Abstract
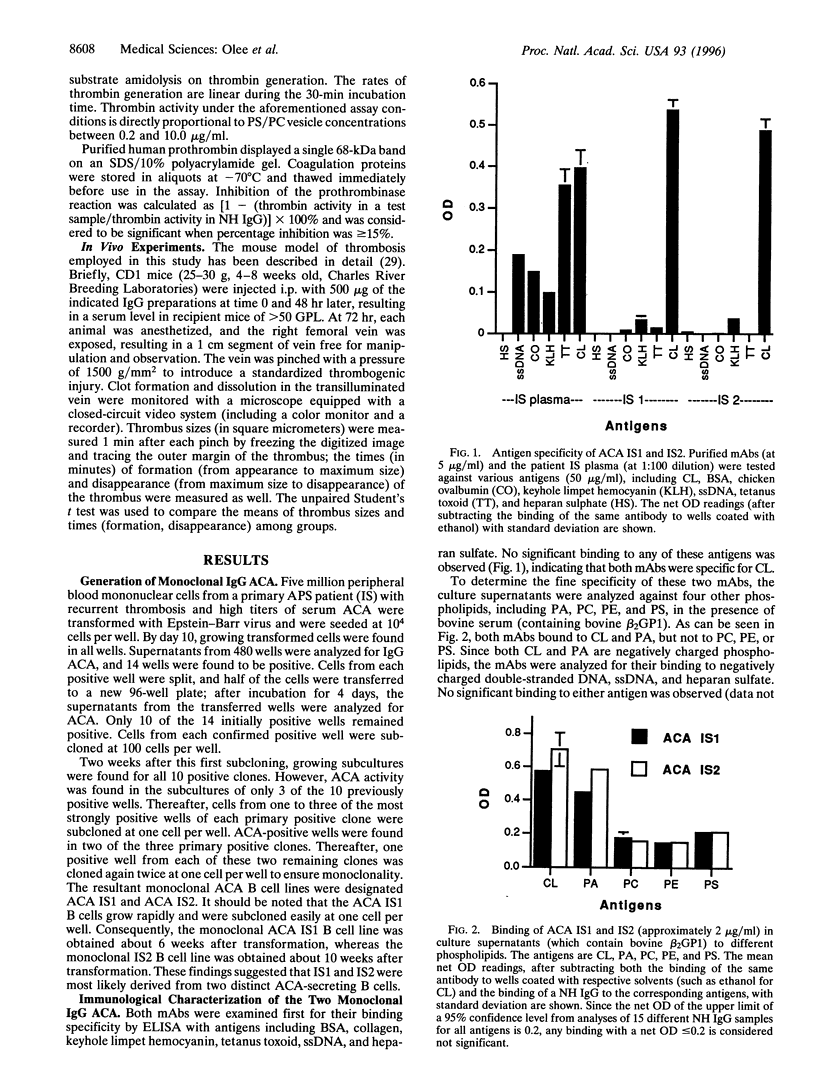
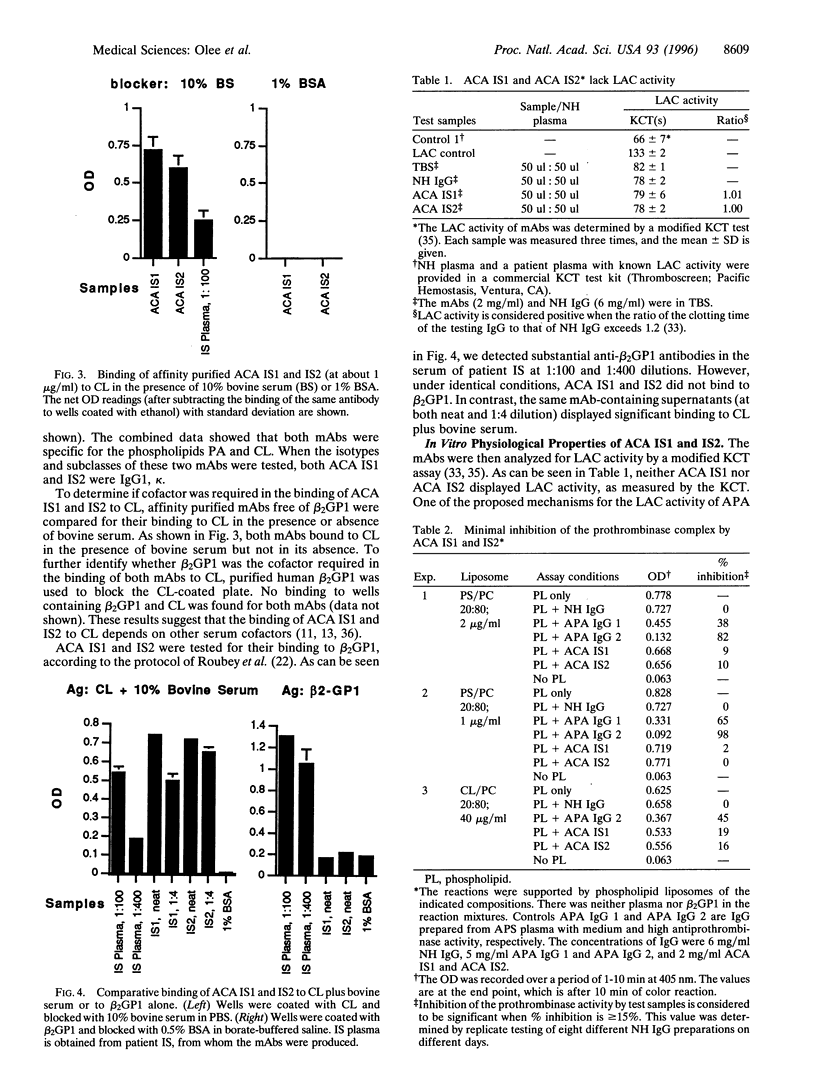
Antiphospholipid antibodies, including anticardiolipin antibodies (ACA), are strongly associated with recurrent thrombosis in patients with the antiphospholipid syndrome (APS). To date, reports about the binding specificities of ACA and their role(s) in causing and/or sustaining thrombosis in APS are conflicting and controversial. The plasmas of patients with APS, usually containing a mixture of autoantibodies, vary in binding specificity for different phospholipids/cofactors and vary in in vitro lupus anticoagulant activity. Although in vivo assays that allow assessment of the pathogenic procoagulant activity of patient autoantibodies have recently been developed, the complex nature of the mixed species prevented determination of the particular species responsible for in vivo thrombosis. We have generated two human IgG monoclonal ACA from an APS patient with recurrent thrombosis. Both bound to cardiolipin in the presence of 10% bovine serum, but not in its absence, and both were reactive against phosphatidic acid, but were nonreactive against purified human beta-2 glycoprotein 1, DNA, heparan sulfate, or four other test antigens. Both monoclonal autoantibodies lacked lupus anticoagulant activity and did not inhibit prothrombinase activity. Remarkably, one of the monoclonal antibodies has thrombogenic properties when tested in an in vivo mouse model. This finding provides the first direct evidence that a particular antiphospholipid antibody specificity may contribute to in vivo thrombosis.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arvieux J., Pouzol P., Roussel B., Jacob M. C., Colomb M. G. Lupus-like anticoagulant properties of murine monoclonal antibodies to beta 2-glycoprotein I. Br J Haematol. 1992 Aug;81(4):568–573. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1992.tb02993.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bakimer R., Fishman P., Blank M., Sredni B., Djaldetti M., Shoenfeld Y. Induction of primary antiphospholipid syndrome in mice by immunization with a human monoclonal anticardiolipin antibody (H-3). J Clin Invest. 1992 May;89(5):1558–1563. doi: 10.1172/JCI115749. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blank M., Cohen J., Toder V., Shoenfeld Y. Induction of anti-phospholipid syndrome in naive mice with mouse lupus monoclonal and human polyclonal anti-cardiolipin antibodies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Apr 15;88(8):3069–3073. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.8.3069. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bona C. A. Postulates defining pathogenic autoantibodies and T cells. Autoimmunity. 1991;10(3):169–172. doi: 10.3109/08916939109001886. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandt J. T., Triplett D. A., Alving B., Scharrer I. Criteria for the diagnosis of lupus anticoagulants: an update. On behalf of the Subcommittee on Lupus Anticoagulant/Antiphospholipid Antibody of the Scientific and Standardisation Committee of the ISTH. Thromb Haemost. 1995 Oct;74(4):1185–1190. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell A. L., Pierangeli S. S., Wellhausen S., Harris E. N. Comparison of the effects of anticardiolipin antibodies from patients with the antiphospholipid syndrome and with syphilis on platelet activation and aggregation. Thromb Haemost. 1995 Mar;73(3):529–534. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chamley L. W., McKay E. J., Pattison N. S. Inhibition of heparin/antithrombin III cofactor activity by anticardiolipin antibodies: a mechanism for thrombosis. Thromb Res. 1993 Jul 15;71(2):103–111. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(93)90176-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dizon-Townson D., Hutchison C., Silver R., Branch D. W., Ward K. The factor V Leiden mutation which predisposes to thrombosis is not common in patients with antiphospholipid syndrome. Thromb Haemost. 1995 Oct;74(4):1029–1031. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eilat D., Zlotnick A. Y., Fischel R. Evaluation of the cross-reaction between anti-DNA and anti-cardiolipin antibodies in SLE and experimental animals. Clin Exp Immunol. 1986 Aug;65(2):269–278. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Exner T., Rickard K. A., Kronenberg H. A sensitive test demonstrating lupus anticoagulant and its behavioural patterns. Br J Haematol. 1978 Sep;40(1):143–151. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1978.tb03648.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faaber P., Rijke T. P., van de Putte L. B., Capel P. J., Berden J. H. Cross-reactivity of human and murine anti-DNA antibodies with heparan sulfate. The major glycosaminoglycan in glomerular basement membranes. J Clin Invest. 1986 Jun;77(6):1824–1830. doi: 10.1172/JCI112508. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galli M., Comfurius P., Barbui T., Zwaal R. F., Bevers E. M. Anticoagulant activity of beta 2-glycoprotein I is potentiated by a distinct subgroup of anticardiolipin antibodies. Thromb Haemost. 1992 Sep 7;68(3):297–300. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galli M., Comfurius P., Maassen C., Hemker H. C., de Baets M. H., van Breda-Vriesman P. J., Barbui T., Zwaal R. F., Bevers E. M. Anticardiolipin antibodies (ACA) directed not to cardiolipin but to a plasma protein cofactor. Lancet. 1990 Jun 30;335(8705):1544–1547. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)91374-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galli M., Cortelazzo S., Viero P., Finazzi G., de Gaetano G., Barbui T. Interaction between platelets and lupus anticoagulant. Eur J Haematol. 1988 Jul;41(1):88–94. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0609.1988.tb00874.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gharavi A. E., Harris E. N., Sammaritano L. R., Pierangeli S. S., Wen J. Do patients with antiphospholipid syndrome have autoantibodies to beta 2-glycoprotein I? J Lab Clin Med. 1993 Oct;122(4):426–431. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris E. N., Gharavi A. E., Boey M. L., Patel B. M., Mackworth-Young C. G., Loizou S., Hughes G. R. Anticardiolipin antibodies: detection by radioimmunoassay and association with thrombosis in systemic lupus erythematosus. Lancet. 1983 Nov 26;2(8361):1211–1214. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)91267-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris E. N., Gharavi A. E., Tincani A., Chan J. K., Englert H., Mantelli P., Allegro F., Ballestrieri G., Hughes G. R. Affinity purified anti-cardiolipin and anti-DNA antibodies. J Clin Lab Immunol. 1985 Aug;17(4):155–162. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris E. N., Pierangeli S. S. Antiphospholipid antibodies and the antiphospholipid syndrome. Springer Semin Immunopathol. 1994;16(2-3):223–245. doi: 10.1007/BF00197519. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris E. N., Pierangeli S., Birch D. Anticardiolipin wet workshop report. Fifth International Symposium on antiphospholipid antibodies. Am J Clin Pathol. 1994 May;101(5):616–624. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/101.5.616. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hasegawa I., Suzuki T., Ishii S., Takakuwa K., Tanaka K. Establishment of two distinct anti-cardiolipin antibody-producing cell lines from the same individual by Epstein-Barr virus transformation. Thromb Res. 1994 Apr 1;74(1):77–84. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(94)90037-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hasselaar P., Derksen R. H., Blokzijl L., de Groot P. G. Crossreactivity of antibodies directed against cardiolipin, DNA, endothelial cells and blood platelets. Thromb Haemost. 1990 Apr 12;63(2):169–173. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang D. F., Olee T., Masuho Y., Matsumoto Y., Carson D. A., Chen P. P. Sequence analyses of three immunoglobulin G anti-virus antibodies reveal their utilization of autoantibody-related immunoglobulin Vh genes, but not V lambda genes. J Clin Invest. 1992 Dec;90(6):2197–2208. doi: 10.1172/JCI116105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes G. R. The antiphospholipid syndrome: ten years on. Lancet. 1993 Aug 7;342(8867):341–344. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(93)91477-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ichikawa K., Khamashta M. A., Koike T., Matsuura E., Hughes G. R. beta 2-Glycoprotein I reactivity of monoclonal anticardiolipin antibodies from patients with the antiphospholipid syndrome. Arthritis Rheum. 1994 Oct;37(10):1453–1461. doi: 10.1002/art.1780371008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones J. V., James H., Tan M. H., Mansour M. Antiphospholipid antibodies require beta 2-glycoprotein I (apolipoprotein H) as cofactor. J Rheumatol. 1992 Sep;19(9):1397–1402. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keeling D. M., Wilson A. J., Mackie I. J., Machin S. J., Isenberg D. A. Some 'antiphospholipid antibodies' bind to beta 2-glycoprotein I in the absence of phospholipid. Br J Haematol. 1992 Nov;82(3):571–574. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1992.tb06469.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lockshin M. D., Letendre C. H. Antiphospholipid antibody/lupus anticoagulant workshop. Arthritis Rheum. 1992 Oct;35(10):1234–1237. doi: 10.1002/art.1780351017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackworth-Young C. Antiphospholipid antibodies: more than just a disease marker? Immunol Today. 1990 Feb;11(2):60–65. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(90)90020-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malia R. G., Kitchen S., Greaves M., Preston F. E. Inhibition of activated protein C and its cofactor protein S by antiphospholipid antibodies. Br J Haematol. 1990 Sep;76(1):101–107. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1990.tb07843.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marciniak E., Romond E. H. Impaired catalytic function of activated protein C: a new in vitro manifestation of lupus anticoagulant. Blood. 1989 Nov 15;74(7):2426–2432. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuura E., Igarashi Y., Fujimoto M., Ichikawa K., Koike T. Anticardiolipin cofactor(s) and differential diagnosis of autoimmune disease. Lancet. 1990 Jul 21;336(8708):177–178. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)91697-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuura E., Igarashi Y., Yasuda T., Triplett D. A., Koike T. Anticardiolipin antibodies recognize beta 2-glycoprotein I structure altered by interacting with an oxygen modified solid phase surface. J Exp Med. 1994 Feb 1;179(2):457–462. doi: 10.1084/jem.179.2.457. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNeil H. P., Hunt J. E., Krilis S. A. Antiphospholipid antibodies--new insights into their specificity and clinical importance. Scand J Immunol. 1992 Nov;36(5):647–652. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1992.tb03124.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNeil H. P., Simpson R. J., Chesterman C. N., Krilis S. A. Anti-phospholipid antibodies are directed against a complex antigen that includes a lipid-binding inhibitor of coagulation: beta 2-glycoprotein I (apolipoprotein H). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jun;87(11):4120–4124. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.11.4120. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oosting J. D., Derksen R. H., Bobbink I. W., Hackeng T. M., Bouma B. N., de Groot P. G. Antiphospholipid antibodies directed against a combination of phospholipids with prothrombin, protein C, or protein S: an explanation for their pathogenic mechanism? Blood. 1993 May 15;81(10):2618–2625. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oosting J. D., Derksen R. H., Entjes H. T., Bouma B. N., de Groot P. G. Lupus anticoagulant activity is frequently dependent on the presence of beta 2-glycoprotein I. Thromb Haemost. 1992 May 4;67(5):499–502. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierangeli S. S., Barker J. H., Stikovac D., Ackerman D., Anderson G., Barquinero J., Acland R., Harris E. N. Effect of human IgG antiphospholipid antibodies on an in vivo thrombosis model in mice. Thromb Haemost. 1994 May;71(5):670–674. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierangeli S. S., Goldsmith G. H., Krnic S., Harris E. N. Differences in functional activity of anticardiolipin antibodies from patients with syphilis and those with antiphospholipid syndrome. Infect Immun. 1994 Sep;62(9):4081–4084. doi: 10.1128/iai.62.9.4081-4084.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierangeli S. S., Harris E. N., Davis S. A., DeLorenzo G. Beta 2-glycoprotein 1 (beta 2GP1) enhances cardiolipin binding activity but is not the antigen for antiphospholipid antibodies. Br J Haematol. 1992 Nov;82(3):565–570. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1992.tb06468.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierangeli S. S., Harris E. N., Gharavi A. E., Goldsmith G., Branch D. W., Dean W. L. Are immunoglobulins with lupus anticoagulant activity specific for phospholipids? Br J Haematol. 1993 Sep;85(1):124–132. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1993.tb08655.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierangeli S. S., Liu X. W., Barker J. H., Anderson G., Harris E. N. Induction of thrombosis in a mouse model by IgG, IgM and IgA immunoglobulins from patients with the antiphospholipid syndrome. Thromb Haemost. 1995 Nov;74(5):1361–1367. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roubey R. A. Antigenic specificities of "antiphospholipid" autoantibodies. Springer Semin Immunopathol. 1994;16(2-3):211–222. doi: 10.1007/BF00197518. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roubey R. A. Autoantibodies to phospholipid-binding plasma proteins: a new view of lupus anticoagulants and other "antiphospholipid" autoantibodies. Blood. 1994 Nov 1;84(9):2854–2867. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roubey R. A., Eisenberg R. A., Harper M. F., Winfield J. B. "Anticardiolipin" autoantibodies recognize beta 2-glycoprotein I in the absence of phospholipid. Importance of Ag density and bivalent binding. J Immunol. 1995 Jan 15;154(2):954–960. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sammaritano L. R., Lockshin M. D., Gharavi A. E. Antiphospholipid antibodies differ in aPL cofactor requirement. Lupus. 1992 Feb;1(2):83–90. doi: 10.1177/096120339200100205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santoro S. A. Antiphospholipid antibodies and thrombotic predisposition: underlying pathogenetic mechanisms. Blood. 1994 May 1;83(9):2389–2391. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schousboe I. beta 2-Glycoprotein I: a plasma inhibitor of the contact activation of the intrinsic blood coagulation pathway. Blood. 1985 Nov;66(5):1086–1091. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shi W., Chong B. H., Hogg P. J., Chesterman C. N. Anticardiolipin antibodies block the inhibition by beta 2-glycoprotein I of the factor Xa generating activity of platelets. Thromb Haemost. 1993 Aug 2;70(2):342–345. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shibata S., Harpel P. C., Gharavi A., Rand J., Fillit H. Autoantibodies to heparin from patients with antiphospholipid antibody syndrome inhibit formation of antithrombin III-thrombin complexes. Blood. 1994 May 1;83(9):2532–2540. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smeenk R. J., Lucassen W. A., Swaak T. J. Is anticardiolipin activity a cross-reaction of anti-DNA or a separate entity? Arthritis Rheum. 1987 Jun;30(6):607–617. doi: 10.1002/art.1780300602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. R., Hansen C. L., Rose R., Canoso R. T. Autoimmune MRL-1 pr/1pr mice are an animal model for the secondary antiphospholipid syndrome. J Rheumatol. 1990 Jul;17(7):911–915. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thiagarajan P., Shapiro S. S., De Marco L. Monoclonal immunoglobulin M lambda coagulation inhibitor with phospholipid specificity. Mechanism of a lupus anticoagulant. J Clin Invest. 1980 Sep;66(3):397–405. doi: 10.1172/JCI109869. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Triplett D. A. Antiphospholipid antibodies and thrombosis. A consequence, coincidence, or cause? Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1993 Jan;117(1):78–88. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Viard J. P., Amoura Z., Bach J. F. Association of anti-beta 2 glycoprotein I antibodies with lupus-type circulating anticoagulant and thrombosis in systemic lupus erythematosus. Am J Med. 1992 Aug;93(2):181–186. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(92)90049-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


