Abstract
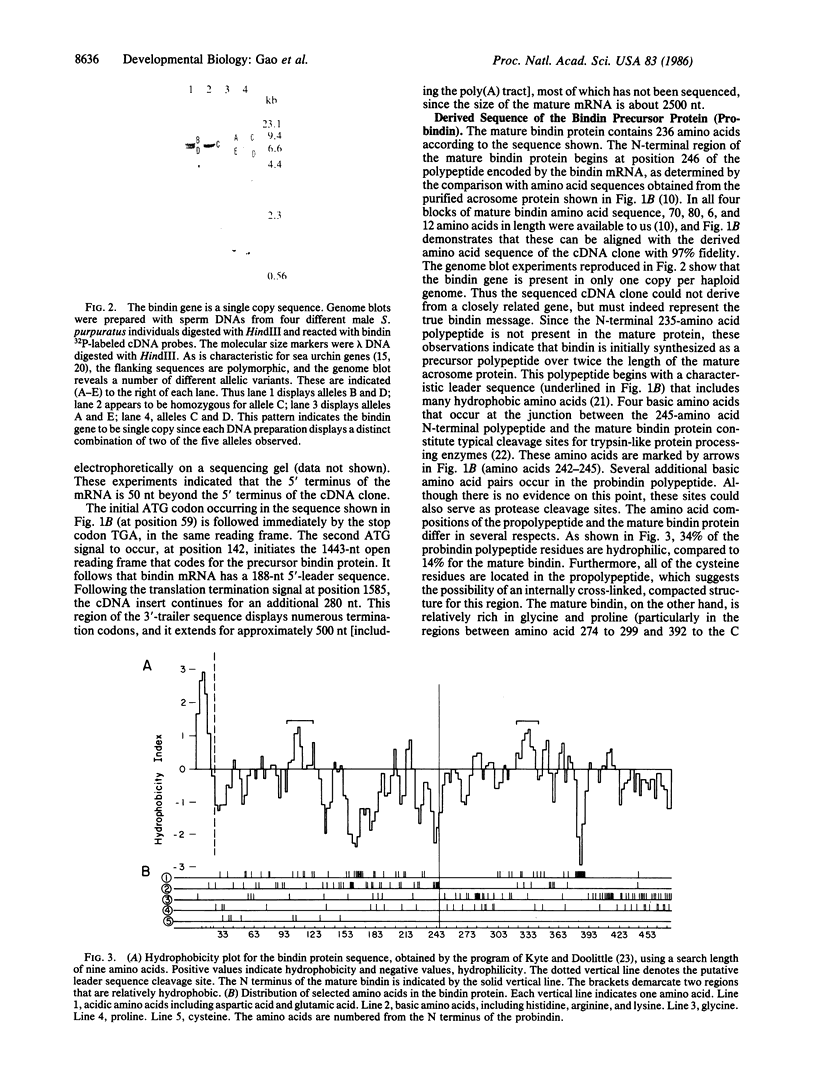
Bindin, a major protein of the sea urchin acrosome granule, mediates the species-specific adhesion and binding of sperm to egg required to effect fertilization. We report the isolation and sequence of bindin cDNA clones prepared from Strongylocentrotus purpuratus testis RNA. The bindin gene appears to be productively expressed only in males and only in testes. The protein is produced from a 51-kDa precursor, which is subsequently processed to yield the mature 24-kDa bindin protein.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BURGOS M. H., FAWCETT D. W. An electron microscope study of spermatid differentiation in the toad, Bufo arenarum Hensel. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1956 May 25;2(3):223–240. doi: 10.1083/jcb.2.3.223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BURGOS M. H., FAWCETT D. W. Studies on the fine structure of the mammalian testis. I. Differentiation of the spermatids in the cat (Felis domestica). J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1955 Jul 25;1(4):287–300. doi: 10.1083/jcb.1.4.287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrett D., Angelo G. M. Maternal characteristics of hatching enzymes in hybrid sea urchin embryos. Exp Cell Res. 1969 Oct;57(2):159–166. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(69)90137-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bornstein P. The biosynthesis of collagen. Annu Rev Biochem. 1974;43(0):567–603. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.43.070174.003031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Britten R. J., Cetta A., Davidson E. H. The single-copy DNA sequence polymorphism of the sea urchin Strongylocentrotus purpuratus. Cell. 1978 Dec;15(4):1175–1186. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90044-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Busslinger M., Barberis A. Synthesis of sperm and late histone cDNAs of the sea urchin with a primer complementary to the conserved 3' terminal palindrome: evidence for tissue-specific and more general histone gene variants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Sep;82(17):5676–5680. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.17.5676. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHAFFEE R. R., MAZIA D. Echinochrome synthesis in hybrid sea urchin embrovos. Dev Biol. 1963 Mar;6:502–512. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(63)90138-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chance R. E., Ellis R. M., Bromer W. W. Porcine proinsulin: characterization and amino acid sequence. Science. 1968 Jul 12;161(3837):165–167. doi: 10.1126/science.161.3837.165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conway A. F., Metz C. B. Phospholipase activity of sea urchin sperm: its possible involvement in membrane fusion. J Exp Zool. 1976 Oct;198(1):39–47. doi: 10.1002/jez.1401980106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Csernansky J. G., Zimmerman M., Troll W. An elastase-like enzyme in the oocytes of Arbacia Punctulata. Dev Biol. 1979 May;70(1):283–286. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(79)90027-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson E. H., Flytzanis C. N., Lee J. J., Robinson J. J., Rose S. J., 3rd, Sucov H. M. Lineage-specific gene expression in the sea urchin embryo. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1985;50:321–328. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1985.050.01.041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glabe C. G., Vacquier V. D. Species specific agglutination of eggs by bindin isolated from sea urchin sperm. Nature. 1977 Jun 30;267(5614):836–838. doi: 10.1038/267836a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henikoff S. Unidirectional digestion with exonuclease III creates targeted breakpoints for DNA sequencing. Gene. 1984 Jun;28(3):351–359. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90153-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kassell B., Kay J. Zymogens of proteolytic enzymes. Science. 1973 Jun 8;180(4090):1022–1027. doi: 10.1126/science.180.4090.1022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessler S. W. Rapid isolation of antigens from cells with a staphylococcal protein A-antibody adsorbent: parameters of the interaction of antibody-antigen complexes with protein A. J Immunol. 1975 Dec;115(6):1617–1624. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyte J., Doolittle R. F. A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J Mol Biol. 1982 May 5;157(1):105–132. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90515-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee J. J., Shott R. J., Rose S. J., 3rd, Thomas T. L., Britten R. J., Davidson E. H. Sea urchin actin gene subtypes. Gene number, linkage and evolution. J Mol Biol. 1984 Jan 15;172(2):149–176. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(84)80035-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine A. E., Walsh K. A., Fodor E. J. Evidence of an acrosin-like enzyme in sea urchin sperm. Dev Biol. 1978 Apr;63(2):299–306. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(78)90135-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J. New M13 vectors for cloning. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:20–78. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01005-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moy G. W., Vacquier V. D. Immunoperoxidase localization of bindin during the adhesion of sperm to sea urchin eggs. Curr Top Dev Biol. 1979;13(Pt 1):31–44. doi: 10.1016/s0070-2153(08)60688-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Podell S. B., Vacquier V. D. Purification of the Mr 80,000 and Mr 210,000 proteins of the sea urchin sperm plasma membrane. Evidence that the Mr 210,000 protein interacts with egg jelly. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 10;260(5):2715–2718. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Posakony J. W., Scheller R. H., Anderson D. M., Britten R. J., Davidson E. H. Repetitive sequences of the sea urchin genome. III. Nucleotide sequences of cloned repeat elements. J Mol Biol. 1981 Jun 15;149(1):41–67. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90259-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossignol D. P., Earles B. J., Decker G. L., Lennarz W. J. Characterization of the sperm receptor on the surface of eggs of Strongylocentrotus purpuratus. Dev Biol. 1984 Aug;104(2):308–321. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(84)90086-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SeGall G. K., Lennarz W. J. Chemical characterization of the component of the jelly coat from sea urchin eggs responsible for induction of the acrosome reaction. Dev Biol. 1979 Jul;71(1):33–48. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(79)90080-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shott R. J., Lee J. J., Britten R. J., Davidson E. H. Differential expression of the actin gene family of Strongylocentrotus purpuratus. Dev Biol. 1984 Feb;101(2):295–306. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(84)90143-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shyu A. B., Raff R. A., Blumenthal T. Expression of the vitellogenin gene in female and male sea urchin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(11):3865–3869. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.11.3865. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strickland M., Strickland W. N., Brandt W. F., Von Holt C. The complete amino-acid sequence of histone H2B(1) from sperm of the sea urchin Parechinus angulosus. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Jul 15;77(2):263–275. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11665.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strickland W. N., Strickland M., de Groot P. C., Von Holt C., Wittmann-Liebold B. The primary structure of histone H1 from sperm of the sea urchin Parechinus angulosus. 1. Chemical and enzymatic fragmentation of the protein and the sequence of amino acids in the four N-terminal cyanogen bromide peptides. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Mar;104(2):559–566. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb04459.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Summers R. G., Hylander B. L. Species-specificity of acrosome reaction and primary gamete binding in echinoids. Exp Cell Res. 1975 Nov;96(1):63–68. doi: 10.1016/s0014-4827(75)80037-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vacquier V. D., Moy G. W. Isolation of bindin: the protein responsible for adhesion of sperm to sea urchin eggs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jun;74(6):2456–2460. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.6.2456. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vacquier V. D. Purification of sea urchin sperm bindin by DEAE-cellulose chromatography. Anal Biochem. 1983 Mar;129(2):497–501. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90583-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Viebrock A., Perz A., Sebald W. The imported preprotein of the proteolipid subunit of the mitochondrial ATP synthase from Neurospora crassa. Molecular cloning and sequencing of the mRNA. EMBO J. 1982;1(5):565–571. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01209.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson M. E. Compilation of published signal sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jul 11;12(13):5145–5164. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.13.5145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]