Abstract
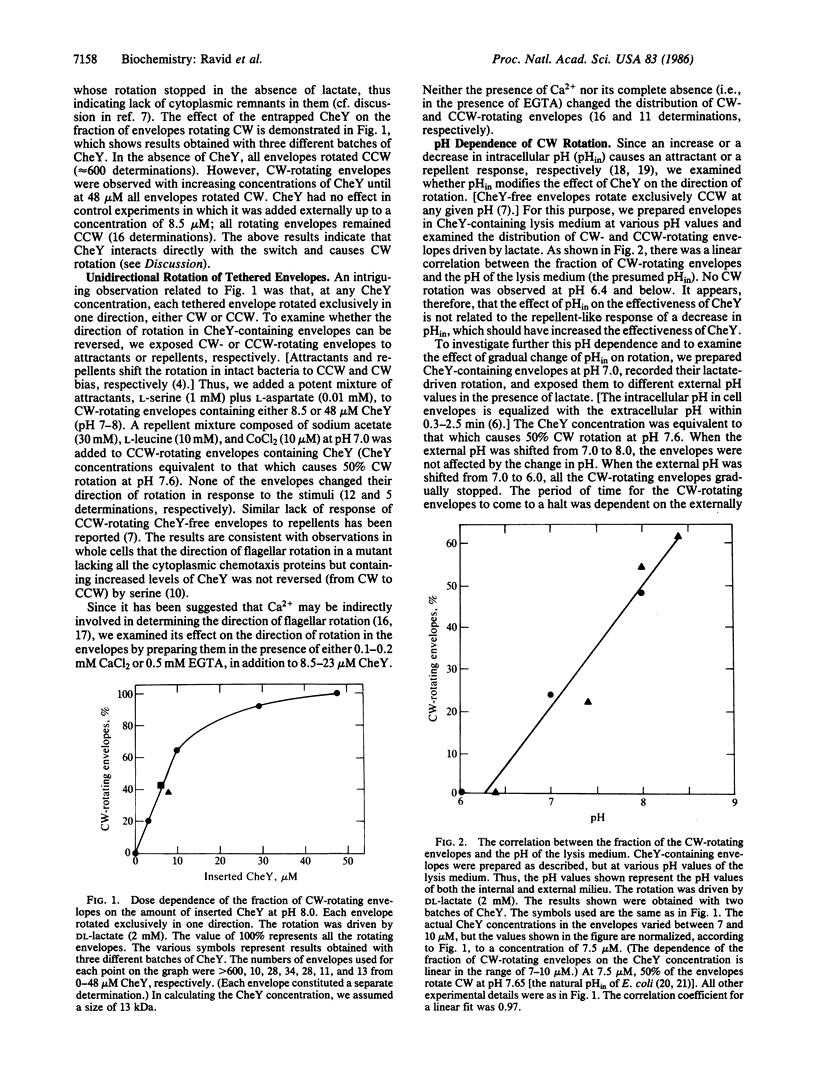
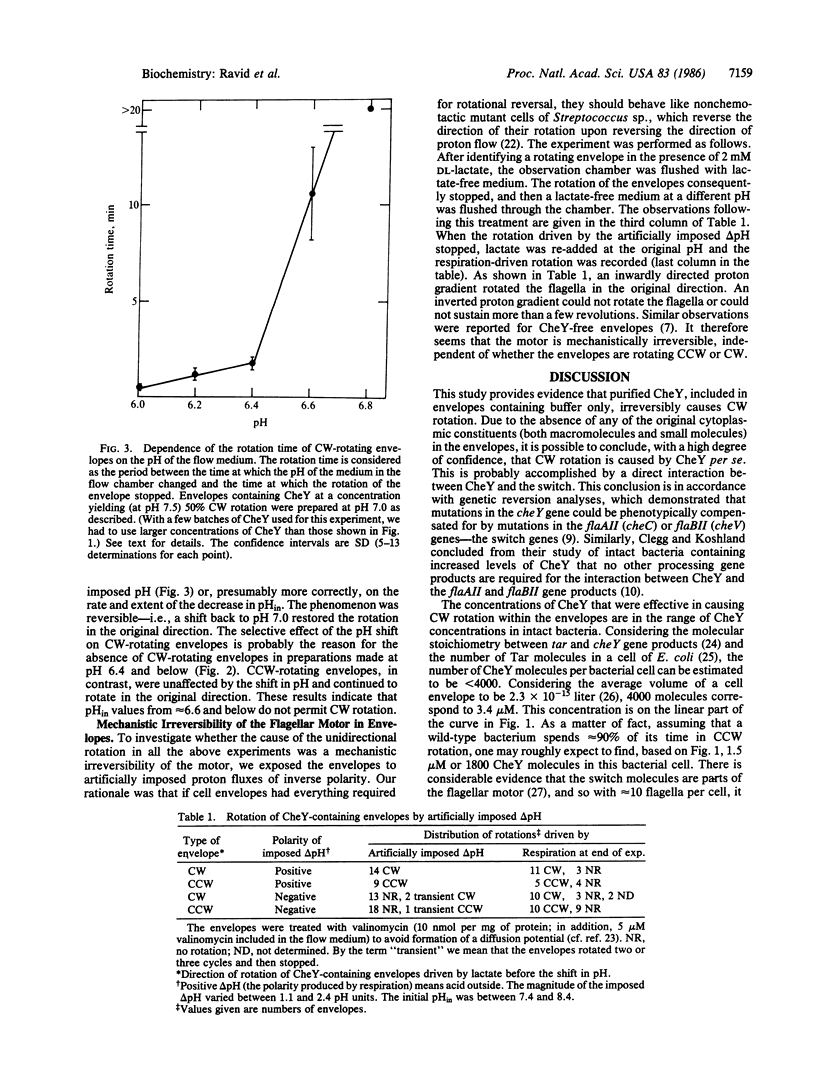
When cells of the bacterium Salmonella typhimurium are incubated with penicillin and lysed in a dilute buffer, flagellated cytoplasm-free envelopes are formed. When the envelopes are tethered to glass by their flagella and then energized, some of them spin. The direction of rotation of wild-type envelopes is exclusively counterclockwise (CCW). We perturbed this system by including in the lysis medium (and hence in the envelopes) the chemotaxis protein CheY. As a result, some of the envelopes rotated exclusively clockwise (CW). The fraction of envelopes that did so increased with the concentration of CheY; at a concentration of 48 microM (pH 8), all functional envelopes spun CW. The fraction also increased with the pH of the lysis medium in the range of 6.6-8.4. The results were the same in the presence or absence of intracellular Ca2+. Reconstituted envelopes failed to respond to chemotactic stimuli. None of them changed the direction of their rotation. However, when the intracellular pH was lowered to 6.6 or below, envelopes that spun CW stopped rotating, while envelopes that spun CCW continued to rotate. This phenomenon was reversible. We conclude that CheY per se, without any additional free cytoplasmic mediators, interacts with a switch at the base of the flagellum to cause CW rotation.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adler J. Chemotaxis in Escherichia coli. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1965;30:289–292. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1965.030.01.030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adler J., Templeton B. The effect of environmental conditions on the motility of Escherichia coli. J Gen Microbiol. 1967 Feb;46(2):175–184. doi: 10.1099/00221287-46-2-175. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aswad D., Koshland D. E., Jr Role of methionine in bacterial chemotaxis. J Bacteriol. 1974 May;118(2):640–645. doi: 10.1128/jb.118.2.640-645.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg H. C., Block S. M. A miniature flow cell designed for rapid exchange of media under high-power microscope objectives. J Gen Microbiol. 1984 Nov;130(11):2915–2920. doi: 10.1099/00221287-130-11-2915. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg H. C., Brown D. A. Chemotaxis in Escherichia coli analysed by three-dimensional tracking. Nature. 1972 Oct 27;239(5374):500–504. doi: 10.1038/239500a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg H. C., Manson M. D., Conley M. P. Dynamics and energetics of flagellar rotation in bacteria. Symp Soc Exp Biol. 1982;35:1–31. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clegg D. O., Koshland D. E., Jr The role of a signaling protein in bacterial sensing: behavioral effects of increased gene expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Aug;81(16):5056–5060. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.16.5056. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeFranco A. L., Koshland D. E., Jr Molecular cloning of chemotaxis genes and overproduction of gene products in the bacterial sensing system. J Bacteriol. 1981 Aug;147(2):390–400. doi: 10.1128/jb.147.2.390-400.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenbach M., Adler J. Bacterial cell envelopes with functional flagella. J Biol Chem. 1981 Aug 25;256(16):8807–8814. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hazelbauer G. L., Harayama S., Engstrom P. Special features of chemotaxis towards maltose. Ann Microbiol (Paris) 1982 Jan;133A(1):191–194. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hazelbauer G. L., Harayama S. Sensory transduction in bacterial chemotaxis. Int Rev Cytol. 1983;81:33–70. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)62334-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khan S., Berg H. C. Isotope and thermal effects in chemiosmotic coupling to the flagellar motor of Streptococcus. Cell. 1983 Mar;32(3):913–919. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90076-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kihara M., Macnab R. M. Cytoplasmic pH mediates pH taxis and weak-acid repellent taxis of bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1981 Mar;145(3):1209–1221. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.3.1209-1221.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsen S. H., Reader R. W., Kort E. N., Tso W. W., Adler J. Change in direction of flagellar rotation is the basis of the chemotactic response in Escherichia coli. Nature. 1974 May 3;249(452):74–77. doi: 10.1038/249074a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lelkes P. I., Klein L., Marikovsky Y., Eisenbach M. Liposome-mediated transfer of macromolecules into flagellated cell envelopes from bacteria. Biochemistry. 1984 Jan 31;23(3):563–568. doi: 10.1021/bi00298a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macnab R. M., Aizawa S. Bacterial motility and the bacterial flagellar motor. Annu Rev Biophys Bioeng. 1984;13:51–83. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.13.060184.000411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macnab R. M., Koshland D. E., Jr The gradient-sensing mechanism in bacterial chemotaxis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Sep;69(9):2509–2512. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.9.2509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsumura P., Rydel J. J., Linzmeier R., Vacante D. Overexpression and sequence of the Escherichia coli cheY gene and biochemical activities of the CheY protein. J Bacteriol. 1984 Oct;160(1):36–41. doi: 10.1128/jb.160.1.36-41.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Northup J. K., Smigel M. D., Gilman A. G. The guanine nucleotide activating site of the regulatory component of adenylate cyclase. Identification by ligand binding. J Biol Chem. 1982 Oct 10;257(19):11416–11423. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ordal G. W. Bacterial chemotaxis: biochemistry of behavior in a single cell. Crit Rev Microbiol. 1985;12(2):95–130. doi: 10.3109/10408418509104426. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padan E., Zilberstein D., Schuldiner S. pH homeostasis in bacteria. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Dec;650(2-3):151–166. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(81)90004-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ravid S., Eisenbach M. Correlation between bacteriophage chi adsorption and mode of flagellar rotation of Escherichia coli chemotaxis mutants. J Bacteriol. 1983 May;154(2):604–611. doi: 10.1128/jb.154.2.604-611.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ravid S., Eisenbach M. Direction of flagellar rotation in bacterial cell envelopes. J Bacteriol. 1984 Apr;158(1):222–230. doi: 10.1128/jb.158.1.222-230.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ravid S., Eisenbach M. Minimal requirements for rotation of bacterial flagella. J Bacteriol. 1984 Jun;158(3):1208–1210. doi: 10.1128/jb.158.3.1208-1210.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Repaske D. R., Adler J. Change in intracellular pH of Escherichia coli mediates the chemotactic response to certain attractants and repellents. J Bacteriol. 1981 Mar;145(3):1196–1208. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.3.1196-1208.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segall J. E., Ishihara A., Berg H. C. Chemotactic signaling in filamentous cells of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1985 Jan;161(1):51–59. doi: 10.1128/jb.161.1.51-59.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segall J. E., Manson M. D., Berg H. C. Signal processing times in bacterial chemotaxis. Nature. 1982 Apr 29;296(5860):855–857. doi: 10.1038/296855a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverman M., Simon M. Flagellar rotation and the mechanism of bacterial motility. Nature. 1974 May 3;249(452):73–74. doi: 10.1038/249073a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slonczewski J. L., Rosen B. P., Alger J. R., Macnab R. M. pH homeostasis in Escherichia coli: measurement by 31P nuclear magnetic resonance of methylphosphonate and phosphate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Oct;78(10):6271–6275. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.10.6271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stock J. B., Koshland D. E., Jr Changing reactivity of receptor carboxyl groups during bacterial sensing. J Biol Chem. 1981 Nov 10;256(21):10826–10833. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


