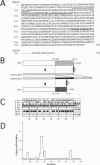
Abstract
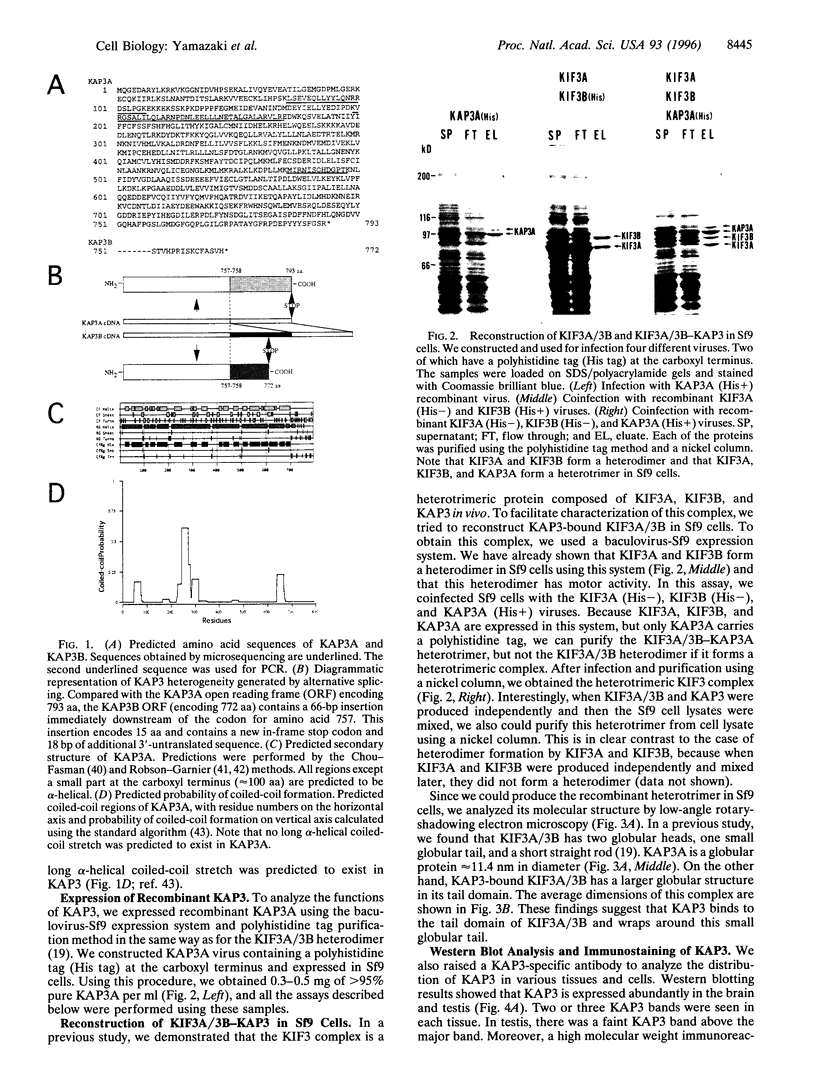
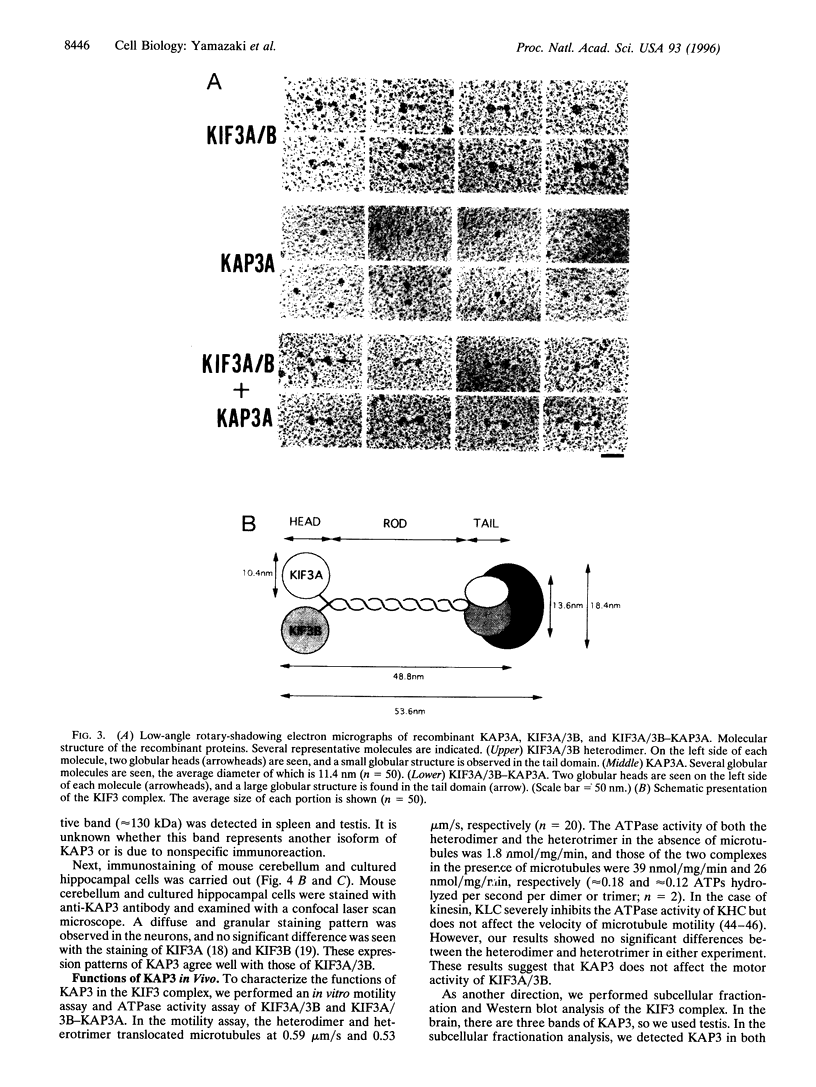
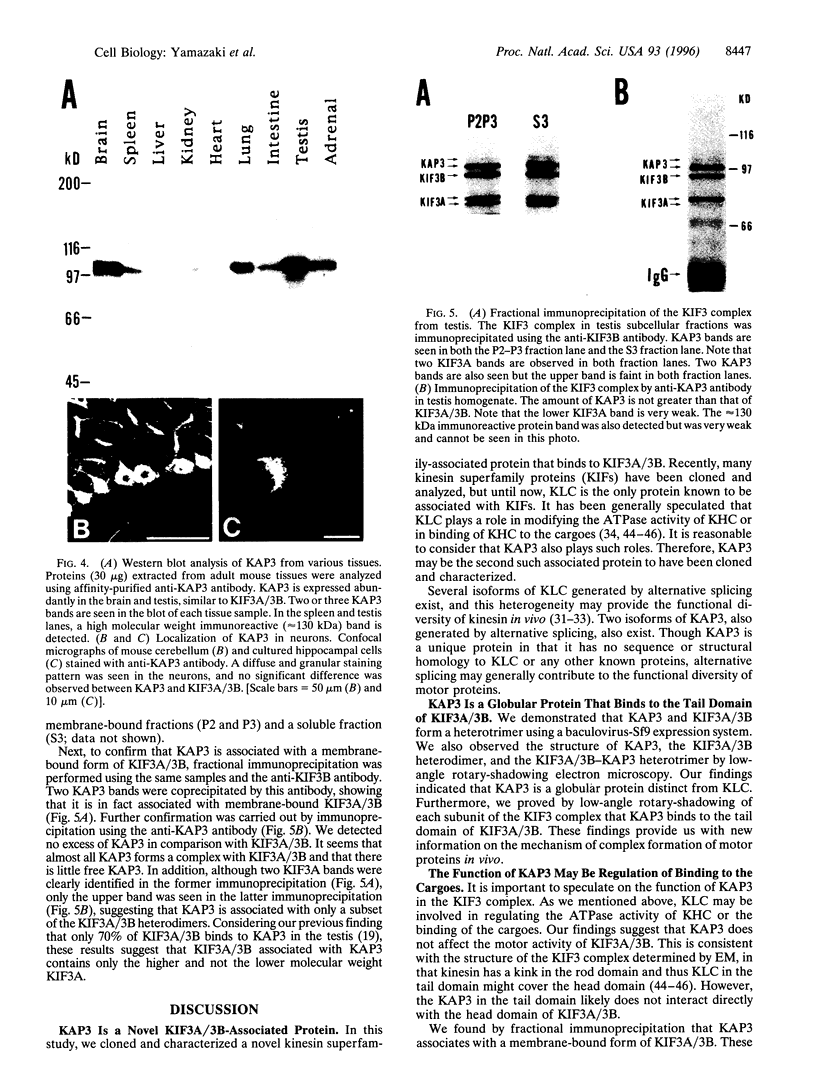
We previously reported that KIF3A and KIF3B form a heterodimer that functions as a microtubule-based fast anterograde translocator of membranous organelles. We have also shown that this KIF3A/3B forms a complex with other associated polypeptides, named kinesin superfamily-associated protein 3 (KAP3). In the present study, we purified KAP3 protein by immunoprecipitation using anti-KIF3B antibody from mouse testis. Microsequencing was carried out, and we cloned the full-length KAP3 cDNA from a mouse brain cDNA library. Two isoforms of KAP3 exist [KAP3A (793 aa) and KAP3B (772 aa)], generated by alternative splicing in the carboxyl terminus region. Their amino acid sequences have no homology with those of any other known proteins, and prediction of their secondary structure indicated that almost the entire KAP3 molecule is alpha-helical. We produced recombinant KAP3 and KIF3A/3B using a baculovirus-Sf9 expression system. A reconstruction study in Sf9 cells revealed that KAP3 is a globular protein that binds to the tail domain of KIF3A/3B. The immunolocalization pattern of KAP3 was similar to that of KIF3A/3B in nerve cells. In addition, we found that KAP3 does not affect the motor activity of KIF3A/3B. KAP3 was associated with a membrane-bound form of KIF3A/3B in a fractional immunoprecipitation experiment, and since the KIF3 complex was found to bind to membranous organelles in an EM study, KAP3 may regulate membrane binding of the KIF3 complex.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aizawa H., Sekine Y., Takemura R., Zhang Z., Nangaku M., Hirokawa N. Kinesin family in murine central nervous system. J Cell Biol. 1992 Dec;119(5):1287–1296. doi: 10.1083/jcb.119.5.1287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banker G. A., Cowan W. M. Rat hippocampal neurons in dispersed cell culture. Brain Res. 1977 May 13;126(3):397–342. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(77)90594-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloom G. S., Endow S. A. Motor proteins. 1: kinesins. Protein Profile. 1994;1(10):1059–1116. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brady S. T. A novel brain ATPase with properties expected for the fast axonal transport motor. Nature. 1985 Sep 5;317(6032):73–75. doi: 10.1038/317073a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brady S. T., Sperry A. O. Biochemical and functional diversity of microtubule motors in the nervous system. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 1995 Oct;5(5):551–558. doi: 10.1016/0959-4388(95)80058-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou P. Y., Fasman G. D. Prediction of protein conformation. Biochemistry. 1974 Jan 15;13(2):222–245. doi: 10.1021/bi00699a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole D. G., Cande W. Z., Baskin R. J., Skoufias D. A., Hogan C. J., Scholey J. M. Isolation of a sea urchin egg kinesin-related protein using peptide antibodies. J Cell Sci. 1992 Feb;101(Pt 2):291–301. doi: 10.1242/jcs.101.2.291. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole D. G., Chinn S. W., Wedaman K. P., Hall K., Vuong T., Scholey J. M. Novel heterotrimeric kinesin-related protein purified from sea urchin eggs. Nature. 1993 Nov 18;366(6452):268–270. doi: 10.1038/366268a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cyr J. L., Pfister K. K., Bloom G. S., Slaughter C. A., Brady S. T. Molecular genetics of kinesin light chains: generation of isoforms by alternative splicing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Nov 15;88(22):10114–10118. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.22.10114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garnier J., Osguthorpe D. J., Robson B. Analysis of the accuracy and implications of simple methods for predicting the secondary structure of globular proteins. J Mol Biol. 1978 Mar 25;120(1):97–120. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90297-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gauger A. K., Goldstein L. S. The Drosophila kinesin light chain. Primary structure and interaction with kinesin heavy chain. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jun 25;268(18):13657–13666. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein L. S. With apologies to scheherazade: tails of 1001 kinesin motors. Annu Rev Genet. 1993;27:319–351. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.27.120193.001535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hackney D. D., Levitt J. D., Suhan J. Kinesin undergoes a 9 S to 6 S conformational transition. J Biol Chem. 1992 Apr 25;267(12):8696–8701. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hackney D. D., Levitt J. D., Wagner D. D. Characterization of alpha 2 beta 2 and alpha 2 forms of kinesin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Jan 31;174(2):810–815. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)91490-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henson J. H., Cole D. G., Terasaki M., Rashid D., Scholey J. M. Immunolocalization of the heterotrimeric kinesin-related protein KRP(85/95) in the mitotic apparatus of sea urchin embryos. Dev Biol. 1995 Sep;171(1):182–194. doi: 10.1006/dbio.1995.1270. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirokawa N. Axonal transport and the cytoskeleton. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 1993 Oct;3(5):724–731. doi: 10.1016/0959-4388(93)90144-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirokawa N. Cross-linker system between neurofilaments, microtubules, and membranous organelles in frog axons revealed by the quick-freeze, deep-etching method. J Cell Biol. 1982 Jul;94(1):129–142. doi: 10.1083/jcb.94.1.129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirokawa N. Organelle transport along microtubules - the role of KIFs. Trends Cell Biol. 1996 Apr;6(4):135–141. doi: 10.1016/0962-8924(96)10003-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirokawa N., Pfister K. K., Yorifuji H., Wagner M. C., Brady S. T., Bloom G. S. Submolecular domains of bovine brain kinesin identified by electron microscopy and monoclonal antibody decoration. Cell. 1989 Mar 10;56(5):867–878. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90691-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirokawa N., Sato-Yoshitake R., Kobayashi N., Pfister K. K., Bloom G. S., Brady S. T. Kinesin associates with anterogradely transported membranous organelles in vivo. J Cell Biol. 1991 Jul;114(2):295–302. doi: 10.1083/jcb.114.2.295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kondo S., Sato-Yoshitake R., Noda Y., Aizawa H., Nakata T., Matsuura Y., Hirokawa N. KIF3A is a new microtubule-based anterograde motor in the nerve axon. J Cell Biol. 1994 Jun;125(5):1095–1107. doi: 10.1083/jcb.125.5.1095. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozminski K. G., Beech P. L., Rosenbaum J. L. The Chlamydomonas kinesin-like protein FLA10 is involved in motility associated with the flagellar membrane. J Cell Biol. 1995 Dec;131(6 Pt 1):1517–1527. doi: 10.1083/jcb.131.6.1517. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lupas A., Van Dyke M., Stock J. Predicting coiled coils from protein sequences. Science. 1991 May 24;252(5009):1162–1164. doi: 10.1126/science.252.5009.1162. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthies H. J., Miller R. J., Palfrey H. C. Calmodulin binding to and cAMP-dependent phosphorylation of kinesin light chains modulate kinesin ATPase activity. J Biol Chem. 1993 May 25;268(15):11176–11187. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakata T., Hirokawa N. Point mutation of adenosine triphosphate-binding motif generated rigor kinesin that selectively blocks anterograde lysosome membrane transport. J Cell Biol. 1995 Nov;131(4):1039–1053. doi: 10.1083/jcb.131.4.1039. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakata T., Iwamoto A., Noda Y., Takemura R., Yoshikura H., Hirokawa N. Predominant and developmentally regulated expression of dynamin in neurons. Neuron. 1991 Sep;7(3):461–469. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90298-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nangaku M., Sato-Yoshitake R., Okada Y., Noda Y., Takemura R., Yamazaki H., Hirokawa N. KIF1B, a novel microtubule plus end-directed monomeric motor protein for transport of mitochondria. Cell. 1994 Dec 30;79(7):1209–1220. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90012-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niclas J., Navone F., Hom-Booher N., Vale R. D. Cloning and localization of a conventional kinesin motor expressed exclusively in neurons. Neuron. 1994 May;12(5):1059–1072. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(94)90314-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noda Y., Sato-Yoshitake R., Kondo S., Nangaku M., Hirokawa N. KIF2 is a new microtubule-based anterograde motor that transports membranous organelles distinct from those carried by kinesin heavy chain or KIF3A/B. J Cell Biol. 1995 Apr;129(1):157–167. doi: 10.1083/jcb.129.1.157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okada Y., Yamazaki H., Sekine-Aizawa Y., Hirokawa N. The neuron-specific kinesin superfamily protein KIF1A is a unique monomeric motor for anterograde axonal transport of synaptic vesicle precursors. Cell. 1995 Jun 2;81(5):769–780. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90538-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pesavento P. A., Stewart R. J., Goldstein L. S. Characterization of the KLP68D kinesin-like protein in Drosophila: possible roles in axonal transport. J Cell Biol. 1994 Nov;127(4):1041–1048. doi: 10.1083/jcb.127.4.1041. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rashid D. J., Wedaman K. P., Scholey J. M. Heterodimerization of the two motor subunits of the heterotrimeric kinesin, KRP85/95. J Mol Biol. 1995 Sep 15;252(2):157–162. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1995.0484. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robson B., Suzuki E. Conformational properties of amino acid residues in globular proteins. J Mol Biol. 1976 Nov 5;107(3):327–356. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(76)80008-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seals J. R., McDonald J. M., Bruns D., Jarett L. A sensitive and precise isotopic assay of ATPase activity. Anal Biochem. 1978 Oct 15;90(2):785–795. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(78)90169-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sekine Y., Okada Y., Noda Y., Kondo S., Aizawa H., Takemura R., Hirokawa N. A novel microtubule-based motor protein (KIF4) for organelle transports, whose expression is regulated developmentally. J Cell Biol. 1994 Oct;127(1):187–201. doi: 10.1083/jcb.127.1.187. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shakir M. A., Fukushige T., Yasuda H., Miwa J., Siddiqui S. S. C. elegans osm-3 gene mediating osmotic avoidance behaviour encodes a kinesin-like protein. Neuroreport. 1993 Jul;4(7):891–894. doi: 10.1097/00001756-199307000-00013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart R. J., Pesavento P. A., Woerpel D. N., Goldstein L. S. Identification and partial characterization of six members of the kinesin superfamily in Drosophila. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Oct 1;88(19):8470–8474. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.19.8470. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabish M., Siddiqui Z. K., Nishikawa K., Siddiqui S. S. Exclusive expression of C. elegans osm-3 kinesin gene in chemosensory neurons open to the external environment. J Mol Biol. 1995 Mar 31;247(3):377–389. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1994.0146. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takemura R., Nakata T., Okada Y., Yamazaki H., Zhang Z., Hirokawa N. mRNA expression of KIF1A, KIF1B, KIF2, KIF3A, KIF3B, KIF4, KIF5, and cytoplasmic dynein during axonal regeneration. J Neurosci. 1996 Jan;16(1):31–35. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.16-01-00031.1996. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vale R. D., Reese T. S., Sheetz M. P. Identification of a novel force-generating protein, kinesin, involved in microtubule-based motility. Cell. 1985 Aug;42(1):39–50. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80099-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vale R. D., Schnapp B. J., Reese T. S., Sheetz M. P. Organelle, bead, and microtubule translocations promoted by soluble factors from the squid giant axon. Cell. 1985 Mar;40(3):559–569. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90204-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walther Z., Vashishtha M., Hall J. L. The Chlamydomonas FLA10 gene encodes a novel kinesin-homologous protein. J Cell Biol. 1994 Jul;126(1):175–188. doi: 10.1083/jcb.126.1.175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wedaman K. P., Knight A. E., Kendrick-Jones J., Scholey J. M. Sequences of sea urchin kinesin light chain isoforms. J Mol Biol. 1993 May 5;231(1):155–158. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1993.1267. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wedaman K. P., Meyer D. W., Rashid D. J., Cole D. G., Scholey J. M. Sequence and submolecular localization of the 115-kD accessory subunit of the heterotrimeric kinesin-II (KRP85/95) complex. J Cell Biol. 1996 Feb;132(3):371–380. doi: 10.1083/jcb.132.3.371. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamazaki H., Nakata T., Okada Y., Hirokawa N. KIF3A/B: a heterodimeric kinesin superfamily protein that works as a microtubule plus end-directed motor for membrane organelle transport. J Cell Biol. 1995 Sep;130(6):1387–1399. doi: 10.1083/jcb.130.6.1387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]