Abstract
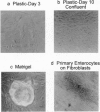
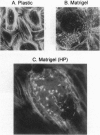
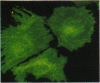
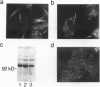
The differentiation of small intestinal epithelial cells may require stimulation by microenvironmental factors in vivo. In this study, the effects of mesenchymal and luminal elements in nonmalignant epithelia] cells isolated from the human fetus were studied in vitro. Enterocytes from the human fetus were cultured and microenvironmental factors were added in stages, each stage more closely approximating the microenvironment in vivo. Four stages were examined: epithelial cells derived on plastic from intestinal culture and grown as a cell clone, the same cells grown on connective tissue support, primary epithelial explants grown on fibroblasts with a laminin base, and primary epithelial explants grown on fibroblasts and laminin with n-butyrate added to the incubation medium. The epithelial cell clone dedifferentiated when grown on plastic; however, the cells expressed cytokeratins and villin as evidence of their epithelial cell origin. Human connective tissue matrix from Engelbreth-Holm-Swarm sarcoma cells (Matrigel) modulated their phenotype: alkaline phosphatase activity increased, microvilli developed on their apical surface, and the profile of insulin-like growth factor binding proteins resembled that secreted by differentiated enterocytes. Epithelial cells taken directly from the human fetus as primary cultures and grown as explants on fibroblasts and laminin expressed greater specific enzyme activities in brush border membrane fractions than the cell clone. These activities were enhanced by the luminal molecule sodium butyrate. Thus the sequential addition of connective tissue and luminal molecules to nonmalignant epithelia] cells in vitro induces a spectrum of changes in the epithelial cell phenotype toward full differentiation.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arpin M., Pringault E., Finidori J., Garcia A., Jeltsch J. M., Vandekerckhove J., Louvard D. Sequence of human villin: a large duplicated domain homologous with other actin-severing proteins and a unique small carboxy-terminal domain related to villin specificity. J Cell Biol. 1988 Nov;107(5):1759–1766. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.5.1759. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baliga B. S., Borowitz S. M., Barnard J. A. Effects of EGF and PMA on the growth and proliferation of IEC-6 cells. Biochem Int. 1989 Nov;19(5):1045–1056. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berschneider H. M., Powell D. W. Fibroblasts modulate intestinal secretory responses to inflammatory mediators. J Clin Invest. 1992 Feb;89(2):484–489. doi: 10.1172/JCI115610. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black B. L., Moog F. Alkaline phosphatase and maltase activity in the embryonic chick intestine in culture. Influence of thyroxine and hydrocortisone. Dev Biol. 1978 Sep;66(1):232–249. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(78)90287-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blay J., Brown K. D. Characterization of an epithelioid cell line derived from rat small intestine: demonstration of cytokeratin filaments. Cell Biol Int Rep. 1984 Jul;8(7):551–560. doi: 10.1016/0309-1651(84)90054-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blum J. L., Zeigler M. E., Wicha M. S. Regulation of rat mammary gene expression by extracellular matrix components. Exp Cell Res. 1987 Dec;173(2):322–340. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(87)90274-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouziges F., Simo P., Simon-Assmann P., Haffen K., Kedinger M. Altered deposition of basement-membrane molecules in co-cultures of colonic cancer cells and fibroblasts. Int J Cancer. 1991 Apr 22;48(1):101–108. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910480119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carroll K. M., Wong T. T., Drabik D. L., Chang E. B. Differentiation of rat small intestinal epithelial cells by extracellular matrix. Am J Physiol. 1988 Mar;254(3 Pt 1):G355–G360. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1988.254.3.G355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu S. H., Walker W. A. Growth factor signal transduction in human intestinal cells. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1991;310:107–112. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4615-3838-7_12. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahlqvist A. Assay of intestinal disaccharidases. Anal Biochem. 1968 Jan;22(1):99–107. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(68)90263-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eckmann L., Jung H. C., Schürer-Maly C., Panja A., Morzycka-Wroblewska E., Kagnoff M. F. Differential cytokine expression by human intestinal epithelial cell lines: regulated expression of interleukin 8. Gastroenterology. 1993 Dec;105(6):1689–1697. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(93)91064-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friederich E., Huet C., Arpin M., Louvard D. Villin induces microvilli growth and actin redistribution in transfected fibroblasts. Cell. 1989 Nov 3;59(3):461–475. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90030-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GAREN A., LEVINTHAL C. A fine-structure genetic and chemical study of the enzyme alkaline phosphatase of E. coli. I. Purification and characterization of alkaline phosphatase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1960 Mar 11;38:470–483. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(60)91282-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon J. I. Understanding gastrointestinal epithelial cell biology: lessons from mice with help from worms and flies. Gastroenterology. 1993 Aug;105(2):315–324. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(93)90703-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gum J. R., Kam W. K., Byrd J. C., Hicks J. W., Sleisenger M. H., Kim Y. S. Effects of sodium butyrate on human colonic adenocarcinoma cells. Induction of placental-like alkaline phosphatase. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jan 25;262(3):1092–1097. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henning S. J. Postnatal development: coordination of feeding, digestion, and metabolism. Am J Physiol. 1981 Sep;241(3):G199–G214. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1981.241.3.G199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hermiston M. L., Gordon J. I. Inflammatory bowel disease and adenomas in mice expressing a dominant negative N-cadherin. Science. 1995 Nov 17;270(5239):1203–1207. doi: 10.1126/science.270.5239.1203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hossenlopp P., Seurin D., Segovia B., Portolan G., Binoux M. Heterogeneity of insulin-like growth factor binding proteins between structure and affinity. 2. Forms released by human and rat liver in culture. Eur J Biochem. 1987 Dec 30;170(1-2):133–142. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1987.tb13677.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingber D. E., Madri J. A., Jamieson J. D. Basement membrane as a spatial organizer of polarized epithelia. Exogenous basement membrane reorients pancreatic epithelial tumor cells in vitro. Am J Pathol. 1986 Jan;122(1):129–139. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joshi S. S., Jackson J. D., Sharp J. G. Differentiation inducing effects of butyrate and DMSO on human intestinal tumor cell lines in culture. Cancer Detect Prev. 1985;8(1-2):237–245. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kedinger M., Simon-Assmann P., Bouziges F., Haffen K. Epithelial-mesenchymal interactions in intestinal epithelial differentiation. Scand J Gastroenterol Suppl. 1988;151:62–69. doi: 10.3109/00365528809095915. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessler M., Acuto O., Storelli C., Murer H., Müller M., Semenza G. A modified procedure for the rapid preparation of efficiently transporting vesicles from small intestinal brush border membranes. Their use in investigating some properties of D-glucose and choline transport systems. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Jan 4;506(1):136–154. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(78)90440-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kédinger M., Simon-Assmann P., Alexandre E., Haffen K. Importance of a fibroblastic support for in vitro differentiation of intestinal endodermal cells and for their response to glucocorticoids. Cell Differ. 1987 Mar;20(2-3):171–182. doi: 10.1016/0045-6039(87)90431-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee E. Y., Lee W. H., Kaetzel C. S., Parry G., Bissell M. J. Interaction of mouse mammary epithelial cells with collagen substrata: regulation of casein gene expression and secretion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Mar;82(5):1419–1423. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.5.1419. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Louvard D., Kedinger M., Hauri H. P. The differentiating intestinal epithelial cell: establishment and maintenance of functions through interactions between cellular structures. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1992;8:157–195. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.08.110192.001105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montesano R., Matsumoto K., Nakamura T., Orci L. Identification of a fibroblast-derived epithelial morphogen as hepatocyte growth factor. Cell. 1991 Nov 29;67(5):901–908. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90363-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neely E. K., Rosenfeld R. G. Insulin-like growth factors (IGFs) reduce IGF-binding protein-4 (IGFBP-4) concentration and stimulate IGFBP-3 independently of IGF receptors in human fibroblasts and epidermal cells. Endocrinology. 1992 Feb;130(2):985–993. doi: 10.1210/endo.130.2.1370799. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nitta T., Allegretta M., Okumura K., Sato K., Steinman L. Neoplastic and reactive human astrocytes express interleukin-8 gene. Neurosurg Rev. 1992;15(3):203–207. doi: 10.1007/BF00345934. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oguchi S., Walker W. A., Sanderson I. R. Insulin-like growth factor binding protein profile secreted by human intestinal epithelial cells varies with polarity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1993 Oct 29;196(2):789–793. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1993.2318. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oguchi S., Walker W. A., Sanderson I. R. Profile of IGF-binding proteins secreted by intestinal epithelial cells changes with differentiation. Am J Physiol. 1994 Nov;267(5 Pt 1):G843–G850. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1994.267.5.G843. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park J. H., McCusker R. H., Vanderhoof J. A., Mohammadpour H., Harty R. F., MacDonald R. G. Secretion of insulin-like growth factor II (IGF-II) and IGF-binding protein-2 by intestinal epithelial (IEC-6) cells: implications for autocrine growth regulation. Endocrinology. 1992 Sep;131(3):1359–1368. doi: 10.1210/endo.131.3.1380441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pringault E., Robine S., Louvard D. Structure of the human villin gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 1;88(23):10811–10815. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.23.10811. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quaroni A., Wands J., Trelstad R. L., Isselbacher K. J. Epithelioid cell cultures from rat small intestine. Characterization by morphologic and immunologic criteria. J Cell Biol. 1979 Feb;80(2):248–265. doi: 10.1083/jcb.80.2.248. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez-Boulan E., Nelson W. J. Morphogenesis of the polarized epithelial cell phenotype. Science. 1989 Aug 18;245(4919):718–725. doi: 10.1126/science.2672330. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanderson I. R. New approaches to the study of human pediatric disease. Acta Paediatr Jpn. 1994 Oct;36(5):572–578. doi: 10.1111/j.1442-200x.1994.tb03248.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santos O. F., Nigam S. K. HGF-induced tubulogenesis and branching of epithelial cells is modulated by extracellular matrix and TGF-beta. Dev Biol. 1993 Dec;160(2):293–302. doi: 10.1006/dbio.1993.1308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schroy P. C., Rustgi A. K., Ikonomu E., Liu X. P., Polito J., Andry C., O'Keane J. C. Growth and intestinal differentiation are independently regulated in HT29 colon cancer cells. J Cell Physiol. 1994 Oct;161(1):111–123. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041610114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simo P., Simon-Assmann P., Arnold C., Kedinger M. Mesenchyme-mediated effect of dexamethasone on laminin in cocultures of embryonic gut epithelial cells and mesenchyme-derived cells. J Cell Sci. 1992 Jan;101(Pt 1):161–171. doi: 10.1242/jcs.101.1.161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon-Assmann P., Duclos B., Orian-Rousseau V., Arnold C., Mathelin C., Engvall E., Kedinger M. Differential expression of laminin isoforms and alpha 6-beta 4 integrin subunits in the developing human and mouse intestine. Dev Dyn. 1994 Sep;201(1):71–85. doi: 10.1002/aja.1002010108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon-Assmann P., Kedinger M., De Arcangelis A., Rousseau V., Simo P. Extracellular matrix components in intestinal development. Experientia. 1995 Sep 29;51(9-10):883–900. doi: 10.1007/BF01921739. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tivey D. R., Shulman R. J. Effect of pancreatic secretions upon ileal disaccharidase activities of neonatal miniature pigs. Experientia. 1991 May 15;47(5):452–454. doi: 10.1007/BF01959941. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiser M. M., Sykes D. E., Killen P. D. Rat intestinal basement membrane synthesis. Epithelial versus nonepithelial contributions. Lab Invest. 1990 Mar;62(3):325–330. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zumkeller W. Relationship between insulin-like growth factor-I and -II and IGF-binding proteins in milk and the gastrointestinal tract: growth and development of the gut. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 1992 Nov;15(4):357–369. doi: 10.1097/00005176-199211000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]