Abstract
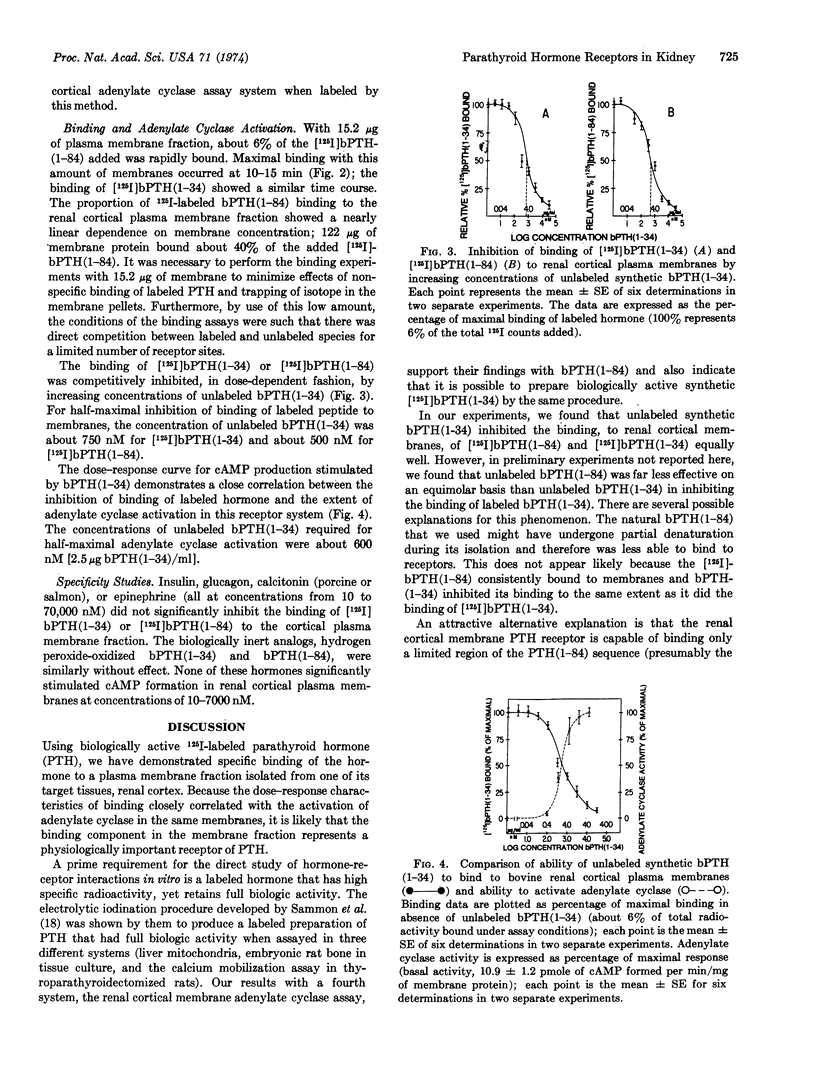
Biologically active 125I-labeled bovine parathyroid hormone (prepared by electrolytic iodination) and its synthetic NH2-terminal (1-34) biologically active fragment bound rapidly and specifically to a purified plasma membrane preparation from bovine renal cortex. Binding of labeled intact hormone or labeled NH2-terminal (1-34) peptide was inhibited competitively by unlabeled (1-34) peptide in the same range of concentrations that activated renal cortical 3′:5′-adenylate cyclase (EC 4.6.1.1) in these membranes. The concentrations of synthetic (1-34) peptide for half-maximal inhibition of binding of labeled hormone as well as half-maximal activation of the enzyme were about 0.6 μM (2.5 μg/ml). Therefore it is likely that the binding activity studied represents a physiologically important renal receptor for parathyroid hormone.
Biologically inactive (oxidized) forms of parathyroid hormone and (1-34) NH2-terminal peptide as well as calcitonin, glucagon, insulin, and epinephrine failed to competitively inhibit the binding of labeled (1-34) parathyroid hormone or activate adenylate cyclase in the renal cortical membrane preparation.
Observations with the NH2-terminal (1-34) biologically active fragment of parathyroid hormone suggest that the COOH-terminal region of the molecule is not required for receptor binding.
Keywords: calcium metabolism, cyclic AMP, electrolytic iodination of peptides, synthetic bovine parathyroid hormone(1-34)
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arnaud C. D., Tsao H. S. Porcine calcitonin. Simple procedure for isolation in high yield. Biochemistry. 1969 Jan;8(1):449–456. doi: 10.1021/bi00829a061. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berson S. A., Yalow R. S. Iodoinsulin used to determine specific activity of iodine-131. Science. 1966 Apr 8;152(3719):205–207. doi: 10.1126/science.152.3719.205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brewer H. B., Jr, Ronan R. Bovine parathyroid hormone: amino acid sequence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Dec;67(4):1862–1869. doi: 10.1073/pnas.67.4.1862. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckle R. M., Potts J. T., Jr Assessment of damage to I-131-labeled parathyroid hormone by chromatoelectrophoresis and adsorption onto dextran-charcoal. J Lab Clin Med. 1970 Jul;76(1):46–53. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bär H. P., Hechter O. Adenyl cyclase assay in fat cell ghosts. Anal Biochem. 1969 Jun;29(3):476–489. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(69)90332-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chase L. R., Aurbach G. D. Parathyroid function and the renal excretion of 3'5'-adenylic acid. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Aug;58(2):518–525. doi: 10.1073/pnas.58.2.518. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chase L. R., Aurbach G. D. Renal adenyl cyclase: anatomically separate sites for parathyroid hormone and vasopressin. Science. 1968 Feb 2;159(3814):545–547. doi: 10.1126/science.159.3814.545. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dousa T., Hechter O., Schwartz I. L., Walter R. Neurohypophyseal hormone-responsive adenylate cyclase from mammalian kidney. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Aug;68(8):1693–1697. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.8.1693. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dousa T., Rychlík I. The effect of parathyroid hormone on adenyl cyclase in rat kidney. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Jun 24;158(3):484–486. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(68)90309-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzpatrick D. F., Davenport G. R., Forte L., Landon E. J. Characterization of plasma membrane proteins in mammalian kidney. I. Preparation of a membrane fraction and separation of the protein. J Biol Chem. 1969 Jul 10;244(13):3561–3569. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREENWOOD F. C., HUNTER W. M., GLOVER J. S. THE PREPARATION OF I-131-LABELLED HUMAN GROWTH HORMONE OF HIGH SPECIFIC RADIOACTIVITY. Biochem J. 1963 Oct;89:114–123. doi: 10.1042/bj0890114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marx S. J., Fedak S. A., Aurbach G. D. Preparation and characterization of a hormone-responsive renal plasma membrane fraction. J Biol Chem. 1972 Nov 10;247(21):6913–6918. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKenzie S. G., Bär H. P. On the mechanism of adenyl cyclase inhibition by adenosine. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1973 Mar;51(3):190–196. doi: 10.1139/y73-027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melson G. L., Chase L. R., Aurbach G. D. Parathyroid hormone-sensitive adenyl cyclase in isolated renal tubules. Endocrinology. 1970 Mar;86(3):511–518. doi: 10.1210/endo-86-3-511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagata N., Rasmussen H. Parathyroid hormone and renal cell metabolism. Biochemistry. 1968 Oct;7(10):3728–3733. doi: 10.1021/bi00850a053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potts J. T., Jr, Murray T. M., Peacock M., Niall H. D., Tregear G. W., Keutmann H. T., Powell D., Deftos L. J. Parathyroid hormone: sequence, synthesis, immunoassay studies. Am J Med. 1971 May;50(5):639–649. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(71)90119-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potts J. T., Jr, Tregear G. W., Keutmann H. T., Niall H. D., Sauer R., Deftos L. J., Dawson B. F., Hogan M. L., Aurbach G. D. Synthesis of a biologically active N-terminal tetratriacontapeptide of parathyroid hormone. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Jan;68(1):63–67. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.1.63. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rasmussen H., Tenenhouse A. Cyclic adenosine monophosphate, CA++, and membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Apr;59(4):1364–1370. doi: 10.1073/pnas.59.4.1364. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robison G. A., Butcher R. W., Sutherland E. W. Cyclic AMP. Annu Rev Biochem. 1968;37:149–174. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.37.070168.001053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodbell M., Krans H. M., Pohl S. L., Birnbaumer L. The glucagon-sensitive adenyl cyclase system in plasma membranes of rat liver. 3. Binding of glucagon: method of assay and specificity. J Biol Chem. 1971 Mar 25;246(6):1861–1871. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SAMIY A. H., HIRSCH P. F., RAMSAY A. G. LOCALIZATION OF PHOSPHATURIC EFFECT OF PARATHYROID HORMONE IN NEPHRON OF THE DOG. Am J Physiol. 1965 Jan;208:73–77. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1965.208.1.73. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sammon P. J., Brand J. S., Neuman W. F., Raisz L. G. Metabolism of labeled parathyroid hormone. I. Preparation of biologically active I-125-labeled parathyroid hormone. Endocrinology. 1973 Jun;92(6):1596–1603. doi: 10.1210/endo-92-6-1596. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TASHJIAN A. H., Jr, ONTJES D. A., MUNSON P. L. ALKYLATION AND OXIDATION OF METHIONINE IN BOVINE PARATHYROID HORMONE: EFFECTS ON HORMONAL ACTIVITY AND ANTIGENICITY. Biochemistry. 1964 Aug;3:1175–1182. doi: 10.1021/bi00896a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


