Abstract
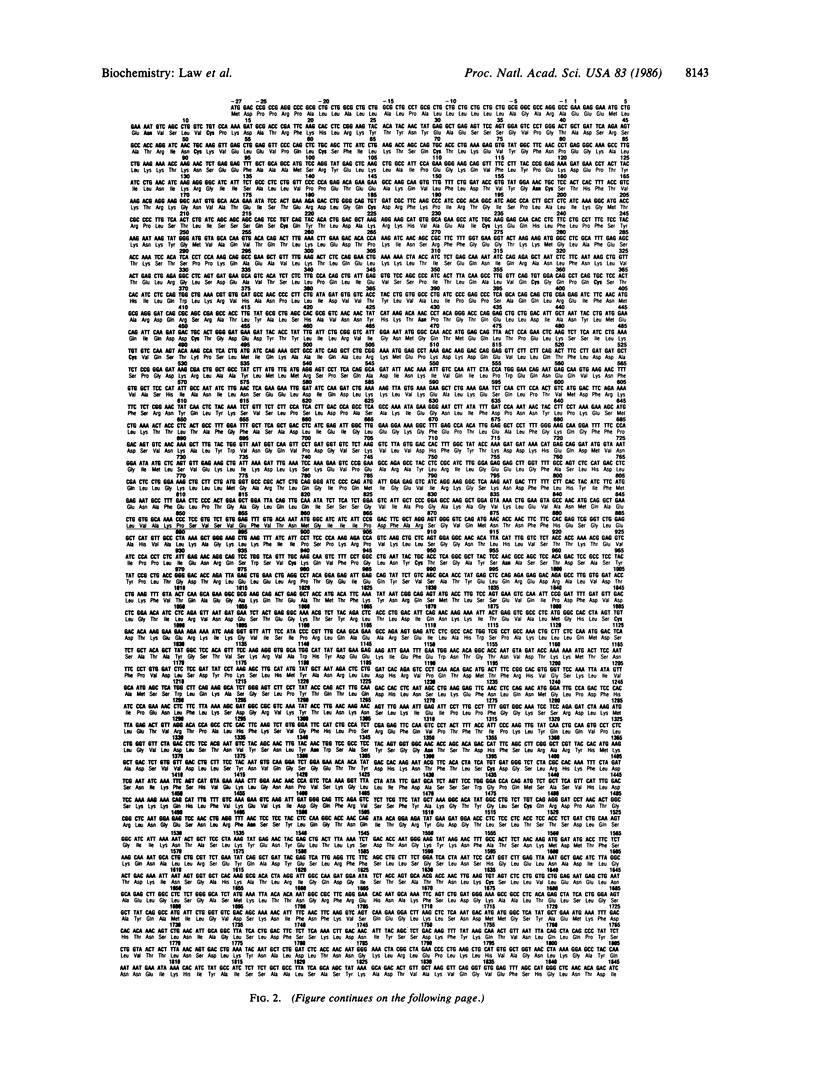
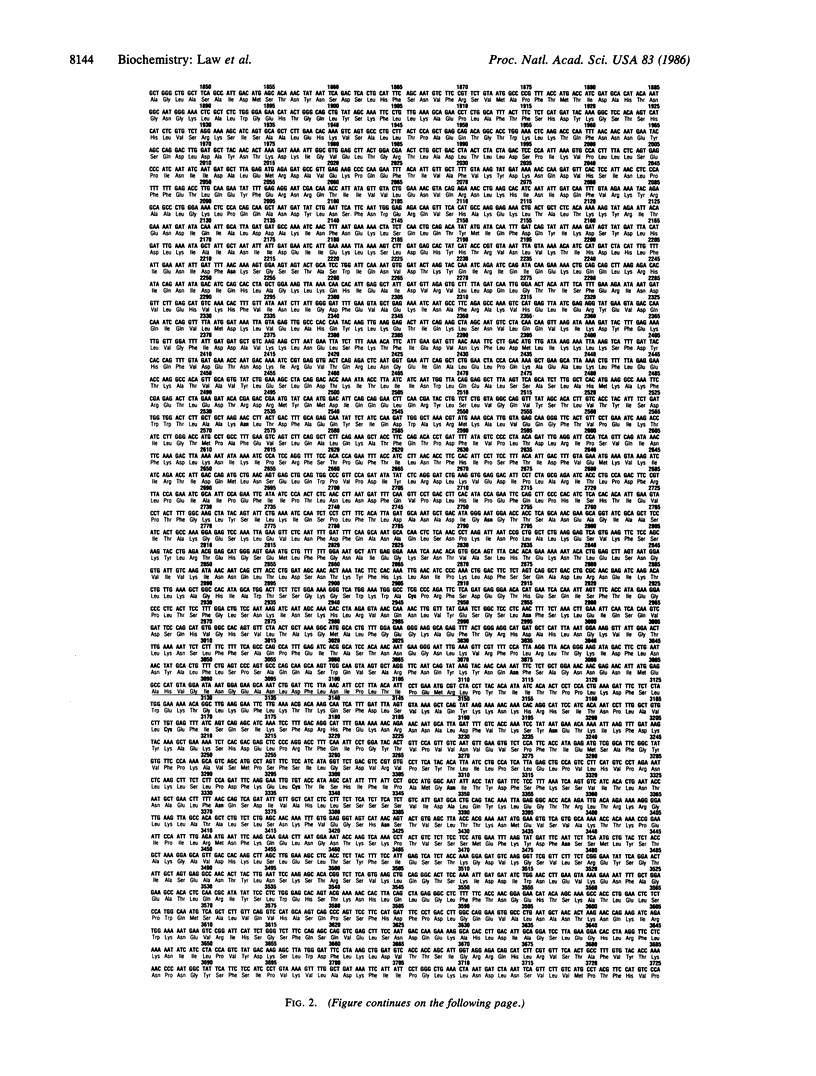
Human apolipoprotein B-100 (apoB-100), the ligand on low density lipoproteins that interacts with the low density lipoprotein receptor and initiates receptor-mediated endocytosis and low density lipoprotein catabolism, has been cloned, and the complete nucleic acid and derived amino acid sequences have been determined. ApoB-100 cDNAs were isolated from normal human liver cDNA libraries utilizing immunoscreening as well as filter hybridization with radiolabeled apoB-100 oligodeoxynucleotides. The apoB-100 mRNA is 14.1 kilobases long encoding a mature apoB-100 protein of 4536 amino acids with a calculated amino acid molecular weight of 512,723. ApoB-100 contains 20 potential glycosylation sites, and 12 of a total of 25 cysteine residues are located in the amino-terminal region of the apolipoprotein providing a potential globular structure of the amino terminus of the protein. ApoB-100 contains relatively few regions of amphipathic helices, but compared to other human apolipoproteins it is enriched in beta-structure. The delineation of the entire human apoB-100 sequence will now permit a detailed analysis of the conformation of the protein, the low density lipoprotein receptor binding domain(s), and the structural relationship between apoB-100 and apoB-48 and will provide the basis for the study of genetic defects in apoB-100 in patients with dyslipoproteinemias.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Belt K. T., Carroll M. C., Porter R. R. The structural basis of the multiple forms of human complement component C4. Cell. 1984 Apr;36(4):907–914. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90040-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cardin A. D., Witt K. R., Chao J., Margolius H. S., Donaldson V. H., Jackson R. L. Degradation of apolipoprotein B-100 of human plasma low density lipoproteins by tissue and plasma kallikreins. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jul 10;259(13):8522–8528. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlsson P., Olofsson S. O., Bondjers G., Darnfors C., Wiklund O., Bjursell G. Molecular cloning of human apolipoprotein B cDNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Dec 20;13(24):8813–8826. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.24.8813. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dale R. M., McClure B. A., Houchins J. P. A rapid single-stranded cloning strategy for producing a sequential series of overlapping clones for use in DNA sequencing: application to sequencing the corn mitochondrial 18 S rDNA. Plasmid. 1985 Jan;13(1):31–40. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(85)90053-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deeb S. S., Motulsky A. G., Albers J. J. A partial cDNA clone for human apolipoprotein B. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Aug;82(15):4983–4986. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.15.4983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elovson J., Jacobs J. C., Schumaker V. N., Puppione D. L. Molecular weights of apoprotein B obtained from human low-density lipoprotein (apoprotein B-PI) and from rat very low density lipoprotein (apoprotein B-PIII). Biochemistry. 1985 Mar 12;24(6):1569–1578. doi: 10.1021/bi00327a042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein J. L., Brown M. S. The low-density lipoprotein pathway and its relation to atherosclerosis. Annu Rev Biochem. 1977;46:897–930. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.46.070177.004341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hospattankar A. V., Fairwell T., Meng M., Ronan R., Brewer H. B., Jr Identification of sequence homology between human plasma apolipoprotein B-100 and apolipoprotein B-48. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 15;261(20):9102–9104. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson R. L., Morrisett J. D., Gotto A. M., Jr Lipoprotein structure and metabolism. Physiol Rev. 1976 Apr;56(2):259–316. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1976.56.2.259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kane J. P. Apolipoprotein B: structural and metabolic heterogeneity. Annu Rev Physiol. 1983;45:637–650. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.45.030183.003225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knott T. J., Rall S. C., Jr, Innerarity T. L., Jacobson S. F., Urdea M. S., Levy-Wilson B., Powell L. M., Pease R. J., Eddy R., Nakai H. Human apolipoprotein B: structure of carboxyl-terminal domains, sites of gene expression, and chromosomal localization. Science. 1985 Oct 4;230(4721):37–43. doi: 10.1126/science.2994225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Law S. W., Brewer H. B., Jr Nucleotide sequence and the encoded amino acids of human apolipoprotein A-I mRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jan;81(1):66–70. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.1.66. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Law S. W., Dugaiczyk A. Homology between the primary structure of alpha-fetoprotein, deduced from a complete cDNA sequence, and serum albumin. Nature. 1981 May 21;291(5812):201–205. doi: 10.1038/291201a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Law S. W., Gray G., Brewer H. B., Jr cDNA cloning of human apoA-I: amino acid sequence of preproapoA-I. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Apr 15;112(1):257–264. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)91824-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Law S. W., Lackner K. J., Hospattankar A. V., Anchors J. M., Sakaguchi A. Y., Naylor S. L., Brewer H. B., Jr Human apolipoprotein B-100: cloning, analysis of liver mRNA, and assignment of the gene to chromosome 2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(24):8340–8344. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.24.8340. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Law S. W., Lee N., Monge J. C., Brewer H. B., Jr, Sakaguchi A. Y., Naylor S. L. Human ApoB-100 gene resides in the p23----pter region of chromosome 2. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Sep 16;131(2):1003–1012. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)91339-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeBoeuf R. C., Miller C., Shively J. E., Schumaker V. N., Balla M. A., Lusis A. J. Human apolipoprotein B: partial amino acid sequence. FEBS Lett. 1984 May 7;170(1):105–108. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(84)81378-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lusis A. J., West R., Mehrabian M., Reuben M. A., LeBoeuf R. C., Kaptein J. S., Johnson D. F., Schumaker V. N., Yuhasz M. P., Schotz M. C. Cloning and expression of apolipoprotein B, the major protein of low and very low density lipoproteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(14):4597–4601. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.14.4597. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. A new method for sequencing DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):560–564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mehrabian M., Schumaker V. N., Fareed G. C., West R., Johnson D. F., Kirchgessner T., Lin H. C., Wang X. B., Ma Y. H., Mendiaz E. Human apolipoprotein B: identification of cDNA clones and characterization of mRNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Oct 11;13(19):6937–6953. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.19.6937. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minghetti P. P., Ruffner D. E., Kuang W. J., Dennison O. E., Hawkins J. W., Beattie W. G., Dugaiczyk A. Molecular structure of the human albumin gene is revealed by nucleotide sequence within q11-22 of chromosome 4. J Biol Chem. 1986 May 25;261(15):6747–6757. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborne J. C., Jr, Brewer H. B., Jr The plasma lipoproteins. Adv Protein Chem. 1977;31:253–337. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60220-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Protter A. A., Hardman D. A., Schilling J. W., Miller J., Appleby V., Chen G. C., Kirsher S. W., McEnroe G., Kane J. P. Isolation of a cDNA clone encoding the amino-terminal region of human apolipoprotein B. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(5):1467–1471. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.5.1467. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shoulders C. C., Myant N. B., Sidoli A., Rodriguez J. C., Cortese C., Baralle F. E., Cortese R. Molecular cloning of human LDL apolipoprotein B cDNA. Evidence for more than one gene per haploid genome. Atherosclerosis. 1985 Dec;58(1-3):277–289. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(85)90073-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wei C. F., Chen S. H., Yang C. Y., Marcel Y. L., Milne R. W., Li W. H., Sparrow J. T., Gotto A. M., Jr, Chan L. Molecular cloning and expression of partial cDNAs and deduced amino acid sequence of a carboxyl-terminal fragment of human apolipoprotein B-100. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Nov;82(21):7265–7269. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.21.7265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


