Abstract
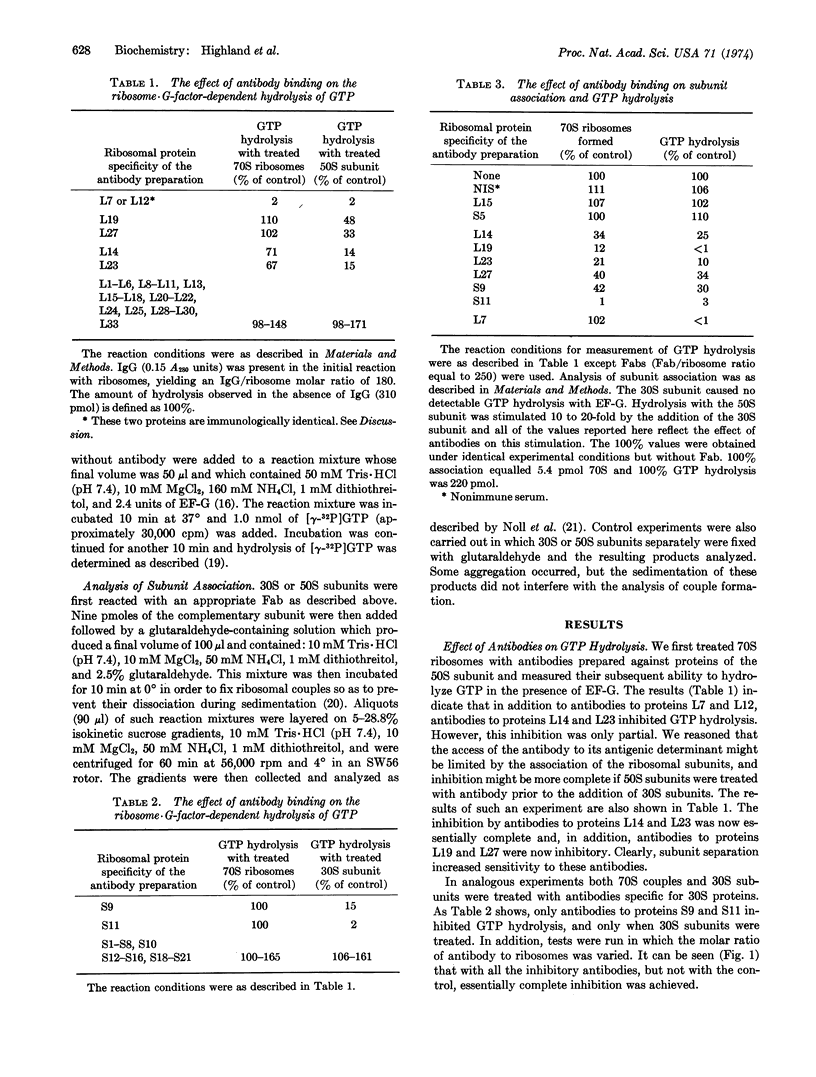
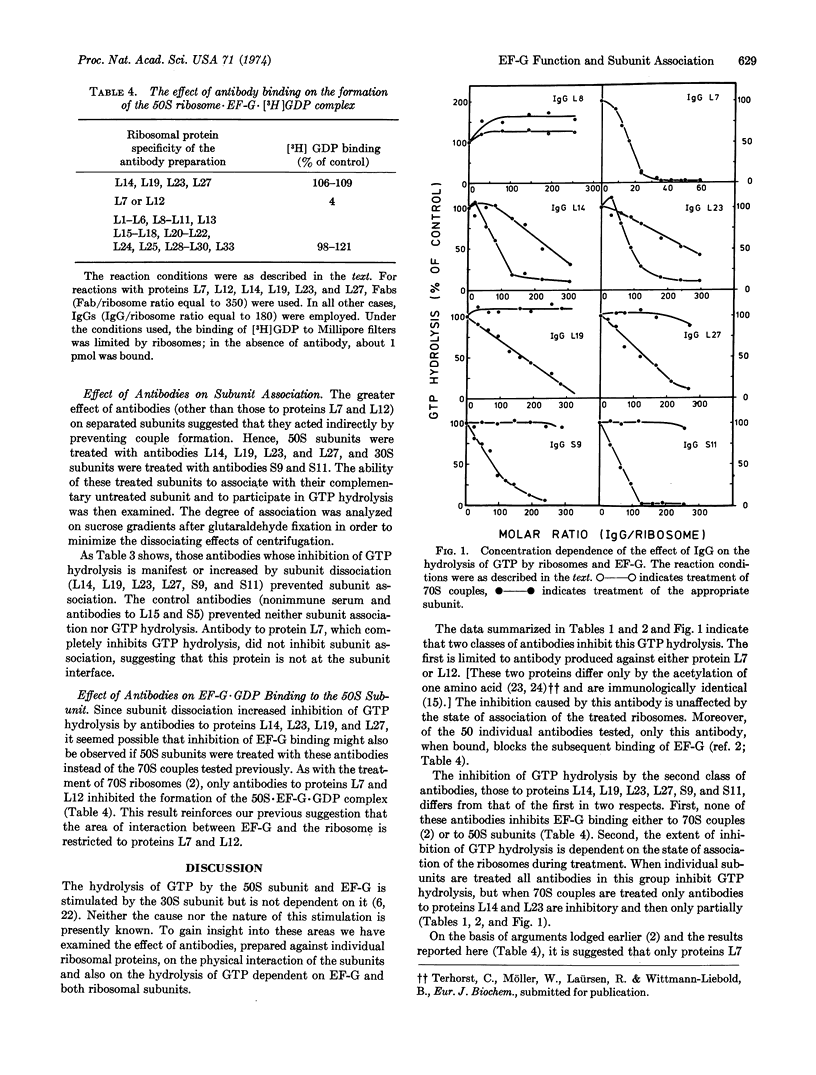
We previously showed that treatment of Escherichia coli ribosomes with antibodies specific for proteins L7 and L12 inhibits both EF-G·GDP binding and ribosome-dependent GTP hydrolysis (Highland et al. (1973) Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 70, 142-150; and Kischa et al. (1971) Nature New Biol. 233, 62-63). We now report that antibodies to six additional proteins also inhibit GTP hydrolysis, but do not inhibit EF-G·GDP binding. Moreover, inhibition by these antibodies is dependent on the state of association of the treated ribosomes. When 70S couples are treated, only antibodies to proteins L14 and L23 are inhibitory and then only partially. However, when separated ribosomal subunits are treated individually and then mixed with the complementary untreated subunits, inhibition by antibodies L14 and L23 is complete, and antibodies to proteins L19, L27, S9, and S11 now show an inhibitory effect. In addition, treatment of subunits with any of these six antibodies (but not those to L7 or L12) results in inhibition of reassociation, which is presumably responsible for the inhibition of hydrolysis. These data suggest that the area of interaction between EF-G and the ribosome is restricted to proteins L7 and L12, and that antibodies to proteins L14, L19, L23, L27, S9, and S11, but not L7 and L12, block the physical association of the subunits.
Keywords: E. coli, GTP hydrolysis, translocation
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bodley J. W., Lin L. Interaction of E. coli G factor with the 50S ribosomal subunit. Nature. 1970 Jul 4;227(5253):60–61. doi: 10.1038/227060a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodley J. W., Zieve F. J., Lin L., Zieve S. T. Studies on translocation. 3. Conditions necessary for the formation and detection of a stable ribosome-G factor-guanosine diphosphate complex in the presence of fusidic acid. J Biol Chem. 1970 Nov 10;245(21):5656–5661. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brot N., Spears C., Weissbach H. The formation of a complex containing ribosomes, transfer factor G and A guanosine nucleotide. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1969 Mar 31;34(6):843–848. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(69)90257-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brot N., Yamasaki E., Redfield B., Weissbach H. The properties of an E. coli ribosomal protein required for the function of factor G. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1972 Jan;148(1):148–155. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(72)90125-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bär H. P., Hechter O. Adenyl cyclase and hormone action. 3. Calcium requirement for ACTH stimulation of adenyl cyclase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1969 Jun 6;35(5):681–686. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(69)90459-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eikenberry E. F., Bickle T. A., Traut R. R., Price C. A. Separation of large quantities of ribosomal subunits by zonal ultracentrifugation. Eur J Biochem. 1970 Jan;12(1):113–116. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1970.tb00827.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon J. Hydrolysis of guanosine 5'-triphosphate associated wh binding of aminoacyl transfer ribonucleic acid to ribosomes. J Biol Chem. 1969 Oct 25;244(20):5680–5686. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamel E., Koka M., Nakamoto T. Requirement of an Escherichia coli 50 S ribosomal protein component for effective interaction of the ribosome with T and G factors and with guanosine triphosphate. J Biol Chem. 1972 Feb 10;247(3):805–814. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Highland J. H., Bodley J. W., Gordon J., Hasenbank R., Stöffler G. Identity of the ribosomal proteins involved in the interaction with elongation factor G. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Jan;70(1):147–150. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.1.147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Highland J. H., Lin L., Bodley J. W. Protection of ribosomes from thiostrepton inactivation by the binding of G factor and guanosine diphosphate. Biochemistry. 1971 Nov 23;10(24):4404–4409. doi: 10.1021/bi00800a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kischa K., Möller W., Stöffler G. Reconstitution of a GTPase activity by a 50S ribosomal protein and E. coli. Nat New Biol. 1971 Sep 8;233(36):62–63. doi: 10.1038/newbio233062a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurland C. G. Structure and function of the bacterial ribosome. Annu Rev Biochem. 1972;41(10):377–408. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.41.070172.002113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucas-Lenard J. Protein biosynthesis. Annu Rev Biochem. 1971;40:409–448. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.40.070171.002205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsh R. C., Parmeggiani A. Requirement of proteins S5 and S9 from 30S subunits for the ribosome-dependent GTPase activity of elongation factor G. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Jan;70(1):151–155. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.1.151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Möller W., Groene A., Terhorst C., Amons R. 50-S ribosomal proteins. Purification and partial characterization of two acidic proteins, A 1 and A 2, isolated from 50-S ribosomes of Escherichia coli. Eur J Biochem. 1972 Jan 31;25(1):5–12. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1972.tb01660.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizuka Y., Lipmann F. The interrelationship between guanosine triphosphatase and amino acid polymerization. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1966 Sep 26;116(1):344–351. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(66)90040-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noll M., Hapke B., Schreier M. H., Noll H. Structural dynamics of bacterial ribosomes. I. Characterization of vacant couples and their relation to complexed ribosomes. J Mol Biol. 1973 Apr 5;75(2):281–294. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90021-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schrier P. I., Maassen J. A., Möller W. Involvement of 50S ribosomal proteins L6 and L10 in the ribosome dependent GTPase activity of elongation factor G. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Jul 2;53(1):90–98. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)91405-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stöffler G., Wittmann H. G. Ribosomal proteins. XXV. Immunological studies on Escherichia coli ribosomal proteins. J Mol Biol. 1971 Dec 14;62(2):407–409. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90436-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stöffler G., Wittmann H. G. Sequence differences of Escherichia coli 30S ribosomal proteins as determined by immunochemical methods. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Sep;68(9):2283–2287. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.9.2283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Subramanian A. R. Glutaraldehyde fixation of ribosomes. Its use in the analysis of ribosome dissociation. Biochemistry. 1972 Jul 4;11(14):2710–2714. doi: 10.1021/bi00764a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terhorst C., Wittmann-Liebold B., Möller W. 50-S ribosomal proteins. Peptide studies on two acidic proteins, A 1 and A 2 , isolated from 50-S ribosomes of Escherichia coli. Eur J Biochem. 1972 Jan 31;25(1):13–19. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1972.tb01661.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zamir A., Miskin R., Elson D. Inactivation and reactivation of ribosomal subunits: amino acyl-transfer RNA binding activity of the 30 s subunit of Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1971 Sep 14;60(2):347–364. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90299-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


