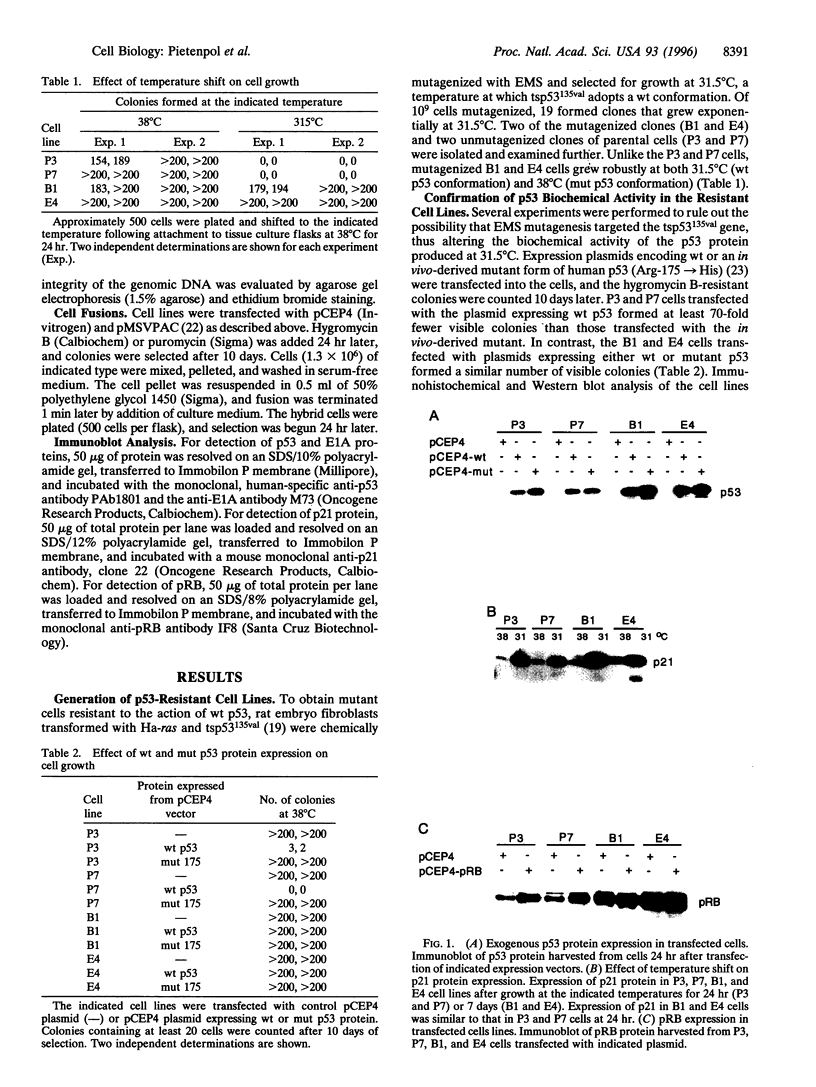
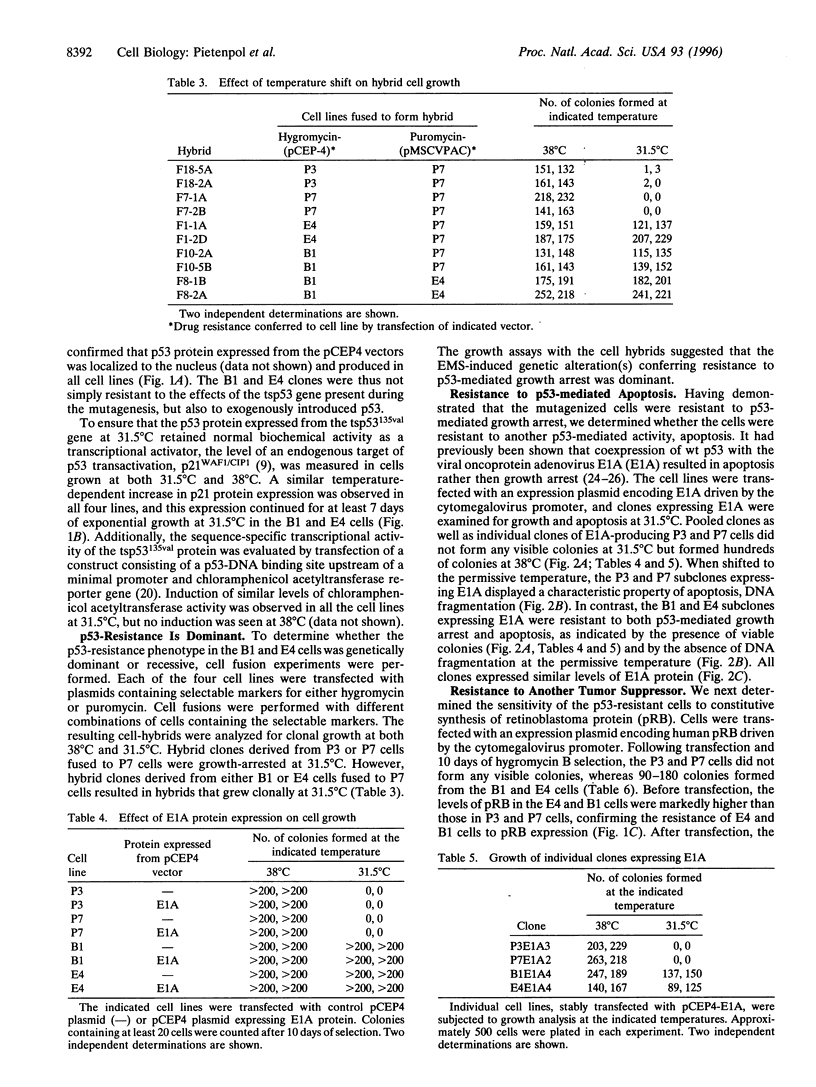
Abstract
Expression of p53 causes growth arrest or apoptosis in many normal and neoplastic cell types, but the relationship between these two effects has remained obscure. To begin to dissect the underlying mechanisms at a genetic level, we have generated mutant cells resistant to the action of wild-type p53. Rat embryo fibroblasts transformed with ras and a temperature-sensitive p53 (tsp53(135val)) gene were chemically mutagenized and selected for growth at a temperature at which p53 adopts a wild-type conformation (31.5 degrees C). Clones that grew exponentially at 31.5 degrees C were selected. Cell fusion experiments demonstrated that the mutations conferring resistance to p53-mediated growth arrest were dominant. The mutagenized clones were resistant not only to p53-mediated growth arrest, but also to the apoptosis induced by E1A in conjunction with p53, and partially resistant to the retinoblastoma tumor suppressor, pRB. The results suggest that a single downstream pathway can control the induction of growth arrest and apoptosis, and that both p53 and RB function through this pathway.
Full text
PDF
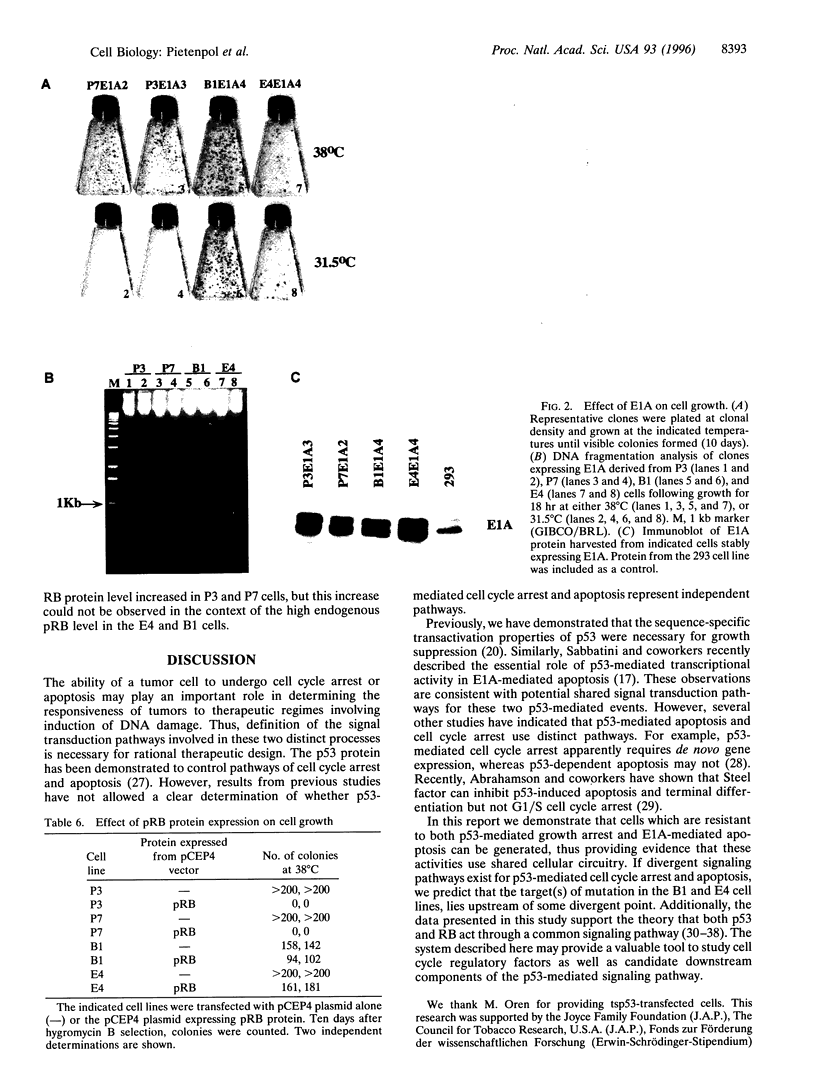

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abrahamson J. L., Lee J. M., Bernstein A. Regulation of p53-mediated apoptosis and cell cycle arrest by Steel factor. Mol Cell Biol. 1995 Dec;15(12):6953–6960. doi: 10.1128/mcb.15.12.6953. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caelles C., Helmberg A., Karin M. p53-dependent apoptosis in the absence of transcriptional activation of p53-target genes. Nature. 1994 Jul 21;370(6486):220–223. doi: 10.1038/370220a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Canman C. E., Gilmer T. M., Coutts S. B., Kastan M. B. Growth factor modulation of p53-mediated growth arrest versus apoptosis. Genes Dev. 1995 Mar 1;9(5):600–611. doi: 10.1101/gad.9.5.600. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke A. R., Purdie C. A., Harrison D. J., Morris R. G., Bird C. C., Hooper M. L., Wyllie A. H. Thymocyte apoptosis induced by p53-dependent and independent pathways. Nature. 1993 Apr 29;362(6423):849–852. doi: 10.1038/362849a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Debbas M., White E. Wild-type p53 mediates apoptosis by E1A, which is inhibited by E1B. Genes Dev. 1993 Apr;7(4):546–554. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.4.546. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demers G. W., Foster S. A., Halbert C. L., Galloway D. A. Growth arrest by induction of p53 in DNA damaged keratinocytes is bypassed by human papillomavirus 16 E7. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 May 10;91(10):4382–4386. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.10.4382. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harper J. W., Adami G. R., Wei N., Keyomarsi K., Elledge S. J. The p21 Cdk-interacting protein Cip1 is a potent inhibitor of G1 cyclin-dependent kinases. Cell. 1993 Nov 19;75(4):805–816. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90499-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haupt Y., Rowan S., Oren M. p53-mediated apoptosis in HeLa cells can be overcome by excess pRB. Oncogene. 1995 Apr 20;10(8):1563–1571. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haupt Y., Rowan S., Shaulian E., Vousden K. H., Oren M. Induction of apoptosis in HeLa cells by trans-activation-deficient p53. Genes Dev. 1995 Sep 1;9(17):2170–2183. doi: 10.1101/gad.9.17.2170. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawley R. G., Lieu F. H., Fong A. Z., Hawley T. S. Versatile retroviral vectors for potential use in gene therapy. Gene Ther. 1994 Mar;1(2):136–138. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hickman E. S., Picksley S. M., Vousden K. H. Cells expressing HPV16 E7 continue cell cycle progression following DNA damage induced p53 activation. Oncogene. 1994 Aug;9(8):2177–2181. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howes K. A., Ransom N., Papermaster D. S., Lasudry J. G., Albert D. M., Windle J. J. Apoptosis or retinoblastoma: alternative fates of photoreceptors expressing the HPV-16 E7 gene in the presence or absence of p53. Genes Dev. 1994 Jun 1;8(11):1300–1310. doi: 10.1101/gad.8.11.1300. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kastan M. B., Onyekwere O., Sidransky D., Vogelstein B., Craig R. W. Participation of p53 protein in the cellular response to DNA damage. Cancer Res. 1991 Dec 1;51(23 Pt 1):6304–6311. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kastan M. B., Zhan Q., el-Deiry W. S., Carrier F., Jacks T., Walsh W. V., Plunkett B. S., Vogelstein B., Fornace A. J., Jr A mammalian cell cycle checkpoint pathway utilizing p53 and GADD45 is defective in ataxia-telangiectasia. Cell. 1992 Nov 13;71(4):587–597. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90593-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee J. M., Abrahamson J. L., Bernstein A. DNA damage, oncogenesis and the p53 tumour-suppressor gene. Mutat Res. 1994 Jun 1;307(2):573–581. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(94)90267-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Livingstone L. R., White A., Sprouse J., Livanos E., Jacks T., Tlsty T. D. Altered cell cycle arrest and gene amplification potential accompany loss of wild-type p53. Cell. 1992 Sep 18;70(6):923–935. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90243-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lotem J., Sachs L. Hematopoietic cells from mice deficient in wild-type p53 are more resistant to induction of apoptosis by some agents. Blood. 1993 Aug 15;82(4):1092–1096. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowe S. W., Ruley H. E. Stabilization of the p53 tumor suppressor is induced by adenovirus 5 E1A and accompanies apoptosis. Genes Dev. 1993 Apr;7(4):535–545. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.4.535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowe S. W., Schmitt E. M., Smith S. W., Osborne B. A., Jacks T. p53 is required for radiation-induced apoptosis in mouse thymocytes. Nature. 1993 Apr 29;362(6423):847–849. doi: 10.1038/362847a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michalovitz D., Halevy O., Oren M. Conditional inhibition of transformation and of cell proliferation by a temperature-sensitive mutant of p53. Cell. 1990 Aug 24;62(4):671–680. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90113-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyashita T., Krajewski S., Krajewska M., Wang H. G., Lin H. K., Liebermann D. A., Hoffman B., Reed J. C. Tumor suppressor p53 is a regulator of bcl-2 and bax gene expression in vitro and in vivo. Oncogene. 1994 Jun;9(6):1799–1805. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyashita T., Reed J. C. Tumor suppressor p53 is a direct transcriptional activator of the human bax gene. Cell. 1995 Jan 27;80(2):293–299. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90412-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgenbesser S. D., Williams B. O., Jacks T., DePinho R. A. p53-dependent apoptosis produced by Rb-deficiency in the developing mouse lens. Nature. 1994 Sep 1;371(6492):72–74. doi: 10.1038/371072a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nigro J. M., Baker S. J., Preisinger A. C., Jessup J. M., Hostetter R., Cleary K., Bigner S. H., Davidson N., Baylin S., Devilee P. Mutations in the p53 gene occur in diverse human tumour types. Nature. 1989 Dec 7;342(6250):705–708. doi: 10.1038/342705a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pan H., Griep A. E. Altered cell cycle regulation in the lens of HPV-16 E6 or E7 transgenic mice: implications for tumor suppressor gene function in development. Genes Dev. 1994 Jun 1;8(11):1285–1299. doi: 10.1101/gad.8.11.1285. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pietenpol J. A., Tokino T., Thiagalingam S., el-Deiry W. S., Kinzler K. W., Vogelstein B. Sequence-specific transcriptional activation is essential for growth suppression by p53. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Mar 15;91(6):1998–2002. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.6.1998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qin X. Q., Livingston D. M., Kaelin W. G., Jr, Adams P. D. Deregulated transcription factor E2F-1 expression leads to S-phase entry and p53-mediated apoptosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Nov 8;91(23):10918–10922. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.23.10918. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed J. C. Bcl-2 and the regulation of programmed cell death. J Cell Biol. 1994 Jan;124(1-2):1–6. doi: 10.1083/jcb.124.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan J. J., Danish R., Gottlieb C. A., Clarke M. F. Cell cycle analysis of p53-induced cell death in murine erythroleukemia cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Jan;13(1):711–719. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.1.711. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabbatini P., Lin J., Levine A. J., White E. Essential role for p53-mediated transcription in E1A-induced apoptosis. Genes Dev. 1995 Sep 1;9(17):2184–2192. doi: 10.1101/gad.9.17.2184. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selvakumaran M., Lin H. K., Miyashita T., Wang H. G., Krajewski S., Reed J. C., Hoffman B., Liebermann D. Immediate early up-regulation of bax expression by p53 but not TGF beta 1: a paradigm for distinct apoptotic pathways. Oncogene. 1994 Jun;9(6):1791–1798. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White E. Death-defying acts: a meeting review on apoptosis. Genes Dev. 1993 Dec;7(12A):2277–2284. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.12a.2277. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whyte P., Buchkovich K. J., Horowitz J. M., Friend S. H., Raybuck M., Weinberg R. A., Harlow E. Association between an oncogene and an anti-oncogene: the adenovirus E1A proteins bind to the retinoblastoma gene product. Nature. 1988 Jul 14;334(6178):124–129. doi: 10.1038/334124a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams B. O., Remington L., Albert D. M., Mukai S., Bronson R. T., Jacks T. Cooperative tumorigenic effects of germline mutations in Rb and p53. Nat Genet. 1994 Aug;7(4):480–484. doi: 10.1038/ng0894-480. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu X., Levine A. J. p53 and E2F-1 cooperate to mediate apoptosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Apr 26;91(9):3602–3606. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.9.3602. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xiong Y., Hannon G. J., Zhang H., Casso D., Kobayashi R., Beach D. p21 is a universal inhibitor of cyclin kinases. Nature. 1993 Dec 16;366(6456):701–704. doi: 10.1038/366701a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yonish-Rouach E., Resnitzky D., Lotem J., Sachs L., Kimchi A., Oren M. Wild-type p53 induces apoptosis of myeloid leukaemic cells that is inhibited by interleukin-6. Nature. 1991 Jul 25;352(6333):345–347. doi: 10.1038/352345a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- el-Deiry W. S., Tokino T., Velculescu V. E., Levy D. B., Parsons R., Trent J. M., Lin D., Mercer W. E., Kinzler K. W., Vogelstein B. WAF1, a potential mediator of p53 tumor suppression. Cell. 1993 Nov 19;75(4):817–825. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90500-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]