Abstract
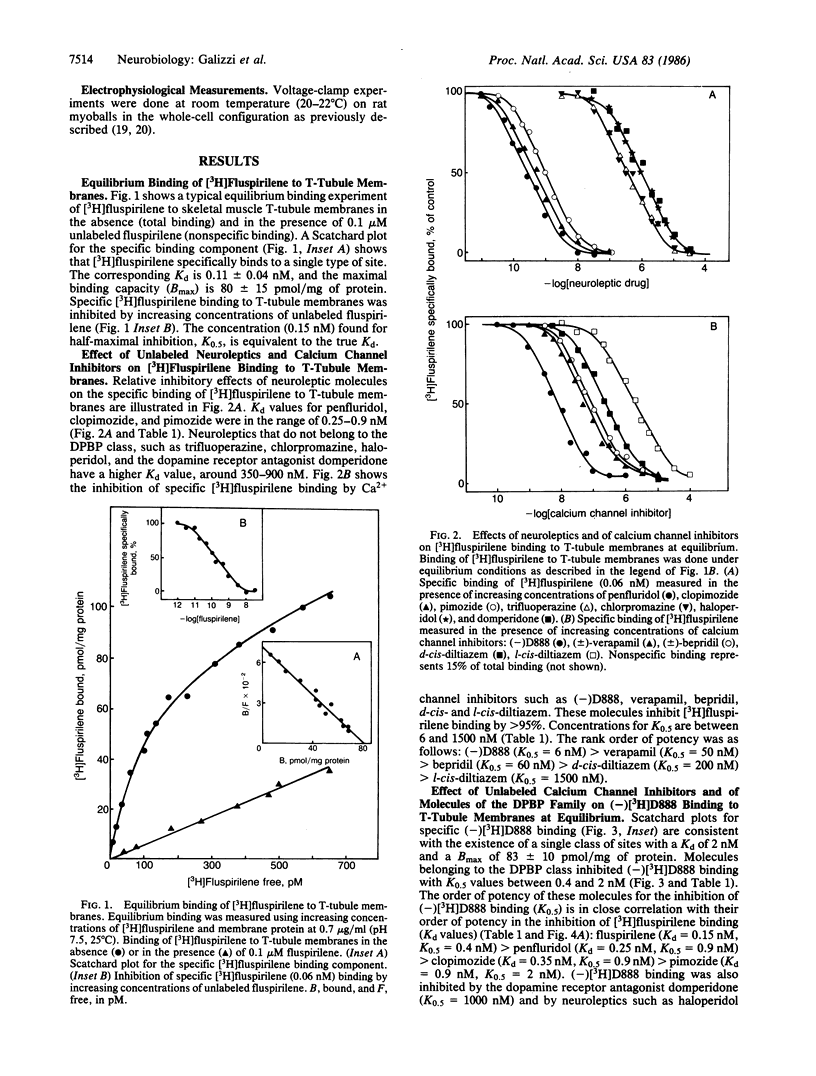
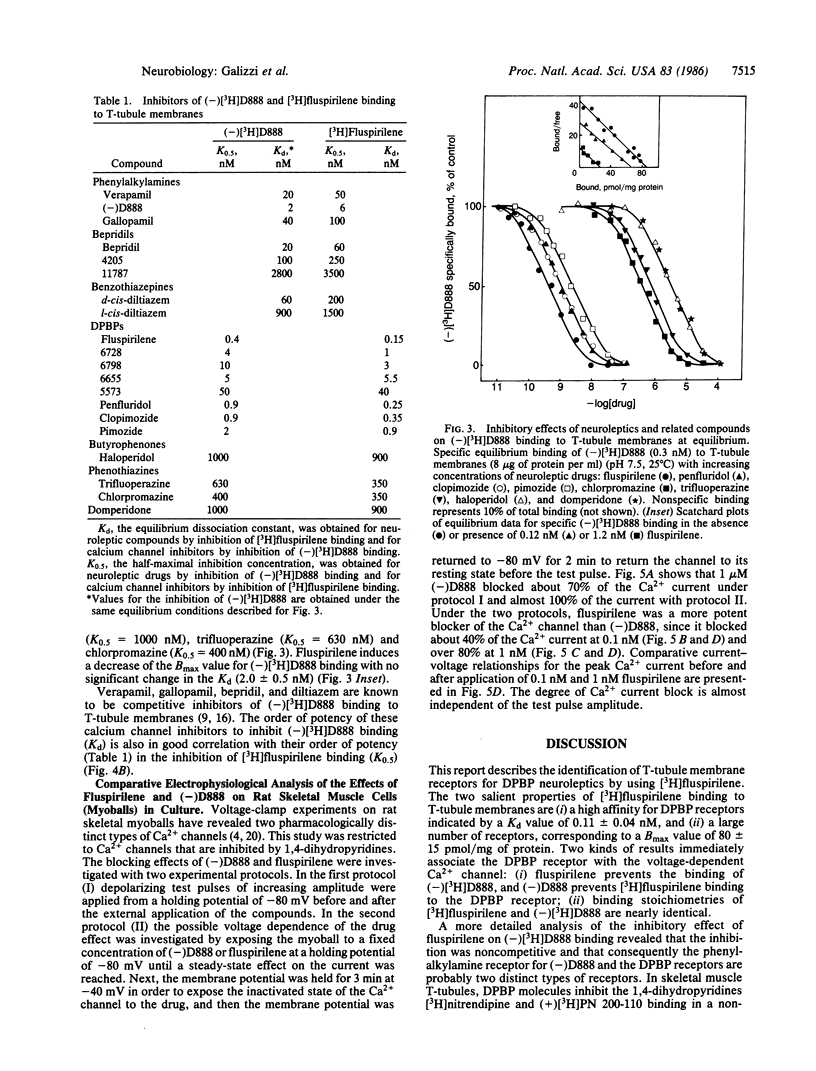
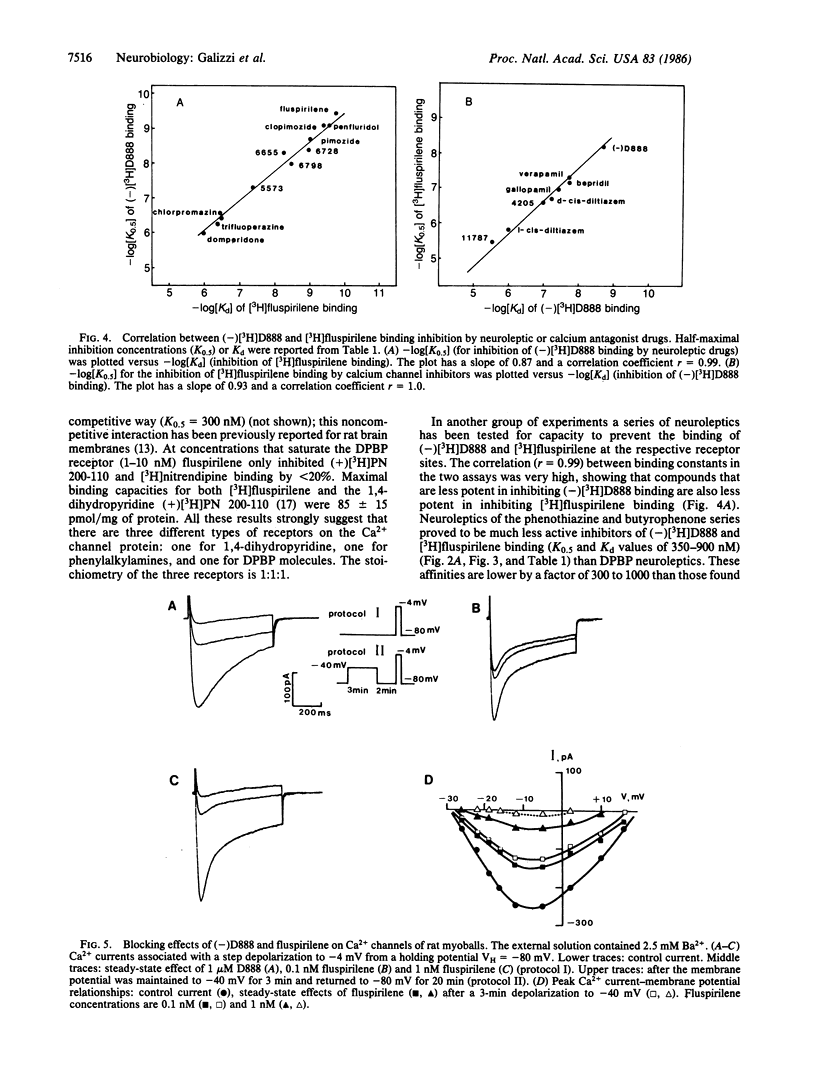
[3H]Fluspirilene, a neuroleptic molecule of the diphenylbutylpiperidine series, binds to skeletal muscle transverse tubule membranes with a high affinity corresponding to a Kd of 0.11 +/- 0.04 nM, A 1:1 stoichiometry was found between [3H]fluspirilene binding and the binding of (-)-[3H]desmethoxyverapamil [(-)[3H]D888], one of the most potent Ca2+ channel inhibitors. Ca2+ channel inhibitors such as D888, verapamil, gallopamil, bepridil, or diltiazem antagonize [3H]fluspirilene binding besides antagonizing (-)[3H]-D888 binding. Neuroleptics, especially those of the diphenylbutylpiperidine family, also antagonize both (-)[3H]D888 binding and [3H]fluspirilene binding. There is an excellent correlation between affinities found from [3H]fluspirilene binding experiments and those found from (-)[3H]D888 binding experiments. Analysis of the properties of these cross-inhibitions indicates that [3H]fluspirilene binds to a site that is not identical to that for phenylalkylamine derivatives (gallopamil, verapamil, diltiazem, and bepridil). Voltage-clamp experiments have shown that fluspirilene is an efficient inhibitor of the voltage dependent Ca2+ channel, achieving a half-maximal effect near 0.1-0.2 nM and nearly complete blockade at 1 nM. Fluspirilene blockade has little voltage dependence.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Borsotto M., Barhanin J., Fosset M., Lazdunski M. The 1,4-dihydropyridine receptor associated with the skeletal muscle voltage-dependent Ca2+ channel. Purification and subunit composition. J Biol Chem. 1985 Nov 15;260(26):14255–14263. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borsotto M., Barhanin J., Norman R. I., Lazdunski M. Purification of the dihydropyridine receptor of the voltage-dependent Ca2+ channel from skeletal muscle transverse tubules using (+) [3H]PN 200-110. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Aug 16;122(3):1357–1366. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)91241-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carbone E., Lux H. D. A low voltage-activated, fully inactivating Ca channel in vertebrate sensory neurones. Nature. 1984 Aug 9;310(5977):501–502. doi: 10.1038/310501a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cognard C., Lazdunski M., Romey G. Different types of Ca2+ channels in mammalian skeletal muscle cells in culture. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jan;83(2):517–521. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.2.517. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cognard C., Romey G., Galizzi J. P., Fosset M., Lazdunski M. Dihydropyridine-sensitive Ca2+ channels in mammalian skeletal muscle cells in culture: electrophysiological properties and interactions with Ca2+ channel activator (Bay K8644) and inhibitor (PN 200-110). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(5):1518–1522. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.5.1518. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtis B. M., Catterall W. A. Purification of the calcium antagonist receptor of the voltage-sensitive calcium channel from skeletal muscle transverse tubules. Biochemistry. 1984 May 8;23(10):2113–2118. doi: 10.1021/bi00305a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fosset M., Jaimovich E., Delpont E., Lazdunski M. [3H]nitrendipine receptors in skeletal muscle. J Biol Chem. 1983 May 25;258(10):6086–6092. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frangos H., Zissis N. P., Leontopoulos I., Diamantas N., Tsitouridis S., Gavriil I., Tsolis K. Double-blind therapeutic evaluation of fluspirilene compared with fluphenazine decanoate in chronic schizophrenics. Acta Psychiatr Scand. 1978 May;57(5):436–446. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0447.1978.tb06912.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frelin C., Vigne P., Lazdunski M. Na+ channels with high and low affinity tetrodotoxin binding sites in the mammalian skeletal muscle cell. Difference in functional properties and sequential appearance during rat skeletal myogenesis. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jun 25;258(12):7256–7259. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galizzi J. P., Borsotto M., Barhanin J., Fosset M., Lazdunski M. Characterization and photoaffinity labeling of receptor sites for the Ca2+ channel inhibitors d-cis-diltiazem, (+/-)-bepridil, desmethoxyverapamil, and (+)-PN 200-110 in skeletal muscle transverse tubule membranes. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jan 25;261(3):1393–1397. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galizzi J. P., Fosset M., Lazdunski M. Properties of receptors for the Ca2+-channel blocker verapamil in transverse-tubule membranes of skeletal muscle. Stereospecificity, effect of Ca2+ and other inorganic cations, evidence for two categories of sites and effect of nucleoside triphosphates. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Oct 15;144(2):211–215. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb08451.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galizzi J. P., Fosset M., Lazdunski M. [3H] verapamil binding sites in skeletal muscle transverse tubule membranes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Jan 13;118(1):239–245. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)91092-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gould R. J., Murphy K. M., Reynolds I. J., Snyder S. H. Antischizophrenic drugs of the diphenylbutylpiperidine type act as calcium channel antagonists. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Aug;80(16):5122–5125. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.16.5122. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamill O. P., Marty A., Neher E., Sakmann B., Sigworth F. J. Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflugers Arch. 1981 Aug;391(2):85–100. doi: 10.1007/BF00656997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hassel P. Experimental comparison of low doses of 1.5 mg fluspirilene and bromazepam in out-patients with psychovegetative disturbances. Pharmacopsychiatry. 1985 Sep;18(5):297–302. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-1017384. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leysen J., Tollenaere J. P., Koch M. H., Laduron P. Differentiation of opiate and neuroleptic receptor binding in rat brain. Eur J Pharmacol. 1977 Jun 1;43(3):253–267. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(77)90025-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martres M. P., Sales N., Bouthenet M. L., Schwartz J. C. Localisation and pharmacological characterisation of D-2 dopamine receptors in rat cerebral neocortex and cerebellum using [125I]iodosulpride. Eur J Pharmacol. 1985 Dec 3;118(3):211–219. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(85)90131-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller R. J., Freedman S. B. Are dihydropyridine binding sites voltage sensitive calcium channels? Life Sci. 1984 Mar 26;34(13):1205–1221. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(84)90543-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilius B., Hess P., Lansman J. B., Tsien R. W. A novel type of cardiac calcium channel in ventricular cells. Nature. 1985 Aug 1;316(6027):443–446. doi: 10.1038/316443a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nowycky M. C., Fox A. P., Tsien R. W. Three types of neuronal calcium channel with different calcium agonist sensitivity. Nature. 1985 Aug 1;316(6027):440–443. doi: 10.1038/316440a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pach J., Waniek W. Vergleichende Untersuchung zum Tranquilizereffekt von Fluspirilene und Diazepam. Pharmakopsychiatr Neuropsychopharmakol. 1976 Mar;9(2):61–66. doi: 10.1055/s-0028-1094479. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quirion R., Lafaille F., Nair N. P. Comparative potencies of calcium channel antagonists and antischizophrenic drugs on central and peripheral calcium channel binding sites. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1985 Jun;37(6):437–440. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1985.tb03033.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


