Abstract
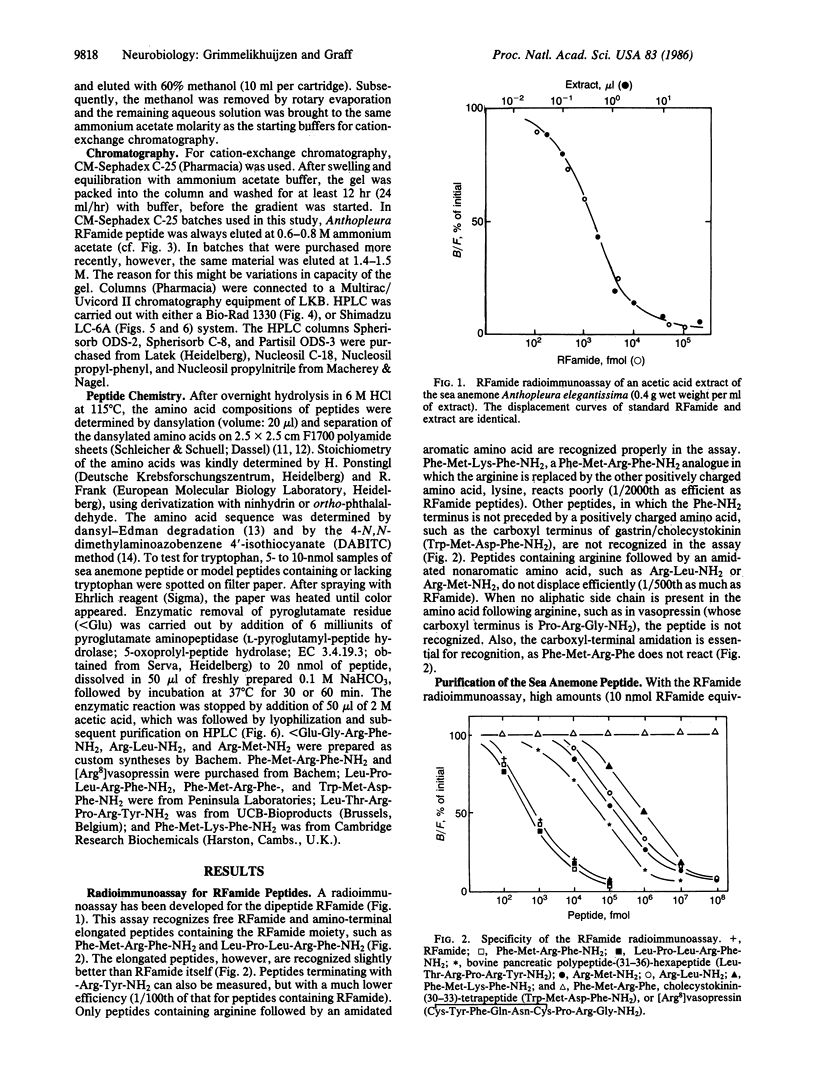
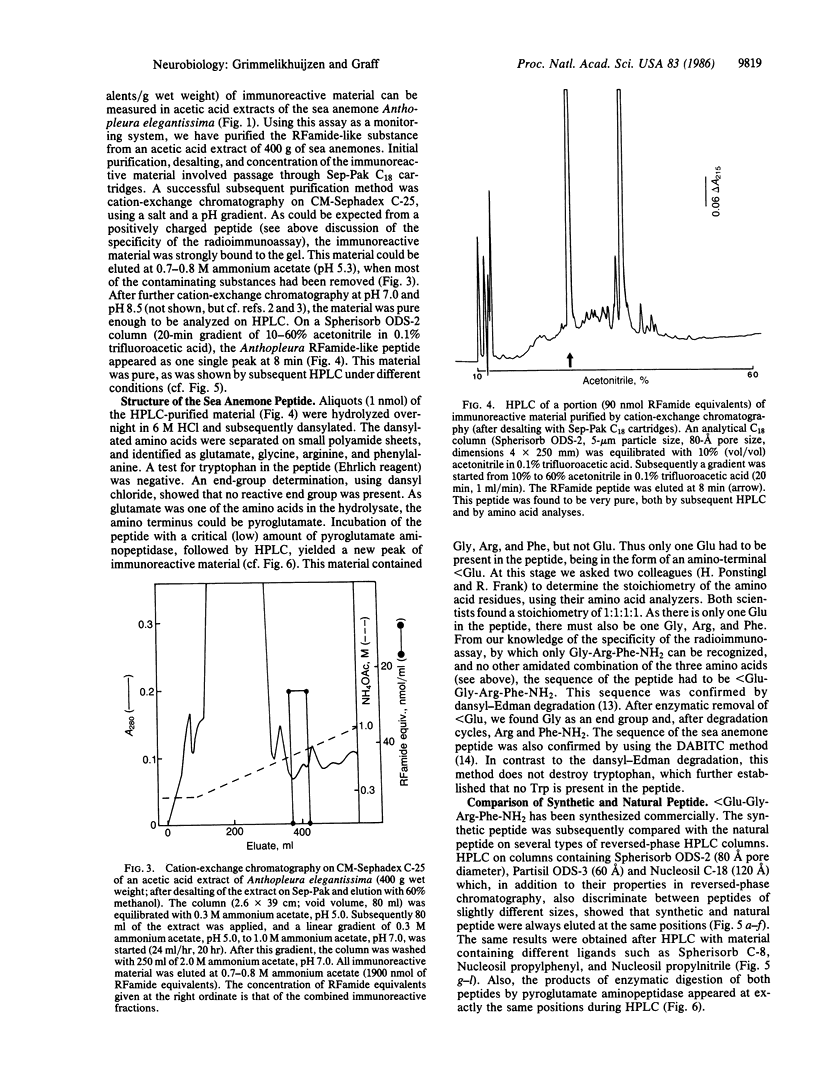
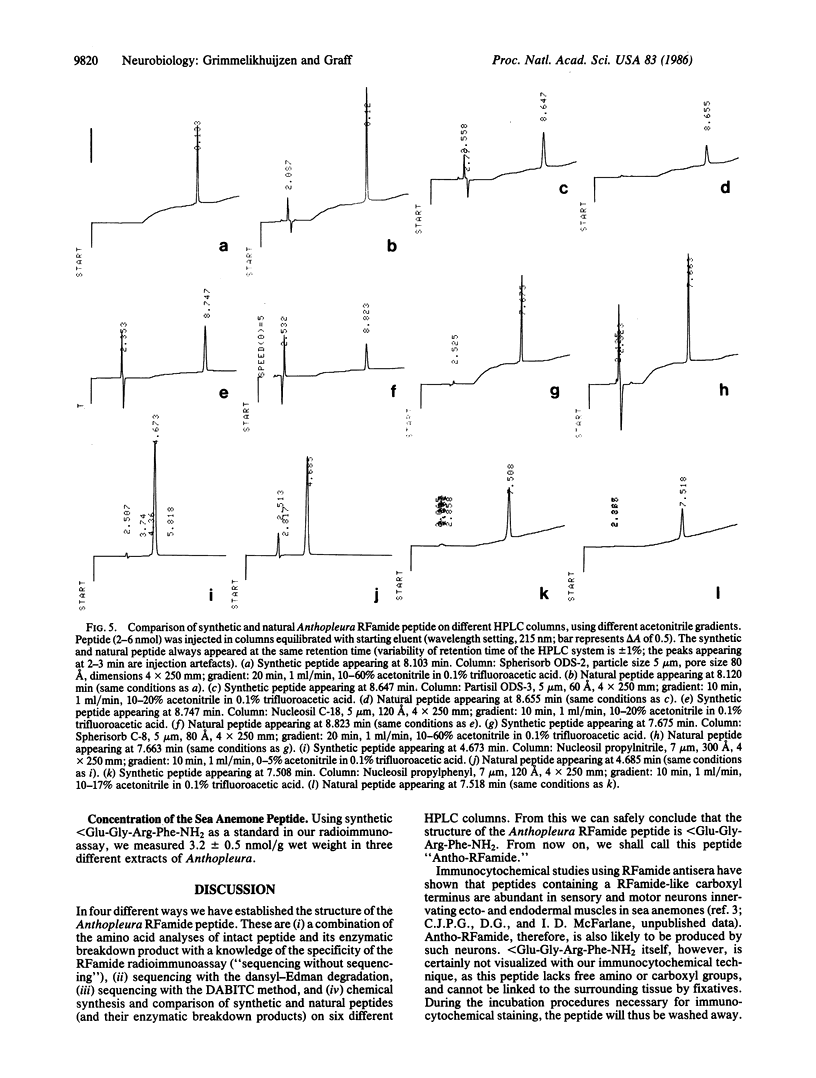
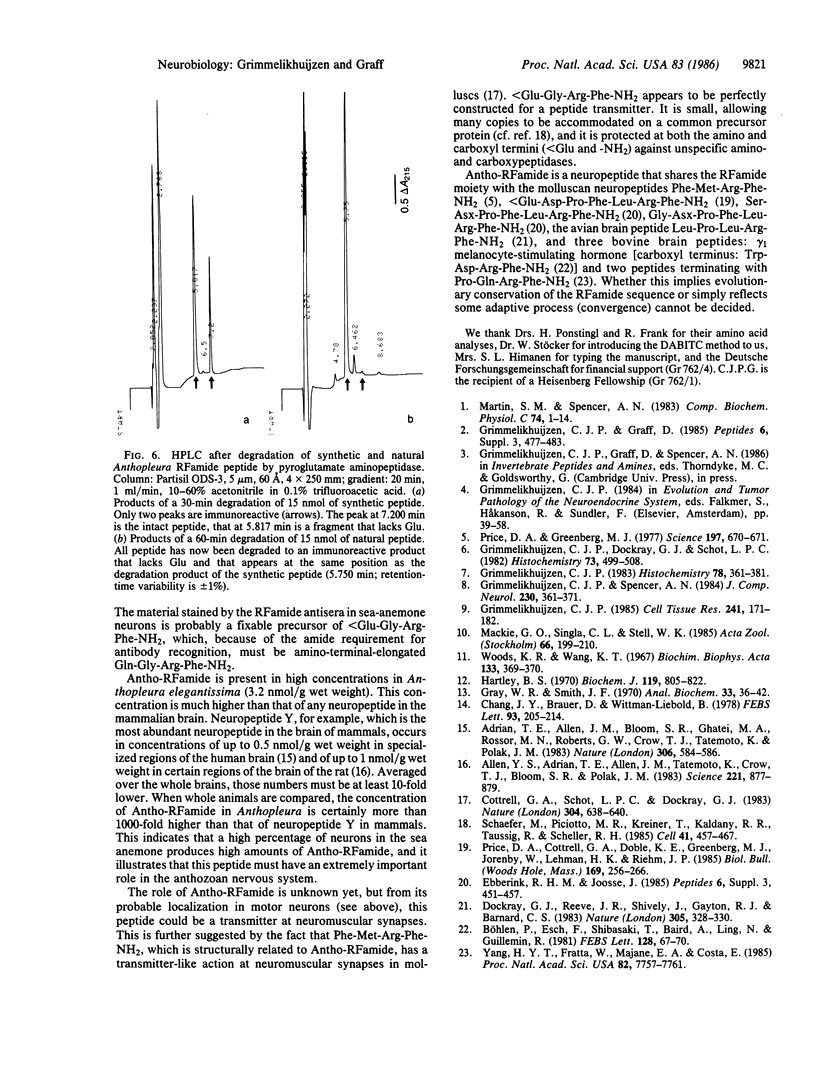
A radioimmunoassay has been developed for peptides containing the carboxyl-terminal sequence Arg-Phe-NH2 (RFamide). Using this radioimmunoassay and applying cation-exchange chromatography and HPLC, we have isolated an RFamide peptide from acetic acid extracts of the sea anemone Anthopleura elegantissima. Three different methods established that the structure of the Anthopleura RFamide peptide (Antho-RFamide) is pyroGlu-Gly-Arg-Phe-NH2. Comparison of synthetic and natural Antho-RFamide and their enzymatic breakdown products on six different HPLC columns confirmed the structure of the sea anemone peptide. Using synthetic Antho-RFamide as a standard in our radioimmunoassay, we measured high concentrations (3.2 nmol/g wet weight) of this peptide in extracts of Anthopleura. It is proposed that Antho-RFamide is a transmitter at neuromuscular synapses in sea anemones.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adrian T. E., Allen J. M., Bloom S. R., Ghatei M. A., Rossor M. N., Roberts G. W., Crow T. J., Tatemoto K., Polak J. M. Neuropeptide Y distribution in human brain. Nature. 1983 Dec 8;306(5943):584–586. doi: 10.1038/306584a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allen Y. S., Adrian T. E., Allen J. M., Tatemoto K., Crow T. J., Bloom S. R., Polak J. M. Neuropeptide Y distribution in the rat brain. Science. 1983 Aug 26;221(4613):877–879. doi: 10.1126/science.6136091. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böhlen P., Esch F., Shibasaki T., Baird A., Ling N., Guillemin R. Isolation and characterization of a gamma 1-melanotropin-like peptide from bovine neurointermediate pituitary. FEBS Lett. 1981 Jun 1;128(1):67–70. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(81)81081-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cottrell G. A., Schot L. P., Dockray G. J. Identification and probable role of a single neurone containing the neuropeptide Helix FMRFamide. Nature. 1983 Aug 18;304(5927):638–640. doi: 10.1038/304638a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dockray G. J., Reeve J. R., Jr, Shively J., Gayton R. J., Barnard C. S. A novel active pentapeptide from chicken brain identified by antibodies to FMRFamide. Nature. 1983 Sep 22;305(5932):328–330. doi: 10.1038/305328a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebberink R. H., Joosse J. Molecular properties of various snail peptides from brain and gut. Peptides. 1985;6 (Suppl 3):451–457. doi: 10.1016/0196-9781(85)90413-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray W. R., Smith J. F. Rapid sequence analysis of small peptides. Anal Biochem. 1970 Jan;33(1):36–42. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(70)90436-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grimmelikhuijzen C. J., Dockray G. J., Schot L. P. FMRFamide-like immunoreactivity in the nervous system of Hydra. Histochemistry. 1982;73(4):499–508. doi: 10.1007/BF00493364. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grimmelikhuijzen C. J. FMRFamide immunoreactivity is generally occurring in the nervous systems of coelenterates. Histochemistry. 1983;78(3):361–381. doi: 10.1007/BF00496623. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grimmelikhuijzen C. J., Graff D. Arg-Phe-amide-like peptides in the primitive nervous systems of coelenterates. Peptides. 1985;6 (Suppl 3):477–483. doi: 10.1016/0196-9781(85)90417-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grimmelikhuijzen C. J., Spencer A. N. FMRFamide immunoreactivity in the nervous system of the medusa Polyorchis penicillatus. J Comp Neurol. 1984 Dec 10;230(3):361–371. doi: 10.1002/cne.902300305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartley B. S. Strategy and tactics in protein chemistry. Biochem J. 1970 Oct;119(5):805–822. doi: 10.1042/bj1190805f. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price D. A., Greenberg M. J. Structure of a molluscan cardioexcitatory neuropeptide. Science. 1977 Aug 12;197(4304):670–671. doi: 10.1126/science.877582. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaefer M., Picciotto M. R., Kreiner T., Kaldany R. R., Taussig R., Scheller R. H. Aplysia neurons express a gene encoding multiple FMRFamide neuropeptides. Cell. 1985 Jun;41(2):457–467. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80019-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woods K. R., Wang K. T. Separation of dansyl-amino acids by polyamide layer chromatography. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 Feb 21;133(2):369–370. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(67)90078-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang H. Y., Fratta W., Majane E. A., Costa E. Isolation, sequencing, synthesis, and pharmacological characterization of two brain neuropeptides that modulate the action of morphine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Nov;82(22):7757–7761. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.22.7757. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


