Abstract
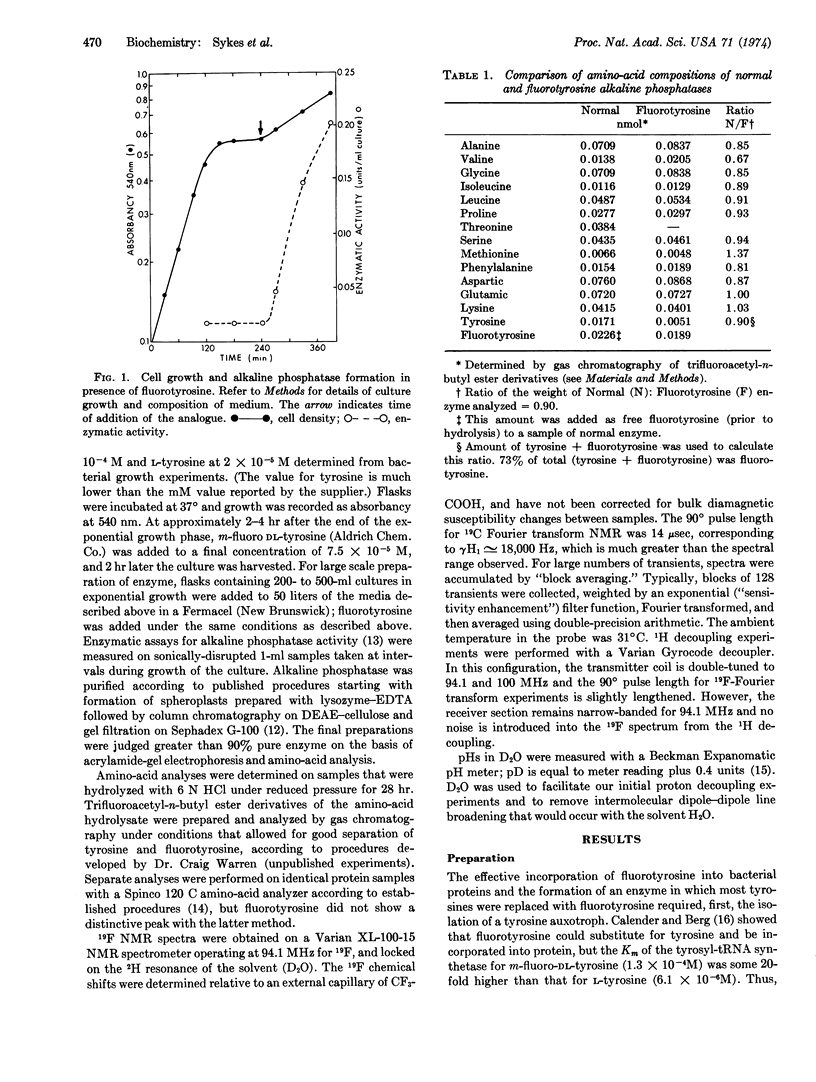
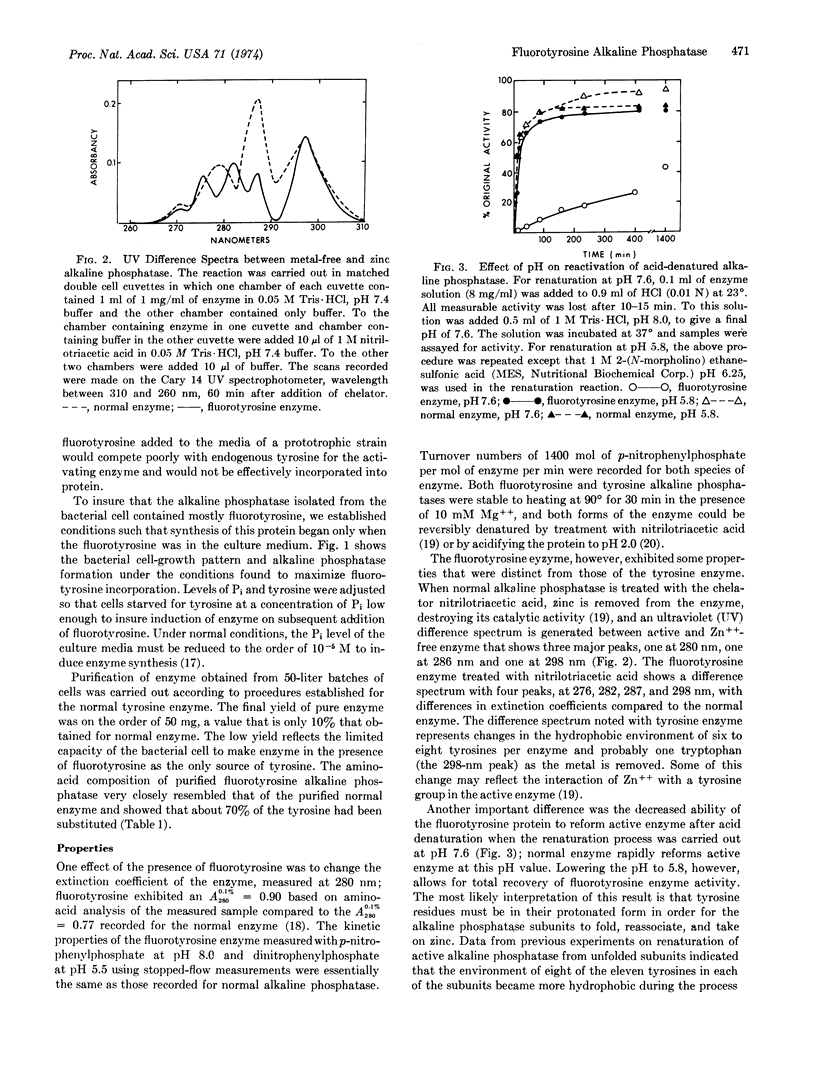
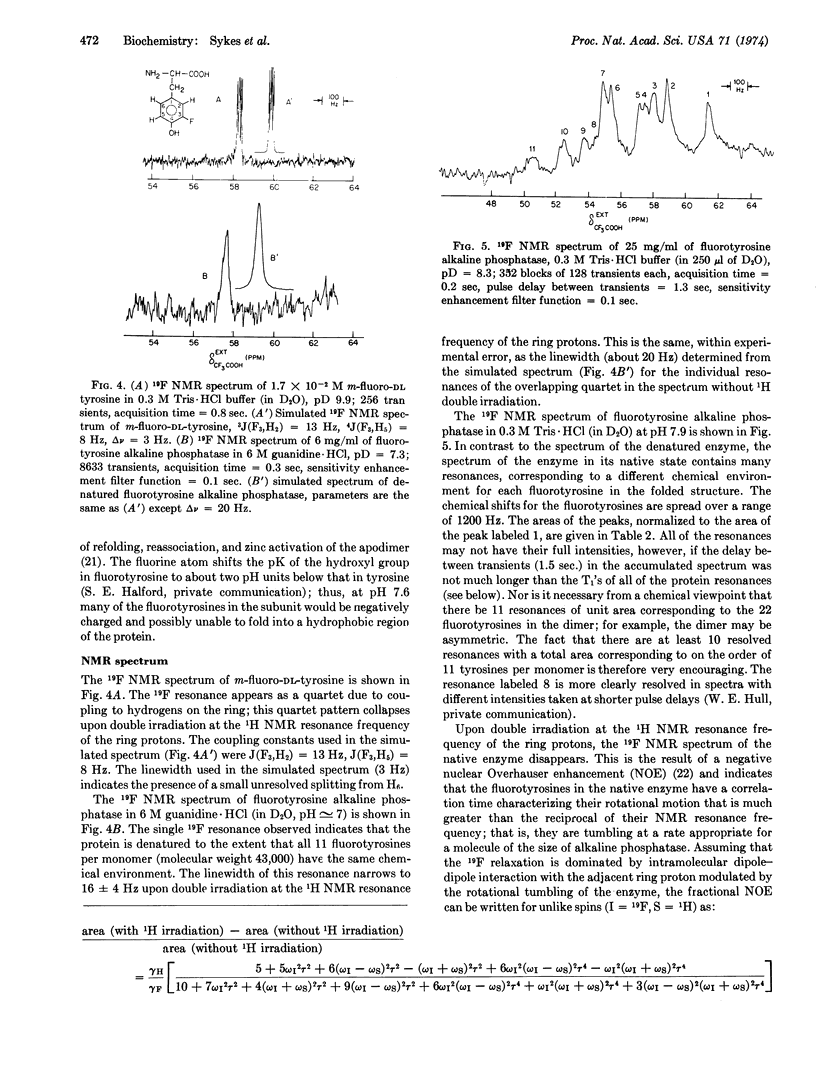
Alkaline phosphatase (EC 3.1.3.1) containing m-flurotyrosine has been prepared from E. coli grown in the presence of m-flurotyrosine. The kinetic properties of the m-fluorotyrosine enzyme measured with p-nitrophenylphosphate at pH 8.0 and dinitrophenylphosphate at pH 5.5 are essentially the same as those of normal alkaline phosphatase. However, the ability of the m-fluorotyrosine protein to refold active enzyme after acid denaturation, while unchanged at pH 5.8, was markedly decreased at pH 7.6. This result implies that the tyrosines must be in their protonated form for the protein to refold, reassociate, and take on zinc. The 19F nuclear magnetic resonance spectrum of m-fluorotyrosine alkaline phosphatase contains resolved resonances corresponding to different chemical environments for each m-fluorotyrosine in the folded protein. This demonstrates that 19F nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy of enzymes specifically labeled with 19F, even with enzymes as large as alkaline phosphatase (molecular weight, 86,000), will provide a very valuable probe for conformational changes in proteins.
Keywords: kinetics, renaturation, ultraviolet spectra, conformational changes
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Balaram P., Bothner-By A. A., Dadok J. Negative nuclear Overhauser effects as probes of macromolecular structure. J Am Chem Soc. 1972 May 31;94(11):4015–4017. doi: 10.1021/ja00766a063. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Browne D. T., Kenyon G. L., Packer E. L., Wilson D. M., Sternlicht H. A study of the dynamic state of histidine residues in tryptophan synthetase subunit by 13 C nuclear magnetic resonance. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Jan 4;50(1):42–47. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)91060-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halford S. E., Lennette D. A., Kelley P. M., Schlesinger M. J. A mutationally altered alkaline phosphatase from Escherichia coli. I. Formation of an active enzyme in vitro and phenotypic suppression in vivo. J Biol Chem. 1972 Apr 10;247(7):2087–2094. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huestis W. H., Raftery M. A. A study of cooperative interactions in hemoglobin using fluorine nuclear magnetic resonance. Biochemistry. 1972 Apr 25;11(9):1648–1654. doi: 10.1021/bi00759a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huestis W. H., Raftery M. A. Use of fluorine-19 nuclear magnetic resonance to study conformation changes in selectively modified ribonuclease S. Biochemistry. 1971 Mar 30;10(7):1181–1186. doi: 10.1021/bi00783a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelley P. M., Neumann P. A., Shriefer K., Cancedda F., Schlesinger M. J., Bradshaw R. A. Amino acid sequence of Escherichia coli alkaline phosphatase. Amino- and carboxyl-terminal sequences and variations between two isozymes. Biochemistry. 1973 Aug 28;12(18):3499–3503. doi: 10.1021/bi00742a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King N. L., Bradbury J. H. Simplification of the proton magnetic resonance spectrum of ribonuclease by difference spectroscopy. Nature. 1971 Feb 5;229(5284):404–406. doi: 10.1038/229404a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knox J. R., Wyckoff H. W. A crystallographic study of alkaline phosphatase at 7-7 Angstrom resolution. J Mol Biol. 1973 Mar 15;74(4):533–545. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90045-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Putter I., Barreto A., Markley J. L., Jardetzky O. Nuclear magnetic resonance studies of the structure and binding sites of enzymes. X. Preparation of selectively deuterated analogs of staphylococcal nuclease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Dec;64(4):1396–1403. doi: 10.1073/pnas.64.4.1396. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RICHMOND M. H. Random replacement of phenylalanine by p-fluorophenylalanine in alkaline phosphatase(s) formed during biosynthesis by E. coli. J Mol Biol. 1963 Apr;6:284–294. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(63)80089-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROTHMAN F., BYRNE R. Fingerprint analysis of alkaline phosphatase of Escherichia coli K12. J Mol Biol. 1963 Apr;6:330–340. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(63)80092-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds J. A., Schlesinger M. J. Alterations in the structure and function of Escherichia coli alkaline phosphatase due to Zn2+ binding. Biochemistry. 1969 Feb;8(2):588–593. doi: 10.1021/bi00830a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds J. A., Schlesinger M. J. Conformational states of the subunit of Escherichia coli alkaline phosphatase. Biochemistry. 1967 Nov;6(11):3552–3559. doi: 10.1021/bi00863a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts G. C., Jardetzky O. Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy of amino acids, peptides, and proteins. Adv Protein Chem. 1970;24:447–545. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60246-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlesinger M. J., Barrett K. The reversible dissociation of the alkaline phosphatase of Escherichia coli. I. Formation and reactivation of subunits. J Biol Chem. 1965 Nov;240(11):4284–4292. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlesinger M. J., Reynolds J. A., Schlesinger S. Formation and localization of the alkaline phosphatase of Escherichia coli. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1969 Oct 14;166(2):368–379. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1969.tb46408.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlesinger S., Nester E. W. Mutants of Escherichia coli with an altered tyrosyl-transfer ribonucleic acid synthetase. J Bacteriol. 1969 Oct;100(1):167–175. doi: 10.1128/jb.100.1.167-175.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TORRIANI A. Influence of inorganic phosphate in the formation of phosphatases by Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1960 Mar 11;38:460–469. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(60)91281-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



