Abstract
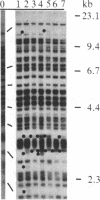
Haploid a and diploid a/alpha and a/a populations of Saccharomyces cerevisiae evolving in laboratory environments for up to 300 generations were analyzed for sequence rearrangements associated with the Ty family of transposable elements. In contrast to results with Escherichia coli, evolving populations of yeast exhibit a high frequency of sequence rearrangements associated with mobile genetic elements. In particular, adaptive shifts in these populations are often associated with such sequence rearrangements. The results are most compatible with the explanation that there is direct selection for some of the sequence rearrangements. In addition, the pattern of changes suggests that the structure of evolving microorganism populations may be more complex than expected.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams C. H., Haskew P. A perspective on appetite disorders. Am Pharm. 1982 Nov;NS22(11):21–24. doi: 10.1016/s0160-3450(16)31799-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adams J., Hansche P. E. Population studies in microorganisms. I. Evolution of diploidy in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics. 1974 Feb;76(2):327–338. doi: 10.1093/genetics/76.2.327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adams J., Paquin C., Oeller P. W., Lee L. W. Physiological characterization of adaptive clones in evolving populations of the yeast, Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics. 1985 Jun;110(2):173–185. doi: 10.1093/genetics/110.2.173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg D. E., Egner C., Hirschel B. J., Howard J., Johnsrud L., Jorgensen R. A., Tlsty T. D. Insertion, excision, and inversion of Tn5. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1981;45(Pt 1):115–123. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1981.045.01.020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biel S. W., Hartl D. L. Evolution of transposons: natural selection for Tn5 in Escherichia coli K12. Genetics. 1983 Apr;103(4):581–592. doi: 10.1093/genetics/103.4.581. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boeke J. D., Garfinkel D. J., Styles C. A., Fink G. R. Ty elements transpose through an RNA intermediate. Cell. 1985 Mar;40(3):491–500. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90197-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calos M. P., Miller J. H. Transposable elements. Cell. 1980 Jul;20(3):579–595. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90305-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cameron J. R., Loh E. Y., Davis R. W. Evidence for transposition of dispersed repetitive DNA families in yeast. Cell. 1979 Apr;16(4):739–751. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90090-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell A. Evolutionary significance of accessory DNA elements in bacteria. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1981;35:55–83. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.35.100181.000415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chao L., McBroom S. M. Evolution of transposable elements: an IS10 insertion increases fitness in Escherichia coli. Mol Biol Evol. 1985 Sep;2(5):359–369. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040356. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chao L., Vargas C., Spear B. B., Cox E. C. Transposable elements as mutator genes in evolution. Nature. 1983 Jun 16;303(5918):633–635. doi: 10.1038/303633a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciriacy M., Williamson V. M. Analysis of mutations affecting Ty-mediated gene expression in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Gen Genet. 1981;182(1):159–163. doi: 10.1007/BF00422784. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denis C. L., Young E. T. Isolation and characterization of the positive regulatory gene ADR1 from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Mar;3(3):360–370. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.3.360. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eibel H., Philippsen P. Preferential integration of yeast transposable element Ty into a promoter region. 1984 Jan 26-Feb 1Nature. 307(5949):386–388. doi: 10.1038/307386a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elder R. T., St John T. P., Stinchcomb D. T., Davis R. W., Scherer S., Davis R. W. Studies on the transposable element Ty1 of yeast. I. RNA homologous to Ty1. II. Recombination and expression of Ty1 and adjacent sequences. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1981;45(Pt 2):581–591. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1981.045.01.075. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garfinkel D. J., Boeke J. D., Fink G. R. Ty element transposition: reverse transcriptase and virus-like particles. Cell. 1985 Sep;42(2):507–517. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90108-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartl D. L., Dykhuizen D. E., Miller R. D., Green L., de Framond J. Transposable element IS50 improves growth rate of E. coli cells without transposition. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(2 Pt 1):503–510. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90184-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paquin C. E., Adams J. Relative fitness can decrease in evolving asexual populations of S. cerevisiae. Nature. 1983 Nov 24;306(5941):368–370. doi: 10.1038/306368a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paquin C. E., Williamson V. M. Temperature effects on the rate of ty transposition. Science. 1984 Oct 5;226(4670):53–55. doi: 10.1126/science.226.4670.53. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paquin C. E., Williamson V. M. Ty insertions at two loci account for most of the spontaneous antimycin A resistance mutations during growth at 15 degrees C of Saccharomyces cerevisiae strains lacking ADH1. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jan;6(1):70–79. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.1.70. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paquin C., Adams J. Frequency of fixation of adaptive mutations is higher in evolving diploid than haploid yeast populations. Nature. 1983 Apr 7;302(5908):495–500. doi: 10.1038/302495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roeder G. S., Fink G. R. DNA rearrangements associated with a transposable element in yeast. Cell. 1980 Aug;21(1):239–249. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90131-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roeder G. S., Smith M., Lambie E. J. Intrachromosomal movement of genetically marked Saccharomyces cerevisiae transposons by gene conversion. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Apr;4(4):703–711. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.4.703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. M., Haigh J. The hitch-hiking effect of a favourable gene. Genet Res. 1974 Feb;23(1):23–35. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutcliffe J. G. Complete nucleotide sequence of the Escherichia coli plasmid pBR322. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1979;43(Pt 1):77–90. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1979.043.01.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss R. L., Kukora J. R., Adams J. The relationship between enzyme activity, cell geometry, and fitness in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Mar;72(3):794–798. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.3.794. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williamson V. M., Young E. T., Ciriacy M. Transposable elements associated with constitutive expression of yeast alcohol dehydrogenase II. Cell. 1981 Feb;23(2):605–614. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90156-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]