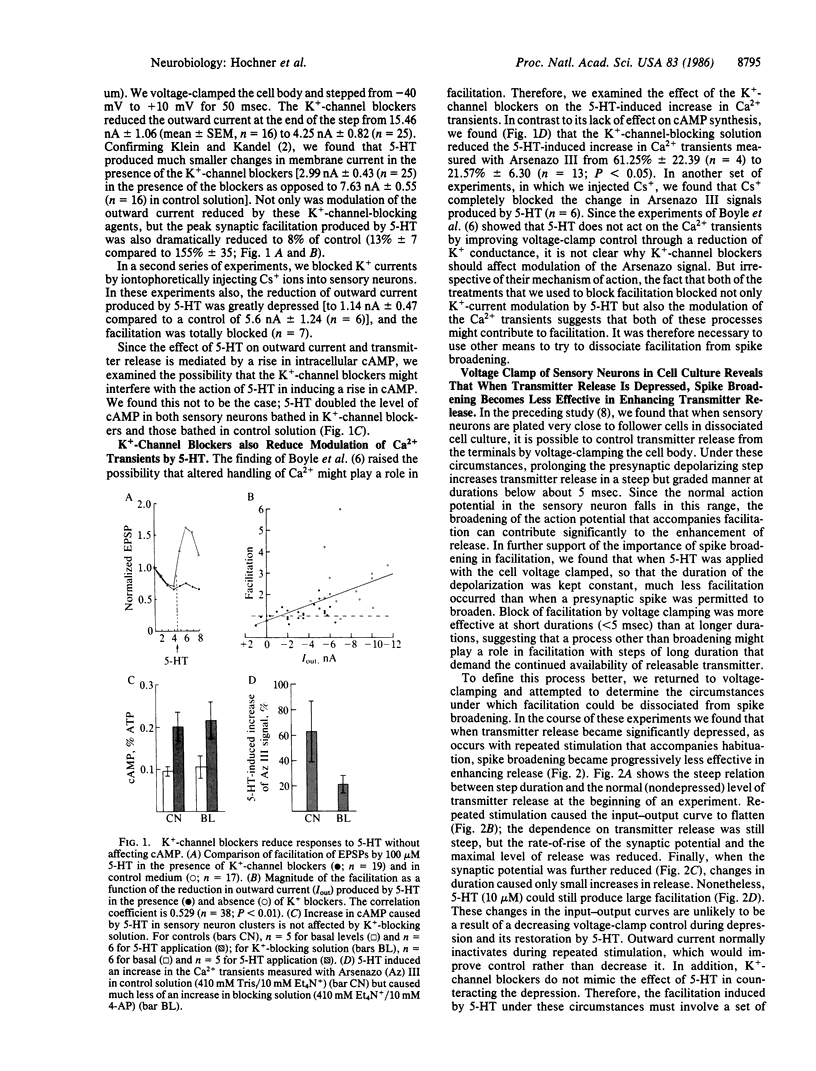
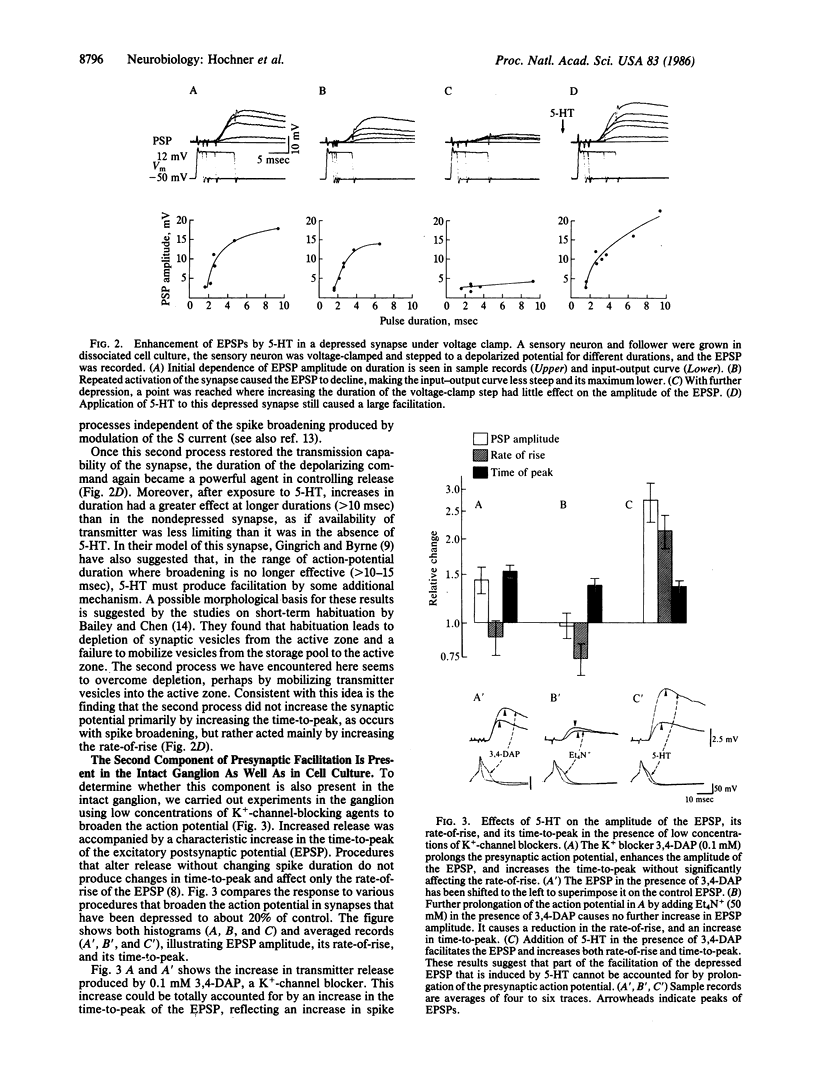
Abstract
Sensitization of defensive gill and siphon withdrawal reflexes in Aplysia results, in part, from presynaptic facilitation of transmitter release from mechanoreceptor sensory neurons that innervate the siphon skin and synapse with interneurons and motor neurons. Presynaptic facilitation also can be elicited by application of serotonin. This facilitation is associated with two phenomena, a prolongation of the presynaptic action potential resulting from a decrease in a specific K+ current and an enhancement of the Ca2+ transients elicited by depolarization. Previous work has shown that prolongation of the action potential enhances synaptic transmission at normal levels of release. Here we report that an additional set of processes also contributes to facilitation. When repeated activation of the sensory neurons induces profound homosynaptic depression, prolonging the duration of action potentials (or of depolarizing commands under voltage clamp) has little effect on transmitter release. Nonetheless, serotonin is still capable of enhancing release. Since homosynaptic depression underlies the behavioral process of habituation, the second set of processes, by counteracting the consequences of the depression, seems to mediate the effects of dishabituation in the sensory neuron. Prolongation of the action potential by closure of the K+ channel seems to mediate the effects of sensitization.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abrams T. W., Castellucci V. F., Camardo J. S., Kandel E. R., Lloyd P. E. Two endogenous neuropeptides modulate the gill and siphon withdrawal reflex in Aplysia by presynaptic facilitation involving cAMP-dependent closure of a serotonin-sensitive potassium channel. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(24):7956–7960. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.24.7956. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyle M. B., Klein M., Smith S. J., Kandel E. R. Serotonin increases intracellular Ca2+ transients in voltage-clamped sensory neurons of Aplysia californica. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(23):7642–7646. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.23.7642. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunelli M., Castellucci V., Kandel E. R. Synaptic facilitation and behavioral sensitization in Aplysia: possible role of serotonin and cyclic AMP. Science. 1976 Dec 10;194(4270):1178–1181. doi: 10.1126/science.186870. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carew T. J., Castellucci V. F., Kandel E. R. An analysis of dishabituation and sensitization of the gill-withdrawal reflex in Aplysia. Int J Neurosci. 1971 Aug;2(2):79–98. doi: 10.3109/00207457109146995. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castellucci V. F., Kandel E. R., Schwartz J. H., Wilson F. D., Nairn A. C., Greengard P. Intracellular injection of t he catalytic subunit of cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase simulates facilitation of transmitter release underlying behavioral sensitization in Aplysia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7492–7496. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7492. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castellucci V. F., Kandel E. R., Schwartz J. H., Wilson F. D., Nairn A. C., Greengard P. Intracellular injection of t he catalytic subunit of cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase simulates facilitation of transmitter release underlying behavioral sensitization in Aplysia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7492–7496. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7492. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castellucci V., Kandel E. R. Presynaptic facilitation as a mechanism for behavioral sensitization in Aplysia. Science. 1976 Dec 10;194(4270):1176–1178. doi: 10.1126/science.11560. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cedar H., Kandel E. R., Schwartz J. H. Cyclic adenosine monophosphate in the nervous system of Aplysia californica. I. Increased synthesis in response to synaptic stimulation. J Gen Physiol. 1972 Nov;60(5):558–569. doi: 10.1085/jgp.60.5.558. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cedar H., Schwartz J. H. Cyclic adenosine monophosphate in the nervous system of Aplysia californica. II. Effect of serotonin and dopamine. J Gen Physiol. 1972 Nov;60(5):570–587. doi: 10.1085/jgp.60.5.570. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gingrich K. J., Byrne J. H. Simulation of synaptic depression, posttetanic potentiation, and presynaptic facilitation of synaptic potentials from sensory neurons mediating gill-withdrawal reflex in Aplysia. J Neurophysiol. 1985 Mar;53(3):652–669. doi: 10.1152/jn.1985.53.3.652. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groves P. M., Thompson R. F. Habituation: a dual-process theory. Psychol Rev. 1970 Sep;77(5):419–450. doi: 10.1037/h0029810. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hochner B., Klein M., Schacher S., Kandel E. R. Action-potential duration and the modulation of transmitter release from the sensory neurons of Aplysia in presynaptic facilitation and behavioral sensitization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(21):8410–8414. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.21.8410. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JASPER H., SHARPLESS S. Habituation of the arousal reaction. Brain. 1956 Dec;79(4):655–680. doi: 10.1093/brain/79.4.655. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein M., Camardo J., Kandel E. R. Serotonin modulates a specific potassium current in the sensory neurons that show presynaptic facilitation in Aplysia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Sep;79(18):5713–5717. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.18.5713. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein M., Hochner B., Kandel E. R. Facilitatory transmitters and cAMP can modulate accommodation as well as transmitter release in Aplysia sensory neurons: Evidence for parallel processing in a single cell. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(20):7994–7998. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.20.7994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein M., Kandel E. R. Presynaptic modulation of voltage-dependent Ca2+ current: mechanism for behavioral sensitization in Aplysia californica. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jul;75(7):3512–3516. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.7.3512. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Llinás R., McGuinness T. L., Leonard C. S., Sugimori M., Greengard P. Intraterminal injection of synapsin I or calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II alters neurotransmitter release at the squid giant synapse. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(9):3035–3039. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.9.3035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollard H. B., Creutz C. E., Fowler V., Scott J., Pazoles C. J. Calcium-dependent regulation of chromaffin granule movement, membrane contact, and fusion during exocytosis. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1982;46(Pt 2):819–834. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1982.046.01.077. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schacher S., Proshansky E. Neurite regeneration by Aplysia neurons in dissociated cell culture: modulation by Aplysia hemolymph and the presence of the initial axonal segment. J Neurosci. 1983 Dec;3(12):2403–2413. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.03-12-02403.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shuster M. J., Camardo J. S., Siegelbaum S. A., Kandel E. R. Cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase closes the serotonin-sensitive K+ channels of Aplysia sensory neurones in cell-free membrane patches. 1985 Jan 31-Feb 6Nature. 313(6001):392–395. doi: 10.1038/313392a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegelbaum S. A., Camardo J. S., Kandel E. R. Serotonin and cyclic AMP close single K+ channels in Aplysia sensory neurones. Nature. 1982 Sep 30;299(5882):413–417. doi: 10.1038/299413a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spencer W. A., Thompson R. F., Neilson D. R., Jr Response decrement of the flexion reflex in the acute spinal cat and transient restoration by strong stimuli. J Neurophysiol. 1966 Mar;29(2):221–239. doi: 10.1152/jn.1966.29.2.221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zucker R. S. Tetraethylammonium contains an impurity which alkalizes cytoplasm and reduce calcium buffering in neurons. Brain Res. 1981 Mar 16;208(2):473–478. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(81)90580-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


