Abstract
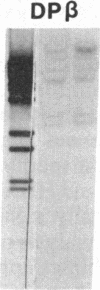
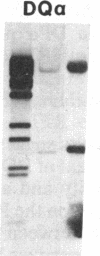
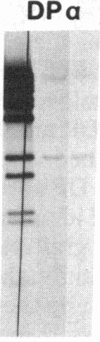
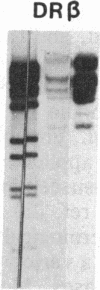
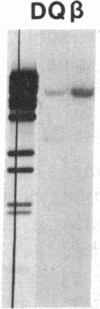
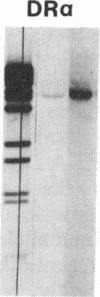
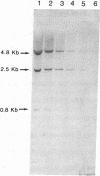
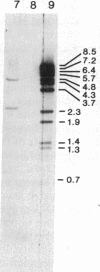
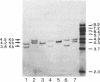
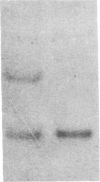
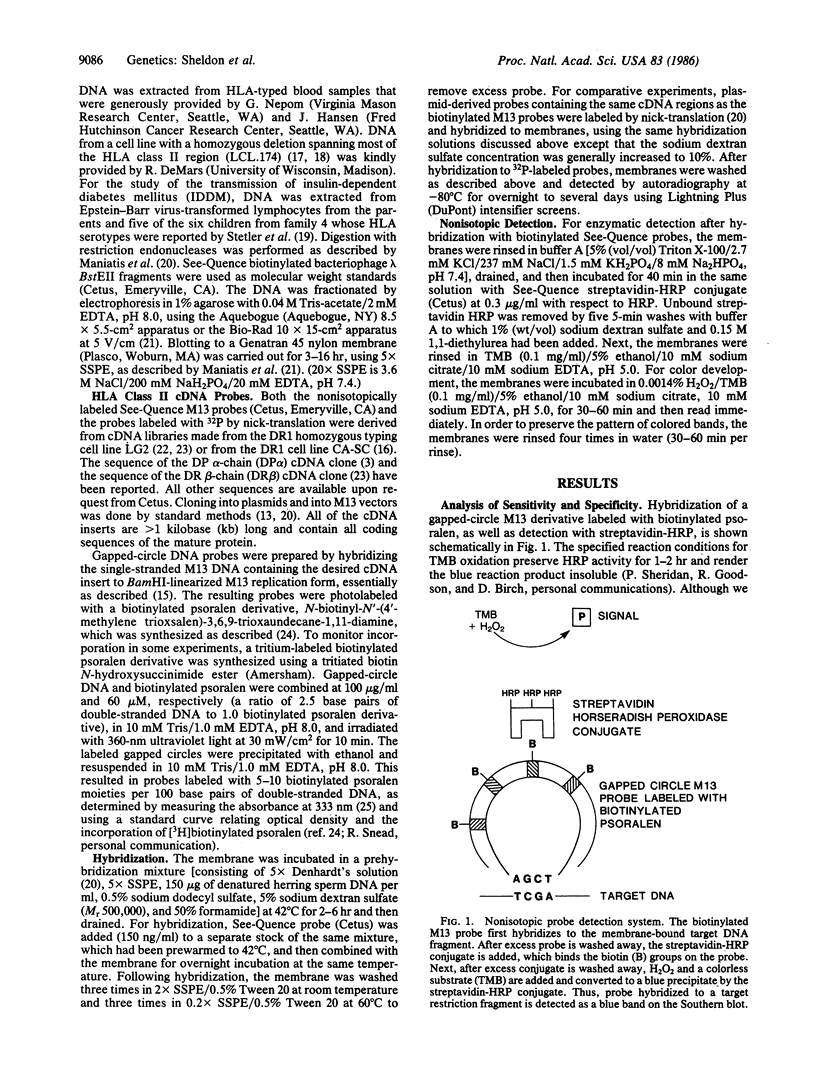
Previously, DNA polymorphisms in the HLA gene cluster have been analyzed using radioactive probes in Southern blot experiments; the restriction fragment length polymorphisms (RFLPs) revealed by this analysis are capable of subdividing HLA serological types. Here, we report the use of DNA probes labeled with biotinylated psoralen to provide nonisotopic detection of HLA class II RFLP patterns. These biotinylated probes contain cDNA sequences encoding the alpha and beta chains of DP, DQ, and DR HLA class II genes as inserts in M13 vectors. The recombinant M13 molecules are partially double-stranded with single-stranded HLA cDNA regions and contain biotinylated psoralen covalently linked to duplex DNA by UV irradiation. Following hybridization, the presence of biotinylated probe bound to target DNA is detected using a streptavidin-horseradish peroxidase conjugate, which converts the colorless substrate 3,3',5,5'-tetramethylbenzidine to a blue precipitate in less than 1 hr. The probe and detection system described here can detect single-copy genes in less than 0.5 microgram of total human DNA on Southern blots and generates the same specific RFLP patterns as do probes labeled with 32P by nick-translation. These biotinylated HLA class II probes have been applied to tissue typing for bone marrow transplantation and the study of insulin-dependent diabetes susceptibility, revealing in each case relevant polymorphisms not detected by serologic typing.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bell J. I., Estess P., St John T., Saiki R., Watling D. L., Erlich H. A., McDevitt H. O. DNA sequence and characterization of human class II major histocompatibility complex beta chains from the DR1 haplotype. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(10):3405–3409. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.10.3405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broker T. R., Angerer L. M., Yen P. H., Hershey N. D., Davidson N. Electron microscopic visualization of tRNA genes with ferritin-avidin: biotin labels. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Feb;5(2):363–384. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.2.363. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan V. T., Fleming K. A., McGee J. O. Detection of sub-picogram quantities of specific DNA sequences on blot hybridization with biotinylated probes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Nov 25;13(22):8083–8091. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.22.8083. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cimino G. D., Gamper H. B., Isaacs S. T., Hearst J. E. Psoralens as photoactive probes of nucleic acid structure and function: organic chemistry, photochemistry, and biochemistry. Annu Rev Biochem. 1985;54:1151–1193. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.54.070185.005443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen D., Paul P., Le Gall I., Marcadet A., Font M. P., Cohen-Haguenauer O., Sayagh B., Cann H., Lalouel J. M., Dausset J. DNA polymorphism of HLA class I and class II regions. Immunol Rev. 1985 Jul;85:87–105. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1985.tb01131.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courage-Tebbe U., Kemper B. Construction of gapped circular DNA from phage M13 by in vitro hybridization. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Apr 26;697(1):1–5. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(82)90037-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeMars R., Chang C. C., Shaw S., Reitnauer P. J., Sondel P. M. Homozygous deletions that simultaneously eliminate expressions of class I and class II antigens of EBV-transformed B-lymphoblastoid cells. I. Reduced proliferative responses of autologous and allogeneic T cells to mutant cells that have decreased expression of class II antigens. Hum Immunol. 1984 Oct;11(2):77–97. doi: 10.1016/0198-8859(84)90047-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erlich H., Lee J. S., Petersen J. W., Bugawan T., DeMars R. Molecular analysis of HLA class I and class II antigen loss mutants reveals a homozygous deletion of the DR, DQ, and part of the DP region: implications for class II gene order. Hum Immunol. 1986 Jun;16(2):205–219. doi: 10.1016/0198-8859(86)90049-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erlich H., Stetler D., Sheng-Dong R., Saiki R. Analysis by molecular cloning of the human class II genes. Fed Proc. 1984 Dec;43(15):3025–3030. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garbutt G. J., Wilson J. T., Schuster G. S., Leary J. J., Ward D. C. Use of biotinylated probes for detecting sickle cell anemia. Clin Chem. 1985 Jul;31(7):1203–1206. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garner R. C. Testing of some benzidine analogues for microsomal activation to bacterial mutagens. Cancer Lett. 1975 Sep;1(1):39–42. doi: 10.1016/s0304-3835(75)94960-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Josephy P. D., Eling T. E., Mason R. P. Co-oxidation of benzidine by prostaglandin synthase and comparison with the action of horseradish peroxidase. J Biol Chem. 1983 May 10;258(9):5561–5569. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kan Y. W., Dozy A. M. Polymorphism of DNA sequence adjacent to human beta-globin structural gene: relationship to sickle mutation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Nov;75(11):5631–5635. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.11.5631. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langer P. R., Waldrop A. A., Ward D. C. Enzymatic synthesis of biotin-labeled polynucleotides: novel nucleic acid affinity probes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Nov;78(11):6633–6637. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.11.6633. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Law D. J., Frossard P. M., Rucknagel D. L. Highly sensitive and rapid gene mapping using miniaturized blot hybridization: application to prenatal diagnosis. Gene. 1984 May;28(2):153–158. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90252-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leary J. J., Brigati D. J., Ward D. C. Rapid and sensitive colorimetric method for visualizing biotin-labeled DNA probes hybridized to DNA or RNA immobilized on nitrocellulose: Bio-blots. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(13):4045–4049. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.13.4045. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manning J. E., Hershey N. D., Broker T. R., Pellegrini M., Mitchell H. K., Davidson N. A new method of in situ hybridization. Chromosoma. 1975 Nov 24;53(2):107–117. doi: 10.1007/BF00333039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcadet A., Cohen D., Dausset J., Fischer A., Durandy A., Griscelli C. Genotyping with DNA probes in combined immunodeficiency syndrome with defective expression of HLA. N Engl J Med. 1985 May 16;312(20):1287–1292. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198505163122004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J. New M13 vectors for cloning. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:20–78. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01005-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moseley S. L., Huq I., Alim A. R., So M., Samadpour-Motalebi M., Falkow S. Detection of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli by DNA colony hybridization. J Infect Dis. 1980 Dec;142(6):892–898. doi: 10.1093/infdis/142.6.892. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryder L. P., Svejgaard A., Dausset J. Genetics of HLA disease association. Annu Rev Genet. 1981;15:169–187. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.15.120181.001125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sodja A., Davidson N. Gene mapping and gene enrichment by the avidin-biotin interaction: use of cytochrome-c as a polyamine bridge. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Feb;5(2):385–401. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.2.385. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stetler D., Das H., Nunberg J. H., Saiki R., Sheng-Dong R., Mullis K. B., Weissman S. M., Erlich H. A. Isolation of a cDNA clone for the human HLA-DR antigen alpha chain by using a synthetic oligonucleotide as a hybridization probe. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Oct;79(19):5966–5970. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.19.5966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stetler D., Grumet F. C., Erlich H. A. Polymorphic restriction endonuclease sites linked to the HLA-DR alpha gene: localization and use as genetic markers of insulin-dependent diabetes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(23):8100–8104. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.23.8100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trowsdale J., Young J. A., Kelly A. P., Austin P. J., Carson S., Meunier H., So A., Erlich H. A., Spielman R. S., Bodmer J. Structure, sequence and polymorphism in the HLA-D region. Immunol Rev. 1985 Jul;85:5–43. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1985.tb01129.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]