Abstract
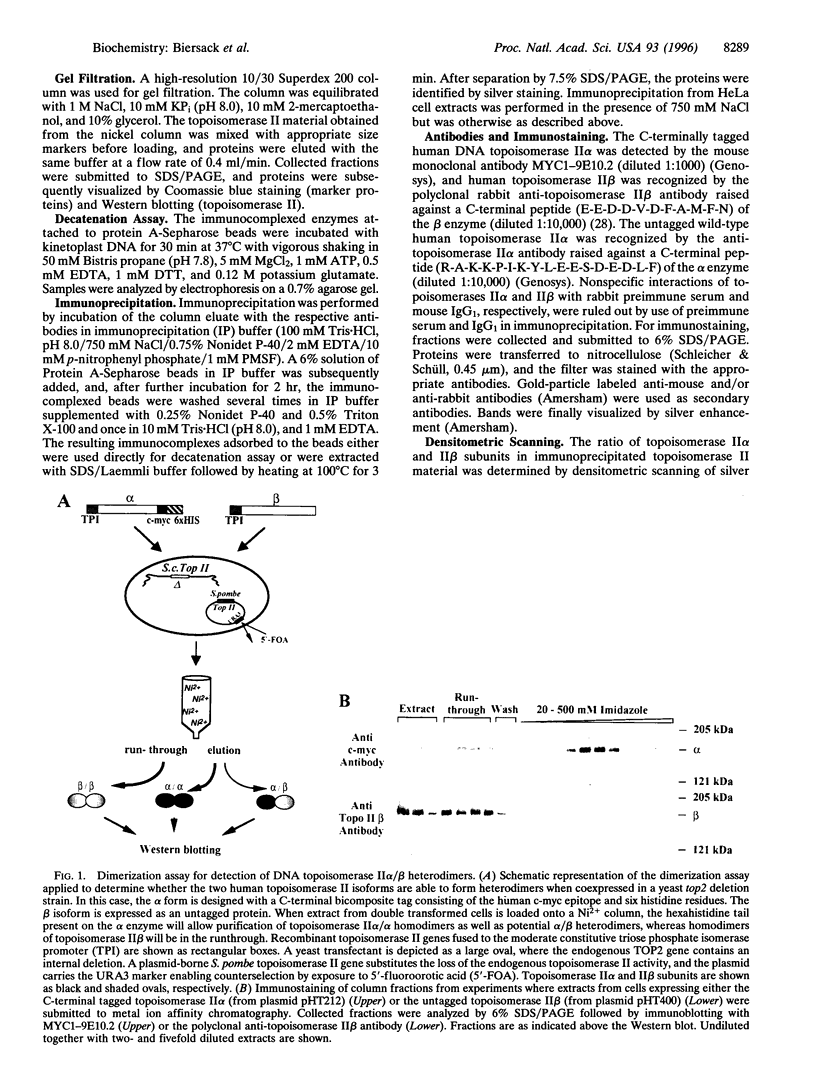
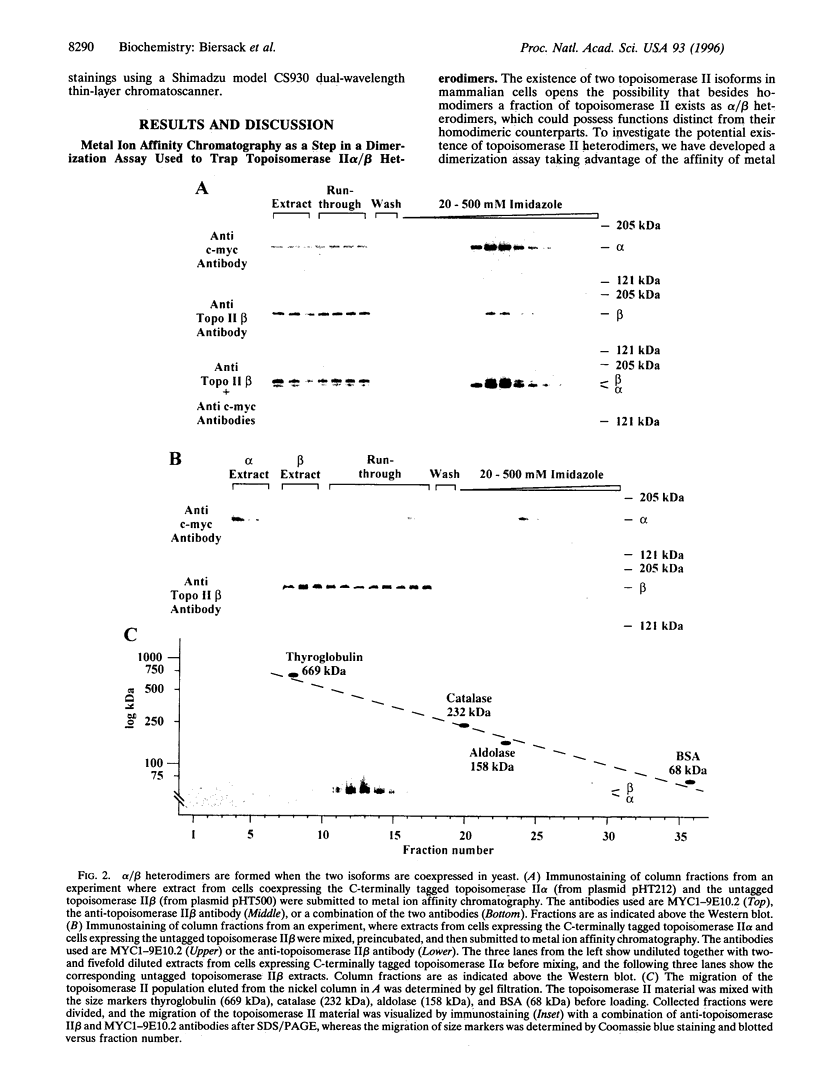
DNA topoisomerase II is a nuclear enzyme essential for chromosome dynamics and DNA metabolism. In mammalian cells, two genetically and biochemically distinct topoisomerase II forms exist, which are designated topoisomerase II alpha and topoisomerase II beta. In our studies of human topoisomerase II, we have found that a substantial fraction of the enzyme exists as alpha/beta heterodimers in HeLa cells. The ability to form heterodimers was verified when human topoisomerases II alpha and II beta were coexpressed in yeast and investigated in a dimerization assay. Analysis of purified heterodimers shows that these enzymes maintain topoisomerase II specific catalytic activities. The natural existence of an active heterodimeric subclass of topoisomerase II merits attention whenever topoisomerases II alpha and II beta function, localization, and cell cycle regulation are investigated.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson A. H., Sørensen B. S., Christiansen K., Svejstrup J. Q., Lund K., Westergaard O. Studies of the topoisomerase II-mediated cleavage and religation reactions by use of a suicidal double-stranded DNA substrate. J Biol Chem. 1991 May 15;266(14):9203–9210. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bae Y. S., Kawasaki I., Ikeda H., Liu L. F. Illegitimate recombination mediated by calf thymus DNA topoisomerase II in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(7):2076–2080. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.7.2076. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boege F., Andersen A., Jensen S., Zeidler R., Kreipe H. Proliferation-associated nuclear antigen Ki-S1 is identical with topoisomerase II alpha. Delineation of a carboxy-terminal epitope with peptide antibodies. Am J Pathol. 1995 Jun;146(6):1302–1308. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drake F. H., Hofmann G. A., Bartus H. F., Mattern M. R., Crooke S. T., Mirabelli C. K. Biochemical and pharmacological properties of p170 and p180 forms of topoisomerase II. Biochemistry. 1989 Oct 3;28(20):8154–8160. doi: 10.1021/bi00446a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gale K. C., Osheroff N. Intrinsic intermolecular DNA ligation activity of eukaryotic topoisomerase II. Potential roles in recombination. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jun 15;267(17):12090–12097. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goto T., Laipis P., Wang J. C. The purification and characterization of DNA topoisomerases I and II of the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem. 1984 Aug 25;259(16):10422–10429. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heck M. M., Hittelman W. N., Earnshaw W. C. Differential expression of DNA topoisomerases I and II during the eukaryotic cell cycle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Feb;85(4):1086–1090. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.4.1086. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holm C., Stearns T., Botstein D. DNA topoisomerase II must act at mitosis to prevent nondisjunction and chromosome breakage. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jan;9(1):159–168. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.1.159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito H., Fukuda Y., Murata K., Kimura A. Transformation of intact yeast cells treated with alkali cations. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jan;153(1):163–168. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.1.163-168.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenkins J. R., Ayton P., Jones T., Davies S. L., Simmons D. L., Harris A. L., Sheer D., Hickson I. D. Isolation of cDNA clones encoding the beta isozyme of human DNA topoisomerase II and localisation of the gene to chromosome 3p24. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Nov 11;20(21):5587–5592. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.21.5587. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim R. A., Wang J. C. A subthreshold level of DNA topoisomerases leads to the excision of yeast rDNA as extrachromosomal rings. Cell. 1989 Jun 16;57(6):975–985. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90336-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura K., Nozaki N., Saijo M., Kikuchi A., Ui M., Enomoto T. Identification of the nature of modification that causes the shift of DNA topoisomerase II beta to apparent higher molecular weight forms in the M phase. J Biol Chem. 1994 Oct 7;269(40):24523–24526. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu L. F. DNA topoisomerase poisons as antitumor drugs. Annu Rev Biochem. 1989;58:351–375. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.58.070189.002031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Negri C., Chiesa R., Cerino A., Bestagno M., Sala C., Zini N., Maraldi N. M., Astaldi Ricotti G. C. Monoclonal antibodies to human DNA topoisomerase I and the two isoforms of DNA topoisomerase II: 170- and 180-kDa isozymes. Exp Cell Res. 1992 Jun;200(2):452–459. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(92)90195-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson W. G., Liu L. F., Coffey D. S. Newly replicated DNA is associated with DNA topoisomerase II in cultured rat prostatic adenocarcinoma cells. Nature. 1986 Jul 10;322(6075):187–189. doi: 10.1038/322187a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osheroff N. Biochemical basis for the interactions of type I and type II topoisomerases with DNA. Pharmacol Ther. 1989;41(1-2):223–241. doi: 10.1016/0163-7258(89)90108-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porath J., Carlsson J., Olsson I., Belfrage G. Metal chelate affinity chromatography, a new approach to protein fractionation. Nature. 1975 Dec 18;258(5536):598–599. doi: 10.1038/258598a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose D., Thomas W., Holm C. Segregation of recombined chromosomes in meiosis I requires DNA topoisomerase II. Cell. 1990 Mar 23;60(6):1009–1017. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90349-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sander M., Hsieh T. Double strand DNA cleavage by type II DNA topoisomerase from Drosophila melanogaster. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jul 10;258(13):8421–8428. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shelton E. R., Osheroff N., Brutlag D. L. DNA topoisomerase II from Drosophila melanogaster. Purification and physical characterization. J Biol Chem. 1983 Aug 10;258(15):9530–9535. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sikorski R. S., Hieter P. A system of shuttle vectors and yeast host strains designed for efficient manipulation of DNA in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics. 1989 May;122(1):19–27. doi: 10.1093/genetics/122.1.19. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snapka R. M., Powelson M. A., Strayer J. M. Swiveling and decatenation of replicating simian virus 40 genomes in vivo. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Feb;8(2):515–521. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.2.515. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai-Pflugfelder M., Liu L. F., Liu A. A., Tewey K. M., Whang-Peng J., Knutsen T., Huebner K., Croce C. M., Wang J. C. Cloning and sequencing of cDNA encoding human DNA topoisomerase II and localization of the gene to chromosome region 17q21-22. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Oct;85(19):7177–7181. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.19.7177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uemura T., Ohkura H., Adachi Y., Morino K., Shiozaki K., Yanagida M. DNA topoisomerase II is required for condensation and separation of mitotic chromosomes in S. pombe. Cell. 1987 Sep 11;50(6):917–925. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90518-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vassetzky Y. S., Dang Q., Benedetti P., Gasser S. M. Topoisomerase II forms multimers in vitro: effects of metals, beta-glycerophosphate, and phosphorylation of its C-terminal domain. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Oct;14(10):6962–6974. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.10.6962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vosberg H. P. DNA topoisomerases: enzymes that control DNA conformation. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1985;114:19–102. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-70227-3_2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watt P. M., Hickson I. D. Structure and function of type II DNA topoisomerases. Biochem J. 1994 Nov 1;303(Pt 3):681–695. doi: 10.1042/bj3030681. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woessner R. D., Chung T. D., Hofmann G. A., Mattern M. R., Mirabelli C. K., Drake F. H., Johnson R. K. Differences between normal and ras-transformed NIH-3T3 cells in expression of the 170kD and 180kD forms of topoisomerase II. Cancer Res. 1990 May 15;50(10):2901–2908. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woessner R. D., Mattern M. R., Mirabelli C. K., Johnson R. K., Drake F. H. Proliferation- and cell cycle-dependent differences in expression of the 170 kilodalton and 180 kilodalton forms of topoisomerase II in NIH-3T3 cells. Cell Growth Differ. 1991 Apr;2(4):209–214. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zini N., Martelli A. M., Sabatelli P., Santi S., Negri C., Astaldi Ricotti G. C., Maraldi N. M. The 180-kDa isoform of topoisomerase II is localized in the nucleolus and belongs to the structural elements of the nucleolar remnant. Exp Cell Res. 1992 Jun;200(2):460–466. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(92)90196-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]