Abstract
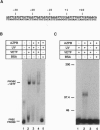
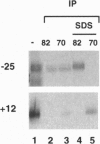
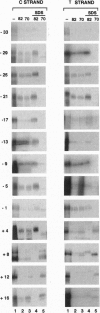
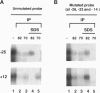
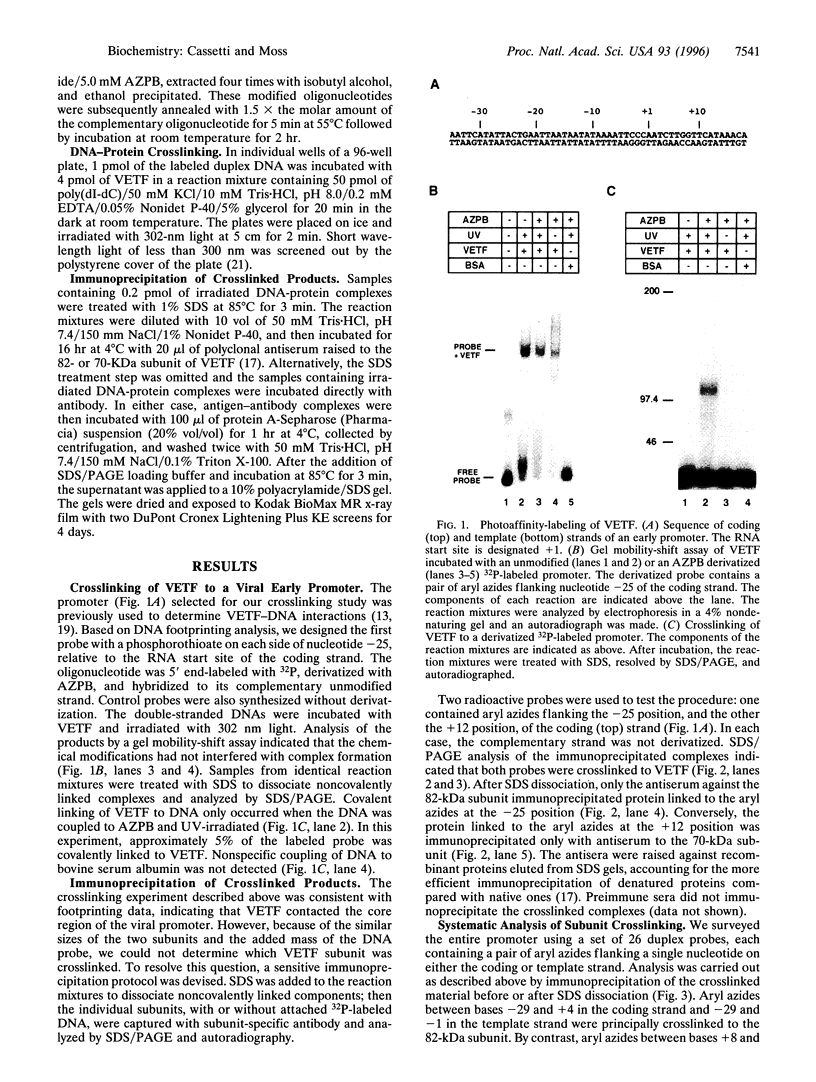
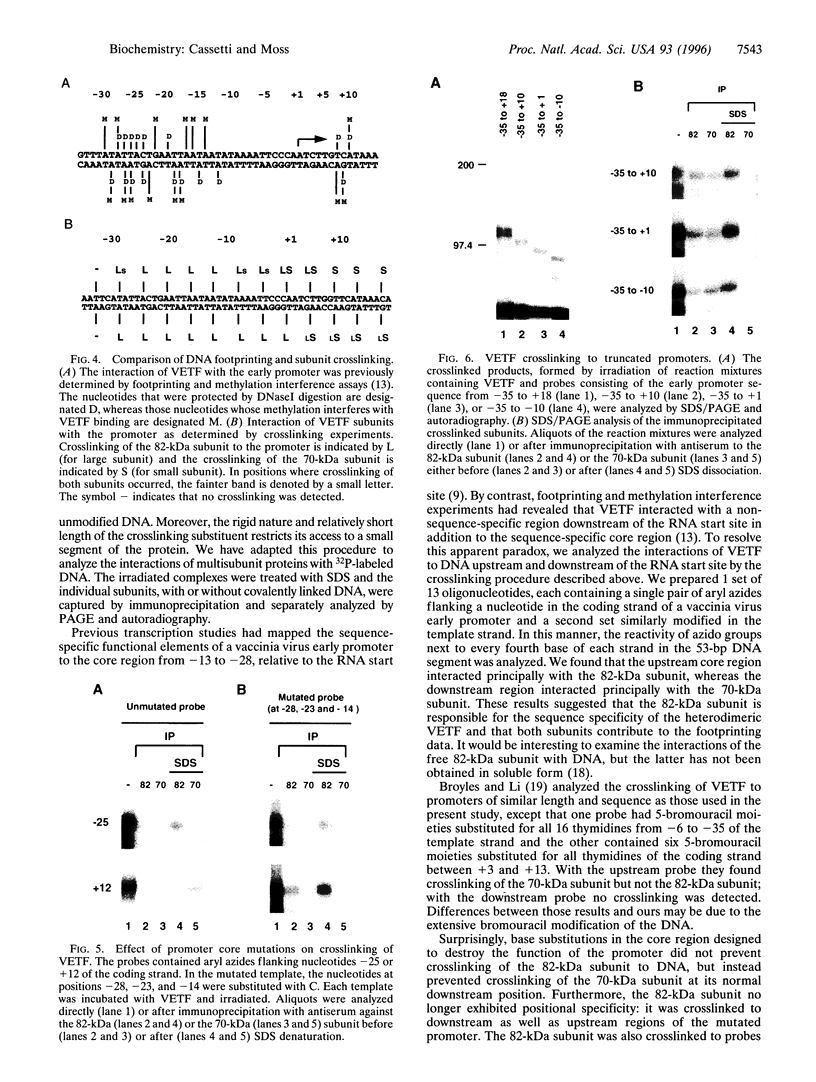
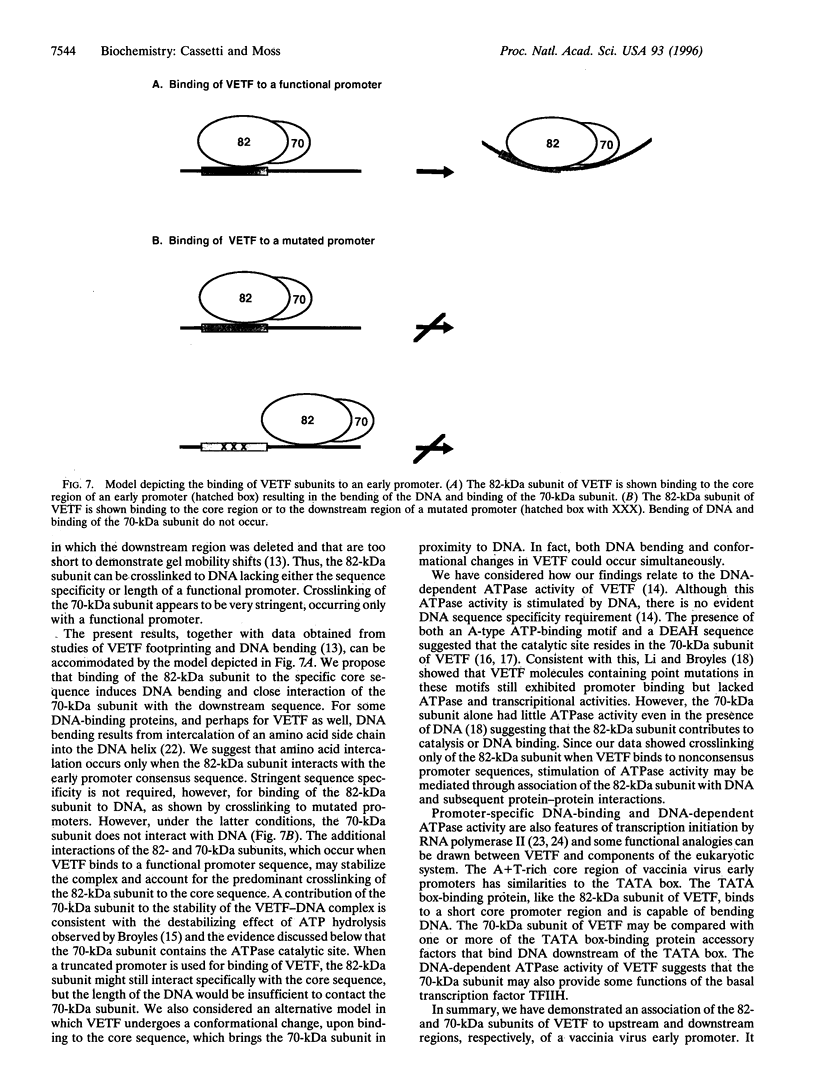
The vaccinia virus early transcription factor (VETF), a heterodimeric protein composed of 82- and 70-kDa subunits, interacts with viral early promoters at both a sequence-specific core region upstream and a sequence-independent region downstream of the RNA start site. To determine the VETF subunit-promoter interactions, 32P-labeled DNA targets were chemically synthesized with uniquely positioned phosphorothioates to which azidophenacyl bromide moieties were coupled. After incubating the derivatized promoter with VETF and exposing the complex to 302-nm light, the protein was denatured and the individual subunits with or without covalently bound DNA were isolated with specific antiserum and analyzed by SDS/polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Using a set of 26 duplex probes, with uniquely positioned aryl azide moieties on the coding or template strands, we found that the 82-kDa subunit interacted primarily with the core region of the promoter, whereas the 70-kDa subunit interacted with the downstream region. Nucleotide substitutions in the core region that downregulate transcription affected the binding of both subunits: the 82-kDa subunit no longer exhibited specificity for upstream regions of the promoter but also bound to downstream regions, whereas the binding of the 70-kDa subunit was abolished even though the mutations were far upstream of its binding site. These results suggested mechanisms by which the interaction of the 82-kDa subunit with the core sequence directs binding of the 70-kDa subunit to DNA downstream.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahn B. Y., Gershon P. D., Moss B. RNA polymerase-associated protein Rap94 confers promoter specificity for initiating transcription of vaccinia virus early stage genes. J Biol Chem. 1994 Mar 11;269(10):7552–7557. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ahn B. Y., Moss B. RNA polymerase-associated transcription specificity factor encoded by vaccinia virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Apr 15;89(8):3536–3540. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.8.3536. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldick C. J., Jr, Cassetti M. C., Harris N., Moss B. Ordered assembly of a functional preinitiation transcription complex, containing vaccinia virus early transcription factor and RNA polymerase, on an immobilized template. J Virol. 1994 Sep;68(9):6052–6056. doi: 10.1128/jvi.68.9.6052-6056.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broyles S. S. A role for ATP hydrolysis in vaccinia virus early gene transcription. Dissociation of the early transcription factor-promoter complex. J Biol Chem. 1991 Aug 15;266(23):15545–15548. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broyles S. S., Fesler B. S. Vaccinia virus gene encoding a component of the viral early transcription factor. J Virol. 1990 Apr;64(4):1523–1529. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.4.1523-1529.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broyles S. S., Li J., Moss B. Promoter DNA contacts made by the vaccinia virus early transcription factor. J Biol Chem. 1991 Aug 15;266(23):15539–15544. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broyles S. S., Li J. The small subunit of the vaccinia virus early transcription factor contacts the transcription promoter DNA. J Virol. 1993 Sep;67(9):5677–5680. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.9.5677-5680.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broyles S. S., Moss B. DNA-dependent ATPase activity associated with vaccinia virus early transcription factor. J Biol Chem. 1988 Aug 5;263(22):10761–10765. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broyles S. S., Yuen L., Shuman S., Moss B. Purification of a factor required for transcription of vaccinia virus early genes. J Biol Chem. 1988 Aug 5;263(22):10754–10760. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davison A. J., Moss B. Structure of vaccinia virus early promoters. J Mol Biol. 1989 Dec 20;210(4):749–769. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90107-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deng L., Shuman S. A role for the H4 subunit of vaccinia RNA polymerase in transcription initiation at a viral early promoter. J Biol Chem. 1994 May 13;269(19):14323–14328. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gershon P. D., Moss B. Early transcription factor subunits are encoded by vaccinia virus late genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jun;87(11):4401–4405. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.11.4401. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kates J. R., McAuslan B. R. Poxvirus DNA-dependent RNA polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Jul;58(1):134–141. doi: 10.1073/pnas.58.1.134. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li J., Broyles S. S. Recruitment of vaccinia virus RNA polymerase to an early gene promoter by the viral early transcription factor. J Biol Chem. 1993 Feb 5;268(4):2773–2780. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li J., Broyles S. S. The DNA-dependent ATPase activity of vaccinia virus early gene transcription factor is essential for its transcription activation function. J Biol Chem. 1993 Sep 25;268(27):20016–20021. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer A. N., Barany F. Photoaffinity cross-linking of TaqI restriction endonuclease using an aryl azide linked to the phosphate backbone. Gene. 1995 Feb 3;153(1):1–8. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(94)00752-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munyon W., Paoletti E., Grace J. T., Jr RNA polymerase activity in purified infectious vaccinia virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Dec;58(6):2280–2287. doi: 10.1073/pnas.58.6.2280. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wei C. M., Moss B. Methylated nucleotides block 5'-terminus of vaccinia virus messenger RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jan;72(1):318–322. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.1.318. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werner M. H., Gronenborn A. M., Clore G. M. Intercalation, DNA kinking, and the control of transcription. Science. 1996 Feb 9;271(5250):778–784. doi: 10.1126/science.271.5250.778. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang S. W., Nash H. A. Specific photocrosslinking of DNA-protein complexes: identification of contacts between integration host factor and its target DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Dec 6;91(25):12183–12187. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.25.12183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuen L., Davison A. J., Moss B. Early promoter-binding factor from vaccinia virions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Sep;84(17):6069–6073. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.17.6069. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]