Abstract
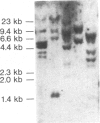
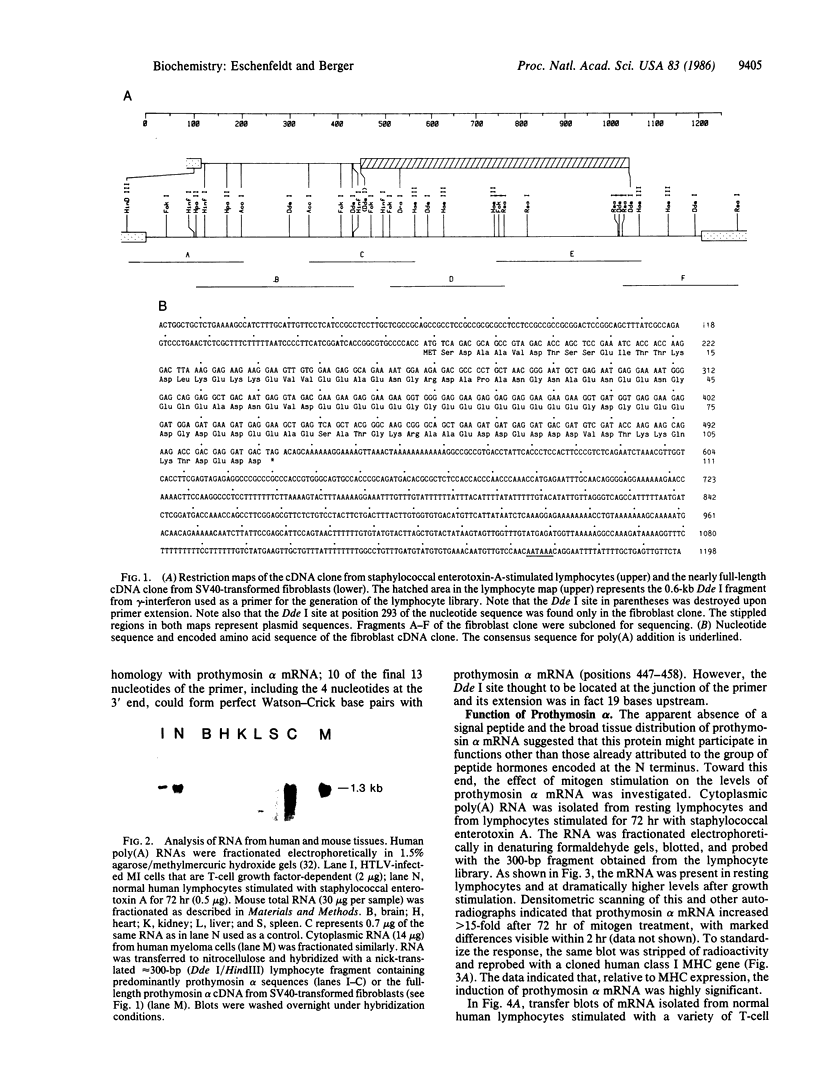
Clones for human prothymosin alpha have been identified in cDNA libraries from staphylococcal enterotoxin A-stimulated normal human lymphocytes and from simian virus 40-transformed fibroblasts. The 1198-base-pair fibroblast clone has been sequenced. The encoded protein is highly acidic (54 residues out of 111) and shares greater than 90% sequence homology with rat prothymosin alpha. The peptide "hormone" thymosin alpha 1 appears at positions 2-29 of the prothymosin alpha amino acid sequence. There is no N-terminal signal peptide. Examination of mouse and human tissues revealed the presence of prothymosin alpha mRNA in kidney, liver, spleen, normal lymphocytes (predominantly T cells), human T-cell leukemia virus-infected T cells, and myeloma cells (B-cell lineage). Prothymosin alpha mRNA is inducible; upon mitogen stimulation it increased greater than 15-fold above the level found in resting lymphocytes. Similarly, serum-deprived NIH 3T3 cells responded to serum restitution with an increase in prothymosin alpha mRNA. Characterization of human genomic DNA by Southern blot analysis disclosed a complicated pattern consistent with genetic polymorphism. These data suggest that prothymosin alpha plays an intracellular role tied to cell proliferation. There is no evidence that it serves as a precursor for secreted thymic peptides. However, given the complexity at the genomic level, multiple functions, including a putative secretory capability, cannot be excluded.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arya S. K., Wong-Staal F., Gallo R. C. T-cell growth factor gene: lack of expression in human T-cell leukemia-lymphoma virus-infected cells. Science. 1984 Mar 9;223(4640):1086–1087. doi: 10.1126/science.6320374. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bailey J. M., Davidson N. Methylmercury as a reversible denaturing agent for agarose gel electrophoresis. Anal Biochem. 1976 Jan;70(1):75–85. doi: 10.1016/s0003-2697(76)80049-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berger S. L., Wallace D. M., Siegal G. P., Hitchcock M. J., Birkenmeier C. S., Reber S. B. Preparation of interferon messenger RNAs with the use of ribonucleoside--vanadyl complexes. Methods Enzymol. 1981;79(Pt B):59–68. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(81)79013-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bistoni F., Marconi P., Frati L., Bonmassar E., Garaci E. Increase of mouse resistance to Candida albicans infection by thymosin alpha 1. Infect Immun. 1982 May;36(2):609–614. doi: 10.1128/iai.36.2.609-614.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caldarella J., Goodall G. J., Felix A. M., Heimer E. P., Salvin S. B., Horecker B. L. Thymosin alpha 11: a peptide related to thymosin alpha 1 isolated from calf thymosin fraction 5. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Dec;80(24):7424–7427. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.24.7424. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campisi J., Gray H. E., Pardee A. B., Dean M., Sonenshein G. E. Cell-cycle control of c-myc but not c-ras expression is lost following chemical transformation. Cell. 1984 Feb;36(2):241–247. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90217-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland D. W., Lopata M. A., MacDonald R. J., Cowan N. J., Rutter W. J., Kirschner M. W. Number and evolutionary conservation of alpha- and beta-tubulin and cytoplasmic beta- and gamma-actin genes using specific cloned cDNA probes. Cell. 1980 May;20(1):95–105. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90238-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douglass J., Civelli O., Herbert E. Polyprotein gene expression: generation of diversity of neuroendocrine peptides. Annu Rev Biochem. 1984;53:665–715. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.53.070184.003313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freire M., Rey-Mendez M., Gomez-Marquez J., Arias P. Evidence for the synthesis of thymosin alpha 1 by calf thymocytes and the production of this peptide by natural processing. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1985 Jun;239(2):480–485. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(85)90715-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein A. L., Guha A., Zatz M. M., Hardy M. A., White A. Purification and biological activity of thymosin, a hormone of the thymus gland. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jul;69(7):1800–1803. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.7.1800. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein A. L., Low T. L., McAdoo M., McClure J., Thurman G. B., Rossio J., Lai C. Y., Chang D., Wang S. S., Harvey C. Thymosin alpha1: isolation and sequence analysis of an immunologically active thymic polypeptide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):725–729. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein A. L., Low T. L., Thurman G. B., Zatz M. M., Hall N., Chen J., Hu S. K., Naylor P. B., McClure J. E. Current status of thymosin and other hormones of the thymus gland. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1981;37:369–415. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-571137-1.50012-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray P. W., Leung D. W., Pennica D., Yelverton E., Najarian R., Simonsen C. C., Derynck R., Sherwood P. J., Wallace D. M., Berger S. L. Expression of human immune interferon cDNA in E. coli and monkey cells. Nature. 1982 Feb 11;295(5849):503–508. doi: 10.1038/295503a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gubler U., Hoffman B. J. A simple and very efficient method for generating cDNA libraries. Gene. 1983 Nov;25(2-3):263–269. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90230-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haritos A. A., Blacher R., Stein S., Caldarella J., Horecker B. L. Primary structure of rat thymus prothymosin alpha. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):343–346. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.343. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haritos A. A., Tsolas O., Horecker B. L. Distribution of prothymosin alpha in rat tissues. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Mar;81(5):1391–1393. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.5.1391. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hooper J. A., McDaniel M. C., Thurman G. B., Cohen G. H., Schulof R. S., Goldstein A. L. Purification and properties of bovine thymosin. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1975 Feb 28;249:125–144. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1975.tb29063.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishitsuka H., Umeda Y., Nakamura J., Yagi Y. Protective activity of thymosin against opportunistic infections in animal models. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 1983;14(3):145–150. doi: 10.1007/BF00205352. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrach H., Diamond D., Wozney J. M., Boedtker H. RNA molecular weight determinations by gel electrophoresis under denaturing conditions, a critical reexamination. Biochemistry. 1977 Oct 18;16(21):4743–4751. doi: 10.1021/bi00640a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipson S. D., Chretien P. B., Makuch R., Kenady D. E., Cohen M. H. Thymosin immunotherapy in patients with small cell carcinoma of the lung: correlation of in vitro studies with clinical course. Cancer. 1979 Mar;43(3):863–870. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(197903)43:3<863::aid-cncr2820430313>3.0.co;2-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Low T. L., Thurman G. B., Chincarini C., McClure J. E., Marshall G. D., Hu S. K., Goldstein A. L. Current status of thymosin research: evidence for the existence of a family of thymic factors that control T-cell maturation. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1979;332:33–48. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1979.tb47095.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meinkoth J., Wahl G. Hybridization of nucleic acids immobilized on solid supports. Anal Biochem. 1984 May 1;138(2):267–284. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90808-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naylor P. H., Schulof R. S., Sztein M. B., Spira T. J., McCurdy P. R., Darr F., Kessler C. M., Simon G. L., Goldstein A. L. Thymosin in the early diagnosis and treatment of high risk homosexuals and hemophiliacs with AIDS-like immune dysfunction. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1984;437:88–99. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1984.tb37125.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okayama H., Berg P. A cDNA cloning vector that permits expression of cDNA inserts in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Feb;3(2):280–289. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.2.280. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payvar F., Schimke R. T. Methylmercury hydroxide enhancement of translation and transcription of ovalbumin and conalbumin mRNA's. J Biol Chem. 1979 Aug 25;254(16):7636–7642. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salvin S. B., Neta R. Resistance and susceptibility to infection in inbred murine strains. I. Variations in the response to thymic hormones in mice infected with Candida albicans. Cell Immunol. 1983 Jan;75(1):160–172. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(83)90315-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarin P. S., Sun D. K., Thornton A. H., Naylor P. H., Goldstein A. L. Neutralization of HTLV-III/LAV replication by antiserum to thymosin alpha 1. Science. 1986 May 30;232(4754):1135–1137. doi: 10.1126/science.3010464. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulof R. S. Thymic peptide hormones: basic properties and clinical applications in cancer. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 1985;3(4):309–376. doi: 10.1016/s1040-8428(85)80035-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sood A. K., Pereira D., Weissman S. M. Isolation and partial nucleotide sequence of a cDNA clone for human histocompatibility antigen HLA-B by use of an oligodeoxynucleotide primer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jan;78(1):616–620. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.1.616. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5201–5205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wara D. W., Barrett D. J., Ammann A. J., Cowan M. J. In vitro and in vivo enhancement of mixed lymphocyte culture reactivity by thymosin in patients with primary immunodeficiency disease. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1979;332:128–134. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1979.tb47106.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson M. E. Compilation of published signal sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jul 11;12(13):5145–5164. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.13.5145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]