Abstract
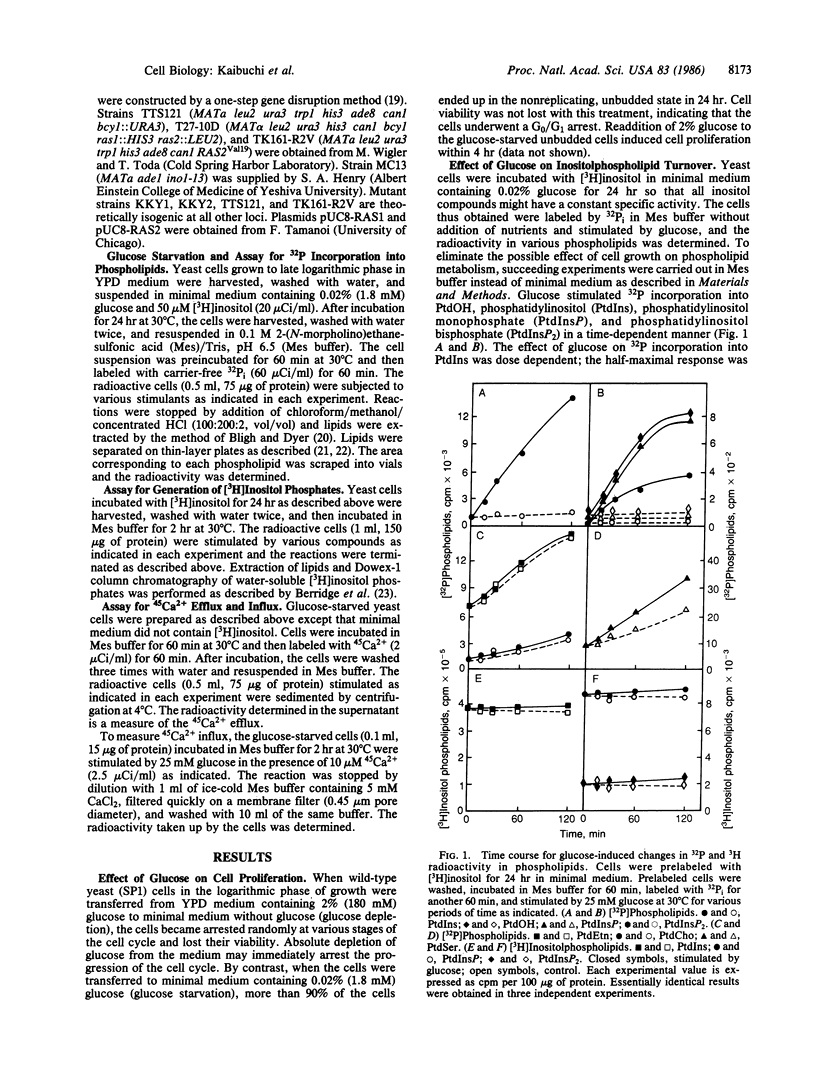
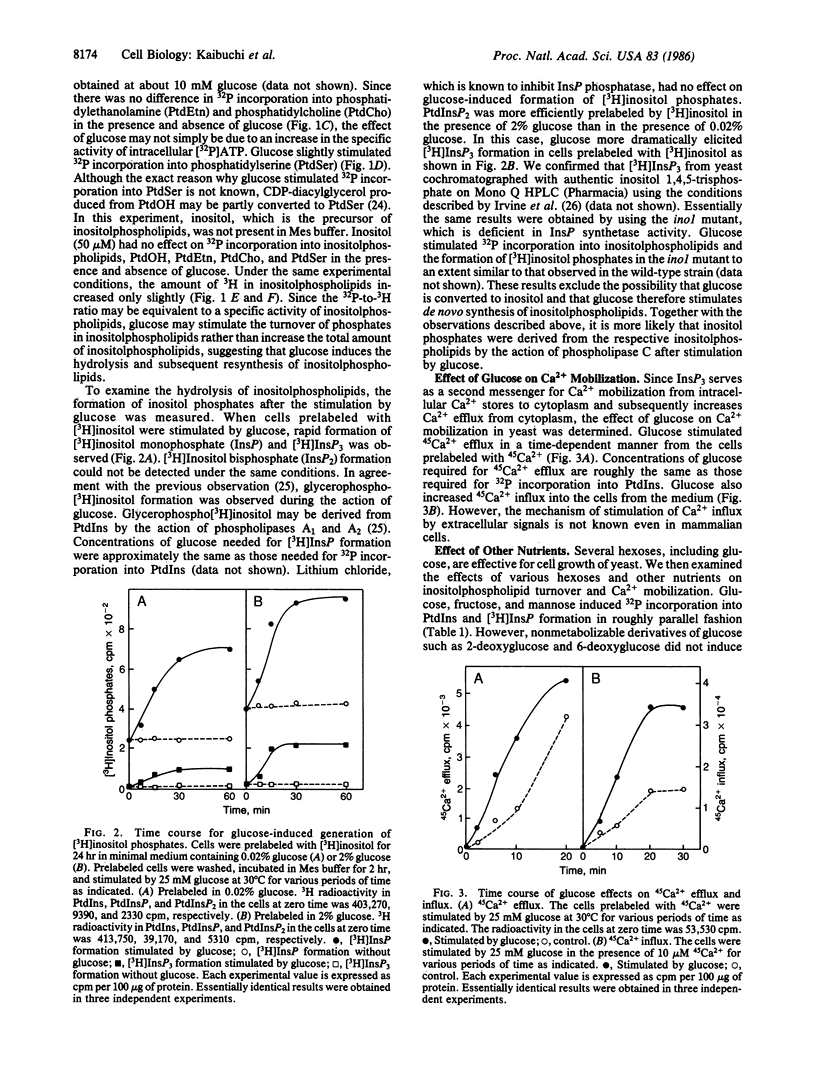
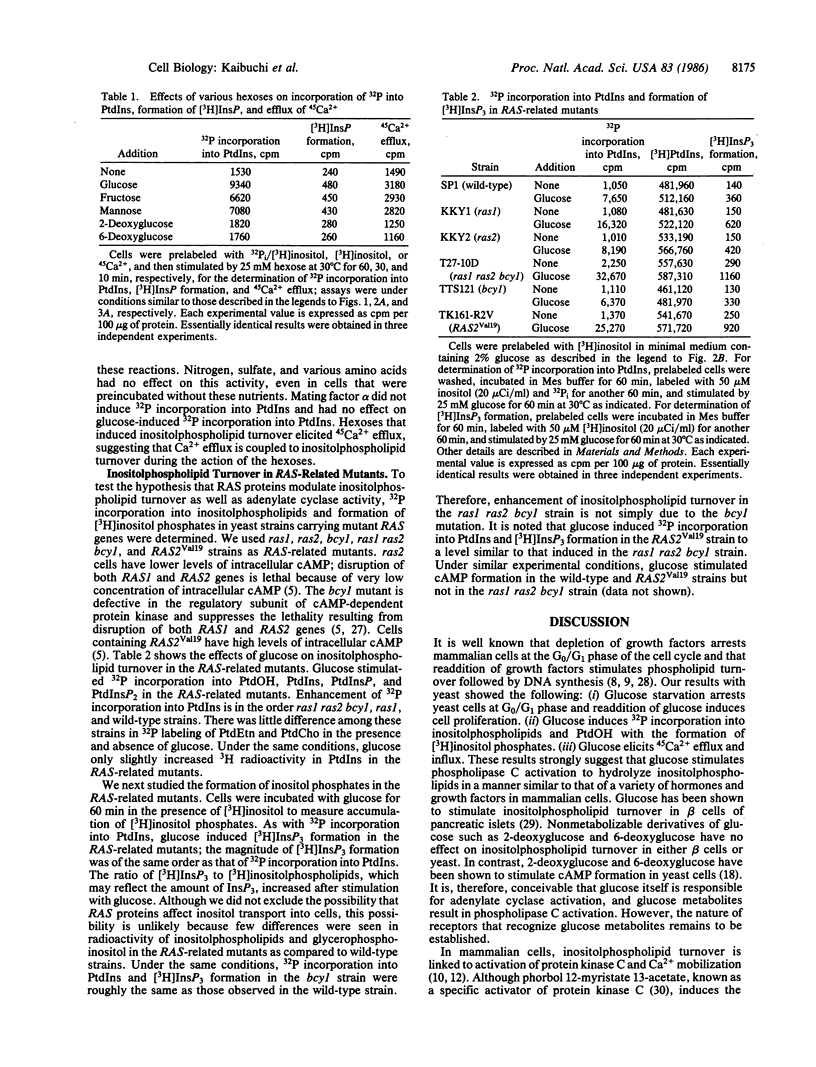
Incubation of yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae at very low (0.02%) glucose levels led to arrest of the cell cycle at the G0/G1 phase. Readdition of glucose to these "starved" yeast resulted in cell proliferation. In glucose-starved yeast, glucose stimulated 32P incorporation into phosphatidic acid, phosphatidylinositol, phosphatidylinositol monophosphate, and phosphatidylinositol bisphosphate but not into phosphatidylethanolamine and phosphatidylcholine. Preincubation of yeast with [3H]inositol and subsequent exposure to glucose resulted in rapid formation of [3H]inositol monophosphate and [3H]inositol trisphosphate, presumably derived from phosphatidylinositol and phosphatidylinositol bisphosphate. Under similar conditions, glucose elicited both efflux and influx of Ca2+ in yeast. Glucose-induced 32P incorporation into inositolphospholipids and formation of [3H]inositol phosphates were more pronounced in RAS-related mutants such as ras1, ras1 ras2 bcy1, and RAS2Val19 than in the wild-type strain. These results strongly suggest that glucose stimulates inositolphospholipid turnover, Ca2+ mobilization, and subsequent cell proliferation in a manner similar to that of growth factors with mammalian cells, and that RAS-encoded proteins are involved in regulation of this glucose-induced inositolphospholipid turnover in yeast.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Angus W. W., Lester R. L. The regulated catabolism of endogenous and exogenous phosphatidylinositol by Saccharomyces cerevisiae leading to extracellular glycerophosphorylinositol and inositol. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jan 10;250(1):22–30. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BLIGH E. G., DYER W. J. A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can J Biochem Physiol. 1959 Aug;37(8):911–917. doi: 10.1139/o59-099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J., Dawson R. M., Downes C. P., Heslop J. P., Irvine R. F. Changes in the levels of inositol phosphates after agonist-dependent hydrolysis of membrane phosphoinositides. Biochem J. 1983 May 15;212(2):473–482. doi: 10.1042/bj2120473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J., Irvine R. F. Inositol trisphosphate, a novel second messenger in cellular signal transduction. Nature. 1984 Nov 22;312(5992):315–321. doi: 10.1038/312315a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Billah M. M., Lapetina E. G. Rapid decrease of phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate in thrombin-stimulated platelets. J Biol Chem. 1982 Nov 10;257(21):12705–12708. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broek D., Samiy N., Fasano O., Fujiyama A., Tamanoi F., Northup J., Wigler M. Differential activation of yeast adenylate cyclase by wild-type and mutant RAS proteins. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):763–769. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80057-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castagna M., Takai Y., Kaibuchi K., Sano K., Kikkawa U., Nishizuka Y. Direct activation of calcium-activated, phospholipid-dependent protein kinase by tumor-promoting phorbol esters. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jul 10;257(13):7847–7851. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clements R. S., Jr, Evans M. H., Pace C. S. Substrate requirements for the phosphoinositide response in rat pancreatic islets. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Apr 17;674(1):1–9. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(81)90340-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeFeo-Jones D., Scolnick E. M., Koller R., Dhar R. ras-Related gene sequences identified and isolated from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Nature. 1983 Dec 15;306(5944):707–709. doi: 10.1038/306707a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleischman L. F., Chahwala S. B., Cantley L. ras-transformed cells: altered levels of phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate and catabolites. Science. 1986 Jan 24;231(4736):407–410. doi: 10.1126/science.3001936. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilman A. G. G proteins and dual control of adenylate cyclase. Cell. 1984 Mar;36(3):577–579. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90336-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Habenicht A. J., Glomset J. A., King W. C., Nist C., Mitchell C. D., Ross R. Early changes in phosphatidylinositol and arachidonic acid metabolism in quiescent swiss 3T3 cells stimulated to divide by platelet-derived growth factor. J Biol Chem. 1981 Dec 10;256(23):12329–12335. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irvine R. F., Letcher A. J., Lander D. J., Downes C. P. Inositol trisphosphates in carbachol-stimulated rat parotid glands. Biochem J. 1984 Oct 1;223(1):237–243. doi: 10.1042/bj2230237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jolles J., Schrama L. H., Gispen W. H. Calcium-dependent turnover of brain polyphosphoinositides in vitro after prelabelling in vivo. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Oct 23;666(1):90–98. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(81)90094-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaibuchi K., Tsuda T., Kikuchi A., Tanimoto T., Yamashita T., Takai Y. Possible involvement of protein kinase C and calcium ion in growth factor-induced expression of c-myc oncogene in Swiss 3T3 fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jan 25;261(3):1187–1192. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsumoto K., Uno I., Ishikawa T. Initiation of meiosis in yeast mutants defective in adenylate cyclase and cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase. Cell. 1983 Feb;32(2):417–423. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90461-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsumoto K., Uno I., Oshima Y., Ishikawa T. Isolation and characterization of yeast mutants deficient in adenylate cyclase and cAMP-dependent protein kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Apr;79(7):2355–2359. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.7.2355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura T., Ui M. Simultaneous inhibitions of inositol phospholipid breakdown, arachidonic acid release, and histamine secretion in mast cells by islet-activating protein, pertussis toxin. A possible involvement of the toxin-specific substrate in the Ca2+-mobilizing receptor-mediated biosignaling system. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 25;260(6):3584–3593. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizuka Y. The role of protein kinase C in cell surface signal transduction and tumour promotion. Nature. 1984 Apr 19;308(5961):693–698. doi: 10.1038/308693a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portillo F., Mazón M. J. Activation of yeast plasma membrane ATPase by phorbol ester. FEBS Lett. 1985 Nov 11;192(1):95–98. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80050-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powers S., Kataoka T., Fasano O., Goldfarb M., Strathern J., Broach J., Wigler M. Genes in S. cerevisiae encoding proteins with domains homologous to the mammalian ras proteins. Cell. 1984 Mar;36(3):607–612. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90340-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothstein R. J. One-step gene disruption in yeast. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:202–211. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01015-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rozengurt E. Synergistic stimulation of DNA synthesis by cyclic AMP derivatives and growth factors in mouse 3T3 cells. J Cell Physiol. 1982 Aug;112(2):243–250. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041120213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. D., Lane B. C., Kusaka I., Verghese M. W., Snyderman R. Chemoattractant receptor-induced hydrolysis of phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate in human polymorphonuclear leukocyte membranes. Requirement for a guanine nucleotide regulatory protein. J Biol Chem. 1985 May 25;260(10):5875–5878. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steiner S., Lester R. L. Metabolism of diphosphoinositide and triphosphoinositide in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Jan 27;260(1):82–87. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(72)90076-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugimoto Y., Whitman M., Cantley L. C., Erikson R. L. Evidence that the Rous sarcoma virus transforming gene product phosphorylates phosphatidylinositol and diacylglycerol. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):2117–2121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.2117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takai Y., Kikkawa U., Kaibuchi K., Nishizuka Y. Membrane phospholipid metabolism and signal transduction for protein phosphorylation. Adv Cyclic Nucleotide Protein Phosphorylation Res. 1984;18:119–158. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toda T., Uno I., Ishikawa T., Powers S., Kataoka T., Broek D., Cameron S., Broach J., Matsumoto K., Wigler M. In yeast, RAS proteins are controlling elements of adenylate cyclase. Cell. 1985 Jan;40(1):27–36. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90305-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuda T., Kaibuchi K., Kawahara Y., Fukuzaki H., Takai Y. Induction of protein kinase C activation and Ca2+ mobilization by fibroblast growth factor in Swiss 3T3 cells. FEBS Lett. 1985 Oct 28;191(2):205–210. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80009-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uno I., Mitsuzawa H., Matsumoto K., Tanaka K., Oshima T., Ishikawa T. Reconstitution of the GTP-dependent adenylate cyclase from products of the yeast CYR1 and RAS2 genes in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(23):7855–7859. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.23.7855. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


