Abstract
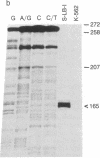
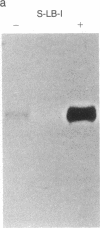
Colony-stimulating factors (CSFs) are glycoproteins that stimulate the growth of hematopoietic progenitors and enhance the functional activity of mature effector cells. Human granulocyte/macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF) is a 22-kDa glycoprotein that stimulates the growth of myeloid and erythroid progenitors in vitro and increases the responsiveness of neutrophils, monocytes, and eosinophils to physiologic stimuli. Elucidation of the cell and tissue sources of CSFs, as well as study of their regulation of expression, is required to understand their role in physiologic and pathophysiologic states. An extensive survey of normal and neoplastic human tissues did not reveal constitutive production of detectable levels of GM-CSF mRNA in any of the 64 samples studied. Antigen- or lectin-activated T lymphocytes have been shown to produce GM-CSF; therefore, to elucidate the genetic sequences required, we constructed recombinant plasmids containing 5' flanking DNA of the GM-CSF gene linked to the marker chloramphenicol acetyltransferase gene. The recombinant constructs were transfected into a human T-cell leukemia virus type I (HTLV)-infected T-lymphoblast cell line that can be stimulated to produce high levels of GM-CSF. We show here that the 5' flanking sequences of the GM-CSF gene can direct increased expression of the chloramphenicol acetyltransferase gene in activated T-lymphoblast cells.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berk A. J., Sharp P. A. Sizing and mapping of early adenovirus mRNAs by gel electrophoresis of S1 endonuclease-digested hybrids. Cell. 1977 Nov;12(3):721–732. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90272-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantrell M. A., Anderson D., Cerretti D. P., Price V., McKereghan K., Tushinski R. J., Mochizuki D. Y., Larsen A., Grabstein K., Gillis S. Cloning, sequence, and expression of a human granulocyte/macrophage colony-stimulating factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Sep;82(18):6250–6254. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.18.6250. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen I. S., Quan S. G., Golde D. W. Human T-cell leukemia virus type II transforms normal human lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Nov;80(22):7006–7009. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.22.7006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dexter T. M. Blood cell development. The message in the medium. 1984 Jun 28-Jul 4Nature. 309(5971):746–747. doi: 10.1038/309746a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dynan W. S., Tjian R. Control of eukaryotic messenger RNA synthesis by sequence-specific DNA-binding proteins. 1985 Aug 29-Sep 4Nature. 316(6031):774–778. doi: 10.1038/316774a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleischmann J., Golde D. W., Weisbart R. H., Gasson J. C. Granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor enhances phagocytosis of bacteria by human neutrophils. Blood. 1986 Sep;68(3):708–711. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gasson J. C., Weisbart R. H., Kaufman S. E., Clark S. C., Hewick R. M., Wong G. G., Golde D. W. Purified human granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor: direct action on neutrophils. Science. 1984 Dec 14;226(4680):1339–1342. doi: 10.1126/science.6390681. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gough N. M., Metcalf D., Gough J., Grail D., Dunn A. R. Structure and expression of the mRNA for murine granulocyte-macrophage colony stimulating factor. EMBO J. 1985 Mar;4(3):645–653. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03678.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hocking W., Goodman J., Golde D. Granulocytosis associated with tumor cell production of colony-stimulating activity. Blood. 1983 Mar;61(3):600–603. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huebner K., Isobe M., Croce C. M., Golde D. W., Kaufman S. E., Gasson J. C. The human gene encoding GM-CSF is at 5q21-q32, the chromosome region deleted in the 5q- anomaly. Science. 1985 Dec 13;230(4731):1282–1285. doi: 10.1126/science.2999978. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Beau M. M., Westbrook C. A., Diaz M. O., Larson R. A., Rowley J. D., Gasson J. C., Golde D. W., Sherr C. J. Evidence for the involvement of GM-CSF and FMS in the deletion (5q) in myeloid disorders. Science. 1986 Feb 28;231(4741):984–987. doi: 10.1126/science.3484837. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. A new method for sequencing DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):560–564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metcalf D., Begley C. G., Johnson G. R., Nicola N. A., Vadas M. A., Lopez A. F., Williamson D. J., Wong G. G., Clark S. C., Wang E. A. Biologic properties in vitro of a recombinant human granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor. Blood. 1986 Jan;67(1):37–45. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metcalf D. The granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factors. Science. 1985 Jul 5;229(4708):16–22. doi: 10.1126/science.2990035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyatake S., Otsuka T., Yokota T., Lee F., Arai K. Structure of the chromosomal gene for granulocyte-macrophage colony stimulating factor: comparison of the mouse and human genes. EMBO J. 1985 Oct;4(10):2561–2568. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03971.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munker R., Gasson J., Ogawa M., Koeffler H. P. Recombinant human TNF induces production of granulocyte-monocyte colony-stimulating factor. Nature. 1986 Sep 4;323(6083):79–82. doi: 10.1038/323079a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norrander J., Kempe T., Messing J. Construction of improved M13 vectors using oligodeoxynucleotide-directed mutagenesis. Gene. 1983 Dec;26(1):101–106. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90040-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato N., Asano S., Ueyama Y., Mori M., Okabe T., Kondo Y., Ohsawa N., Kosaka K. Granulocytosis and colony-stimulating activity (CSA) produced by a human squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer. 1979 Feb;43(2):605–610. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(197902)43:2<605::aid-cncr2820430230>3.0.co;2-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saxon A., Stevens R. H., Quan S. G., Golde D. W. Immunologic characterization of hairy cell leukemias in continuous culture. J Immunol. 1978 Mar;120(3):777–782. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sieff C. A., Emerson S. G., Donahue R. E., Nathan D. G., Wang E. A., Wong G. G., Clark S. C. Human recombinant granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor: a multilineage hematopoietin. Science. 1985 Dec 6;230(4730):1171–1173. doi: 10.1126/science.3877981. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slamon D. J., deKernion J. B., Verma I. M., Cline M. J. Expression of cellular oncogenes in human malignancies. Science. 1984 Apr 20;224(4646):256–262. doi: 10.1126/science.6538699. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanley E., Metcalf D., Sobieszczuk P., Gough N. M., Dunn A. R. The structure and expression of the murine gene encoding granulocyte-macrophage colony stimulating factor: evidence for utilisation of alternative promoters. EMBO J. 1985 Oct;4(10):2569–2573. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03972.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomonaga M., Golde D. W., Gasson J. C. Biosynthetic (recombinant) human granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor: effect on normal bone marrow and leukemia cell lines. Blood. 1986 Jan;67(1):31–36. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weaver R. F., Weissmann C. Mapping of RNA by a modification of the Berk-Sharp procedure: the 5' termini of 15 S beta-globin mRNA precursor and mature 10 s beta-globin mRNA have identical map coordinates. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 10;7(5):1175–1193. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.5.1175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisbart R. H., Golde D. W., Clark S. C., Wong G. G., Gasson J. C. Human granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor is a neutrophil activator. 1985 Mar 28-Apr 3Nature. 314(6009):361–363. doi: 10.1038/314361a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss A., Wiskocil R. L., Stobo J. D. The role of T3 surface molecules in the activation of human T cells: a two-stimulus requirement for IL 2 production reflects events occurring at a pre-translational level. J Immunol. 1984 Jul;133(1):123–128. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong G. G., Witek J. S., Temple P. A., Wilkens K. M., Leary A. C., Luxenberg D. P., Jones S. S., Brown E. L., Kay R. M., Orr E. C. Human GM-CSF: molecular cloning of the complementary DNA and purification of the natural and recombinant proteins. Science. 1985 May 17;228(4701):810–815. doi: 10.1126/science.3923623. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zucali J. R., Dinarello C. A., Oblon D. J., Gross M. A., Anderson L., Weiner R. S. Interleukin 1 stimulates fibroblasts to produce granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating activity and prostaglandin E2. J Clin Invest. 1986 Jun;77(6):1857–1863. doi: 10.1172/JCI112512. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]