Abstract
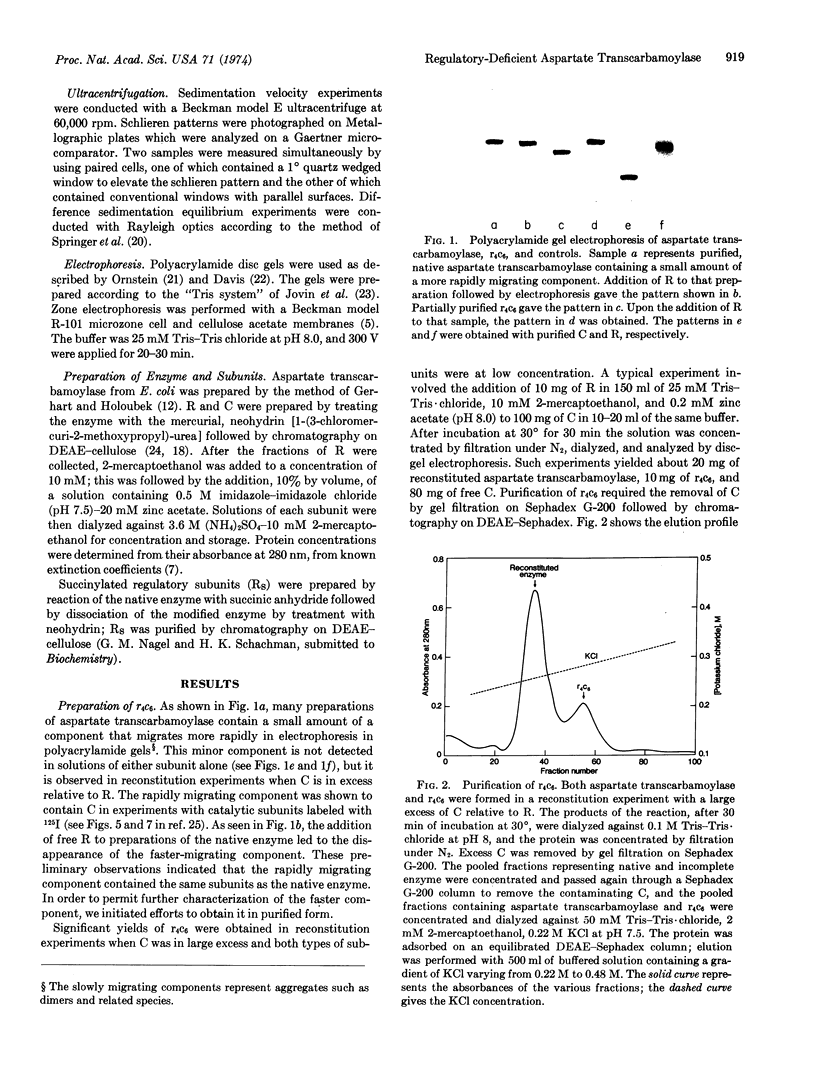
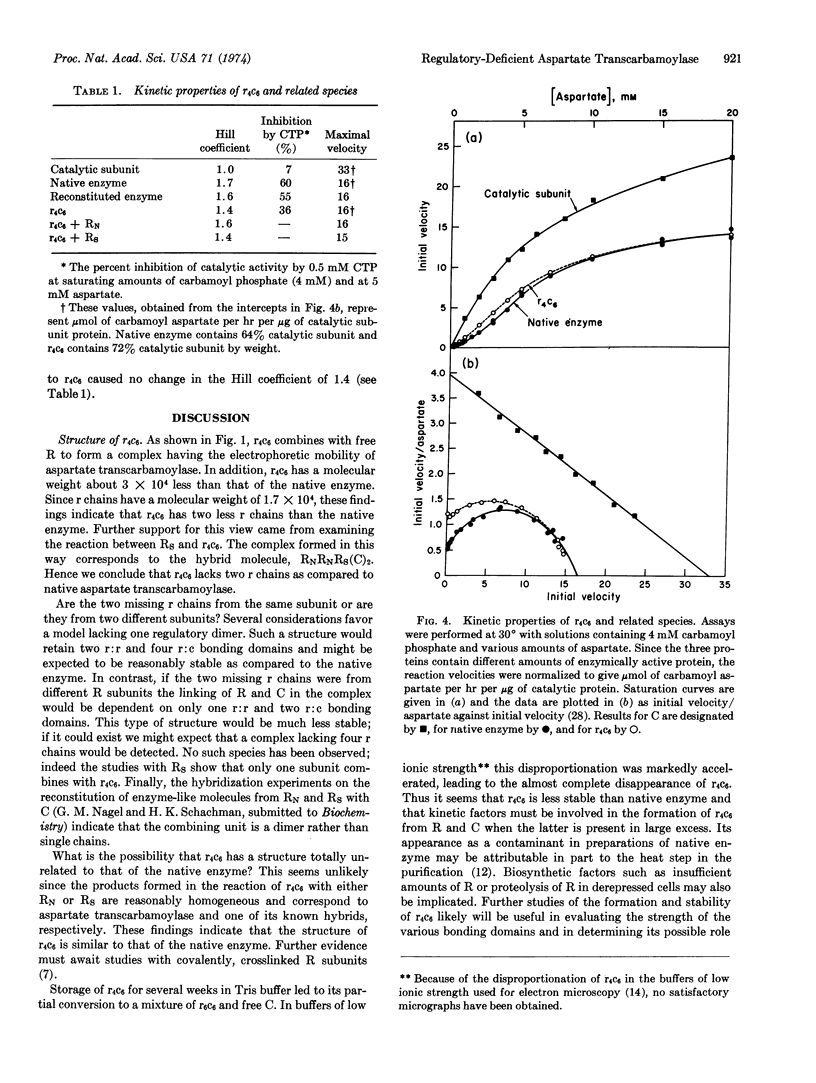
Reconstitution of aspartate transcarbamoylase (EC 2.1.3.2) from dilute solutions of the isolated regulatory and catalytic subunits, with the latter in large excess, led to the formation of appreciable amounts of a second, stable component in addition to the reconstituted enzyme. The purified component, designated r4c6, was found to have a molecular weight about 3 × 104 less than that of the native enzyme, and it combined with isolated regulatory subunit to form aspartate transcarbamoylase. It also combined with one succinylated regulatory subunit to form a hybrid species that was identified electrophoretically. These findings indicate that r4c6 differs from the native enzyme in that only two (rather than three) regulatory subunits participate in “crosslinking” the two catalytic trimers. The “incomplete” enzyme, r4c6, exhibits the characteristic sigmoidal saturation behavior and CTP inhibition of aspartate transcarbamoylase; however these allosteric effects are reduced in extent by about one-third in comparison to the native enzyme and free catalytic subunits. The complex, which may be an intermediate in the assembly and dissociation of the native enzyme, is useful in assessing the role of the various bonding domains responsible for the stability and regulatory properties of the native enzyme.
Keywords: allosteric enzymes, protein-protein interactions, subunit assembly
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cohlberg J. A., Pigiet V. P., Jr, Schachman H. K. Structure and arrangement of the regulatory subunits in aspartate transcarbamylase. Biochemistry. 1972 Aug 29;11(18):3396–3411. doi: 10.1021/bi00768a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS B. J. DISC ELECTROPHORESIS. II. METHOD AND APPLICATION TO HUMAN SERUM PROTEINS. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964 Dec 28;121:404–427. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1964.tb14213.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D. R., Warren S. G., Edwards B. F., McMurray C. H., Bethge P. H., Wiley D. C., Lipscomb W. N. Aqueous central cavity in aspartate transcarbamylase from Escherichia coli. Science. 1973 Feb 16;179(4074):683–685. doi: 10.1126/science.179.4074.683. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GERHART J. C., PARDEE A. B. The enzymology of control by feedback inhibition. J Biol Chem. 1962 Mar;237:891–896. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerhart J. C., Holoubek H. The purification of aspartate transcarbamylase of Escherichia coli and separation of its protein subunits. J Biol Chem. 1967 Jun 25;242(12):2886–2892. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerhart J. C., Schachman H. K. Distinct subunits for the regulation and catalytic activity of aspartate transcarbamylase. Biochemistry. 1965 Jun;4(6):1054–1062. doi: 10.1021/bi00882a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedrick J. L., Smith A. J. Size and charge isomer separation and estimation of molecular weights of proteins by disc gel electrophoresis. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1968 Jul;126(1):155–164. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(68)90569-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heyde E., Nagabhushanam A., Venkataraman S. Enzyme forms produced from aspartate transcarbamoylase by digestion with trypsin. Biochem J. 1973 Sep;135(1):125–132. doi: 10.1042/bj1350125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JOVIN T., CHRAMBACH A., NAUGHTON M. A. AN APPARATUS FOR PREPARATIVE TEMPERATURE-REGULATED POLYACRYLAMIDE GEL ELECTROPHORESIS. Anal Biochem. 1964 Nov;9:351–369. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(64)90192-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson G. R., Stark G. R. Aspartate transcarbamylase. A study of possible roles for the sulfhydryl group at the active site. J Biol Chem. 1973 Dec 10;248(23):8003–8014. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MONOD J., WYMAN J., CHANGEUX J. P. ON THE NATURE OF ALLOSTERIC TRANSITIONS: A PLAUSIBLE MODEL. J Mol Biol. 1965 May;12:88–118. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80285-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meighen E. A., Pigiet V., Schachman H. K. Hybridization of native and chemically modified enzymes. 3. The catalytic subunits of aspartate transcarbamylase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Jan;65(1):234–241. doi: 10.1073/pnas.65.1.234. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ORNSTEIN L. DISC ELECTROPHORESIS. I. BACKGROUND AND THEORY. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964 Dec 28;121:321–349. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1964.tb14207.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter R. W., Modebe M. O., Stark G. R. Aspartate transcarbamylase. Kinetic studies of the catalytic subunit. J Biol Chem. 1969 Apr 10;244(7):1846–1859. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards K. E., Williams R. C. Electron microscopy of aspartate transcarbamylase and its catalytic subunit. Biochemistry. 1972 Aug 29;11(18):3393–3395. doi: 10.1021/bi00768a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenbusch J. P., Weber K. Subunit structure of aspartate transcarbamylase from Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1971 Mar 25;246(6):1644–1657. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Syvanen J. M., Yang Y. R., Kirschiner M. W. Preparation of 125 I-Catalytic subunit of asparatate transcarbamylase and its use in studies of the regulatory subunit. J Biol Chem. 1973 Jun 10;248(11):3762–3768. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warren S. G., Edwards B. F., Evans D. R., Wiley D. C., Lipscomb W. N. Aspartate transcarbamoylase from Escherichia coli: electron density at 5.5 A resolution. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Apr;70(4):1117–1121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.4.1117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K. New structural model of E. coli aspartate transcarbamylase and the amino-acid sequence of the regulatory polypeptide chain. Nature. 1968 Jun 22;218(5147):1116–1119. doi: 10.1038/2181116a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiley D. C., Evans D. R., Warren S. G., McMurray C. H., Edwards B. F., Franks W. A., Lipscomb W. N. The 5.5 Angstrom resolution structure of the regulatory enzyme, asparate transcarbamylase. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1972;36:285–290. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1972.036.01.038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiley D. C., Lipscomb W. N. Crystallographic determination of symmetry of aspartate transcarbamylase. Nature. 1968 Jun 22;218(5147):1119–1121. doi: 10.1038/2181119a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]