;13(12):4365–4378. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.12.4365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witt I., Witz D. Reinigung und Charakterisierung von Phosphopyruvat-Hydratase (=Enolase; EC 4.2.1.11) aud Neugeborenen- und Erwachsenen-Erythrozyten. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1970 Oct;351(10):1232–1240. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]