Abstract
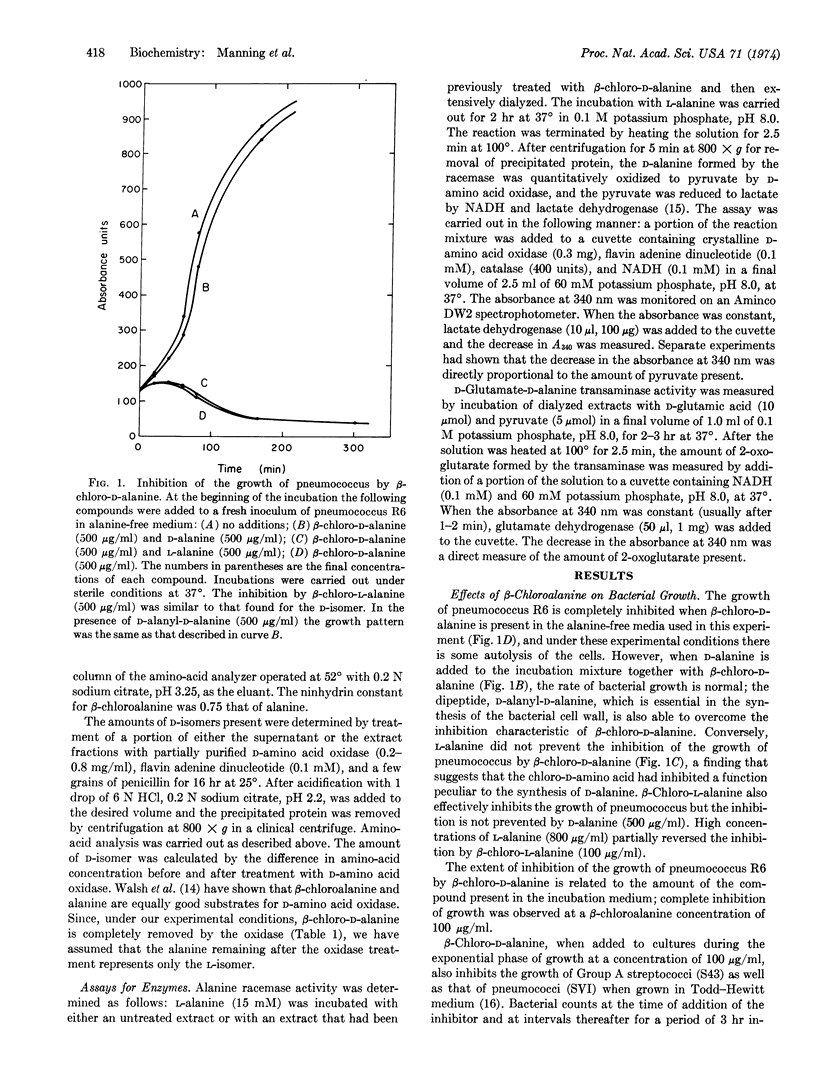
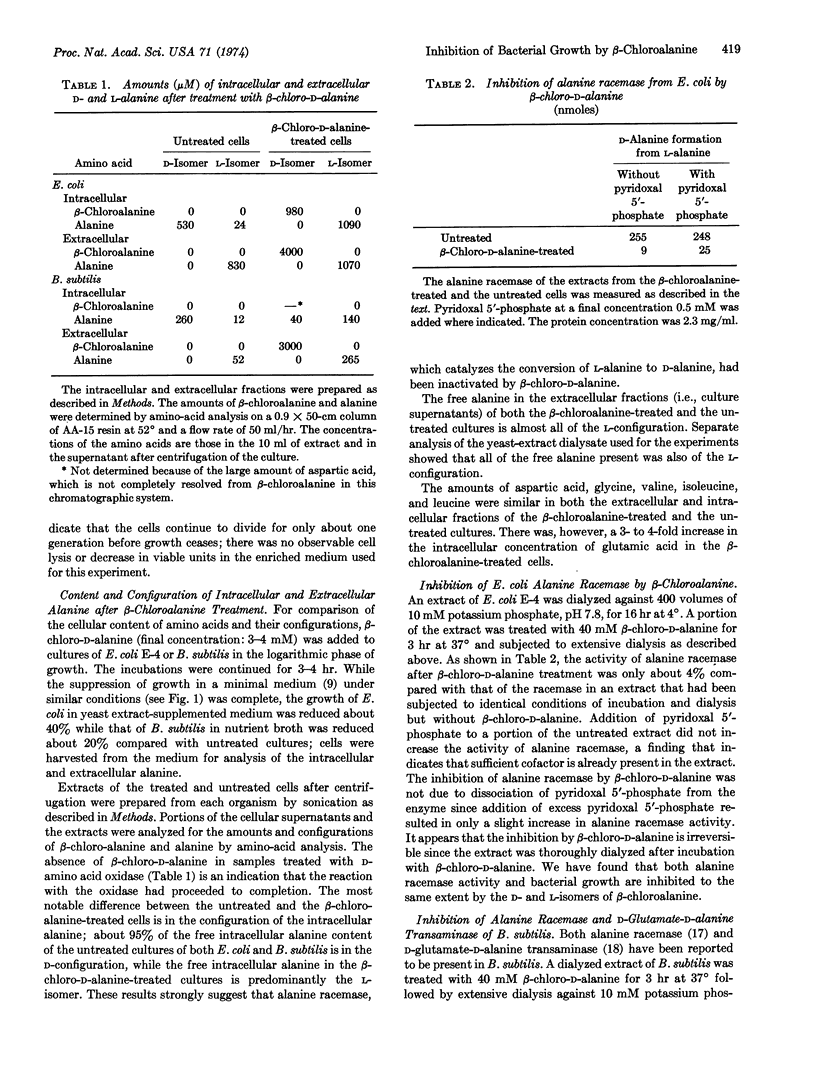
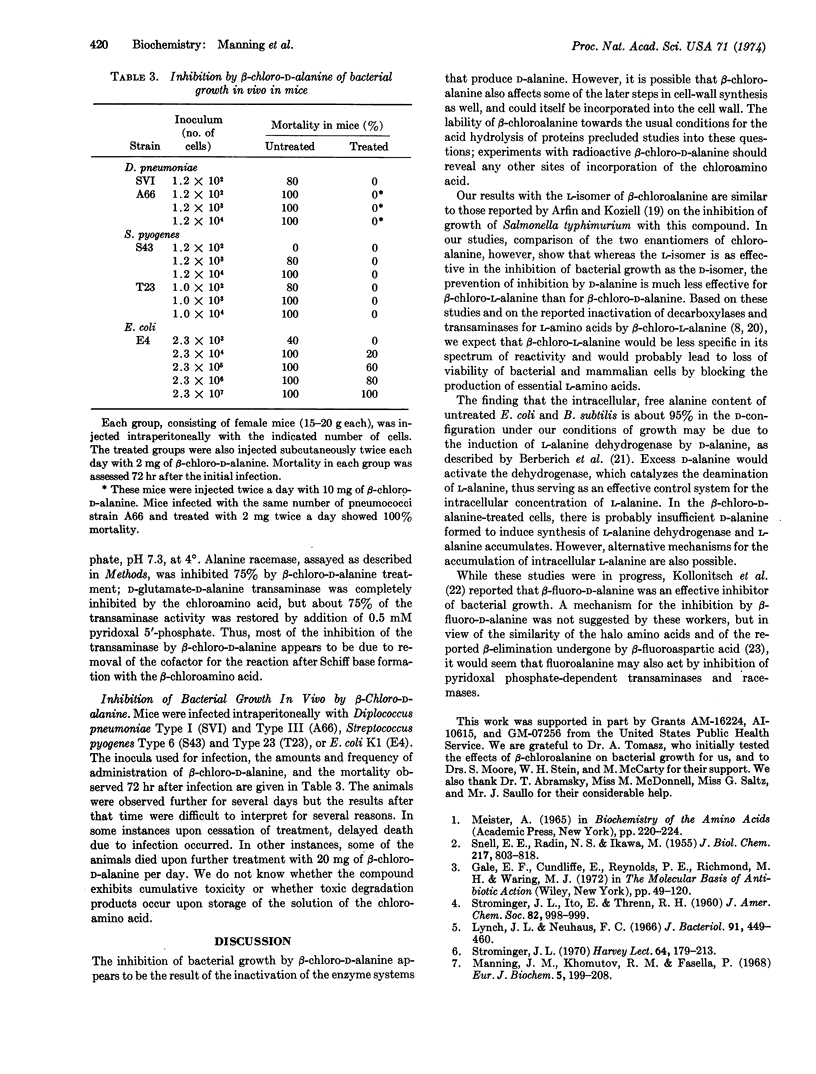
The D- and L-isomers of β-chloroalanine inhibit the growth of Diplococcus pneumoniae, Streptococcus pyogenes, Bacillus subtilis, and Escherichia coli. With pneumococcus the inhibition by β-chloro-D-alanine is completely prevented by either D-alanine or D-alanyl-D-alanine, while L-alanine is not effective in preventing the inhibition. The inhibition of growth by β-chloro-L-alanine is not affected by D-alanine and is only partially prevented by high concentrations of L-alanine. The intracellular free alanine in untreated E. coli and B. subtilis is about 95% in the D-configuration while the free intracellular alanine in both organisms after treatment with β-chloro-D-alanine is predominantly the L-isomer. These results suggested that the β-chloroamino acid inactivates alanine racemase (EC 5.1.1.1). Indeed, when extracts of E. coli or B. subtilis were treated with β-chloro-D-alanine, the activities of alanine racemase and of D-glutamate-D-alanine transaminase were found to be 90-95% inhibited. Studies with mice have shown that β-chloro-D-alanine is an effective antibacterial agent in vivo againt D. pneumoniae, S. pyogenes, and E. coli.
Keywords: cell wall, alanine racemase, D-amino acids
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arfin S. M., Koziell D. A. Inhibition of growth of Salmonella typhimurium and of threonine deaminase and transaminase B by beta-chloroalanine. J Bacteriol. 1971 Feb;105(2):519–522. doi: 10.1128/jb.105.2.519-522.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berberich R., Kaback M., Freese E. D-amino acids as inducers of L-alanine dehydrogenase in Bacillus subtilis. J Biol Chem. 1968 Mar 10;243(5):1006–1011. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frantz I. D. Growth Requirements of the Meningococcus. J Bacteriol. 1942 Jun;43(6):757–761. doi: 10.1128/jb.43.6.757-761.1942. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KUN E., FANSHIER D. W., GRASSETTI D. R. Interaction between beta-fluoro-oxaloacetate and glutamate-aspartate transaminase of heart mitochondria. J Biol Chem. 1960 Feb;235:416–419. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kollonitsch J., Barash L., Kahan F. M., Kropp H. Letter: New antibacterial agent via photofluorination of a bacterial cell wall constituent. Nature. 1973 Jun 8;243(5406):346–347. doi: 10.1038/243346a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lynch J. L., Neuhaus F. C. On the mechanism of action of the antibiotic O-carbamyld-serine in Streptococcus faecalis. J Bacteriol. 1966 Jan;91(1):449–460. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.1.449-460.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manning J. M., Khomutov R. M., Fasella P. The reaction of beta-chloroglutamic acid with glutamate-aspartate transaminase. Eur J Biochem. 1968 Jul;5(2):199–208. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1968.tb00358.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinez-Carrion M., Jenkins W. T. D-Alanine-D-glutamate transaminase. I. Purification and characterization. J Biol Chem. 1965 Sep;240(9):3538–3546. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morino Y., Okamoto M. Labeling of the active site of cytoplasmic aspartate aminotransferase by -chloro-L-alanine. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Feb 20;50(4):1061–1067. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)91514-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SNELL E. E., RADIN N. S., IKAWA M. The nature of D-alanine in lactic acid bacteria. J Biol Chem. 1955 Dec;217(2):803–818. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SRINIVASAN N. G., CORRIGAN J. J., MEISTER A. BIOSYNTHESIS OF D-SERINE IN THE SILKWORM, BOMBYX MORI. J Biol Chem. 1965 Feb;240:796–800. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strominger J. L. Penicillin-sensitive enzymatic reactions in bacterial cell wall synthesis. Harvey Lect. 1968 1969;64:179–213. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THORNE C. B., GOMEZ C. G., HOUSEWRIGHT R. D. Transamination of D-amino acids by Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1955 Mar;69(3):357–362. doi: 10.1128/jb.69.3.357-362.1955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tate S. S., Relyea N. M., Meister A. Interaction of L-aspartate beta-decarboxylase with beta-chloro-L-alanine. Beta-elimination reaction and active-site labeling. Biochemistry. 1969 Dec;8(12):5016–5021. doi: 10.1021/bi00840a051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomasz A., Zanati E., Ziegler R. DNA uptake during genetic transformation and the growing zone of the cell envelope. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Aug;68(8):1848–1852. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.8.1848. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh C. T., Schonbrunn A., Abeles R. H. Studies on the mechanism of action of D-amino acid oxidase. Evidence for removal of substrate -hydrogen as a proton. J Biol Chem. 1971 Nov 25;246(22):6855–6866. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


