Abstract
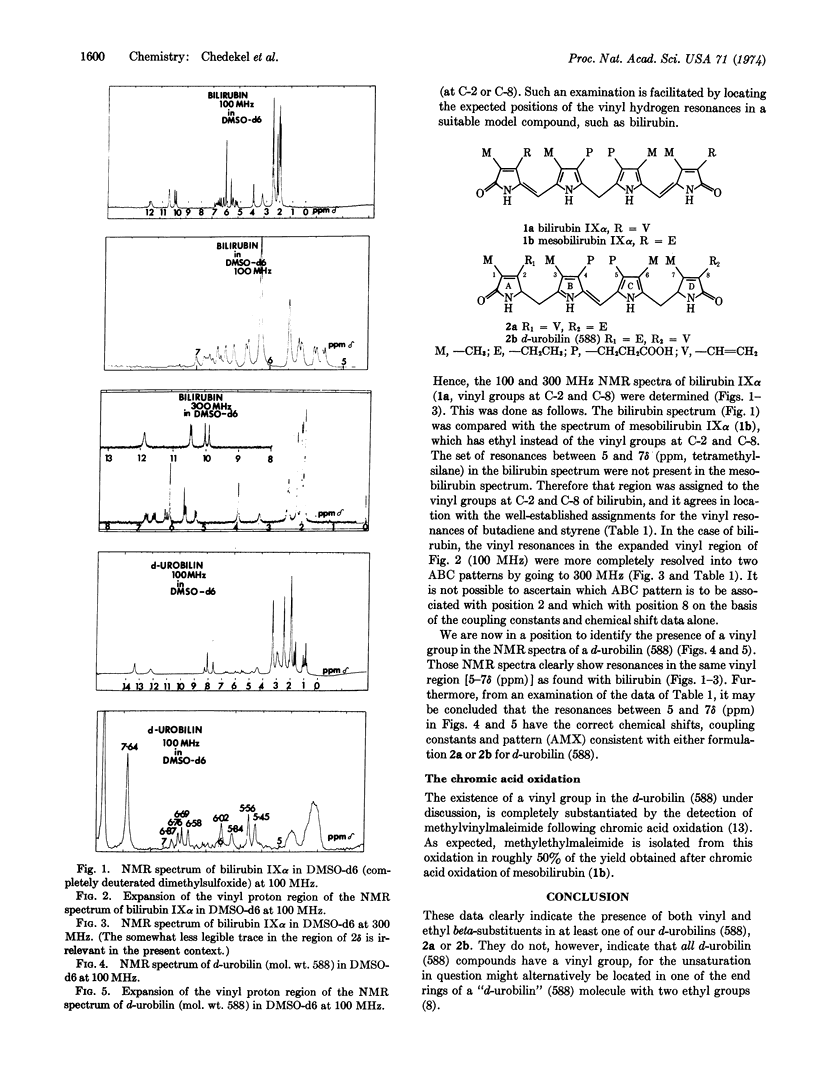
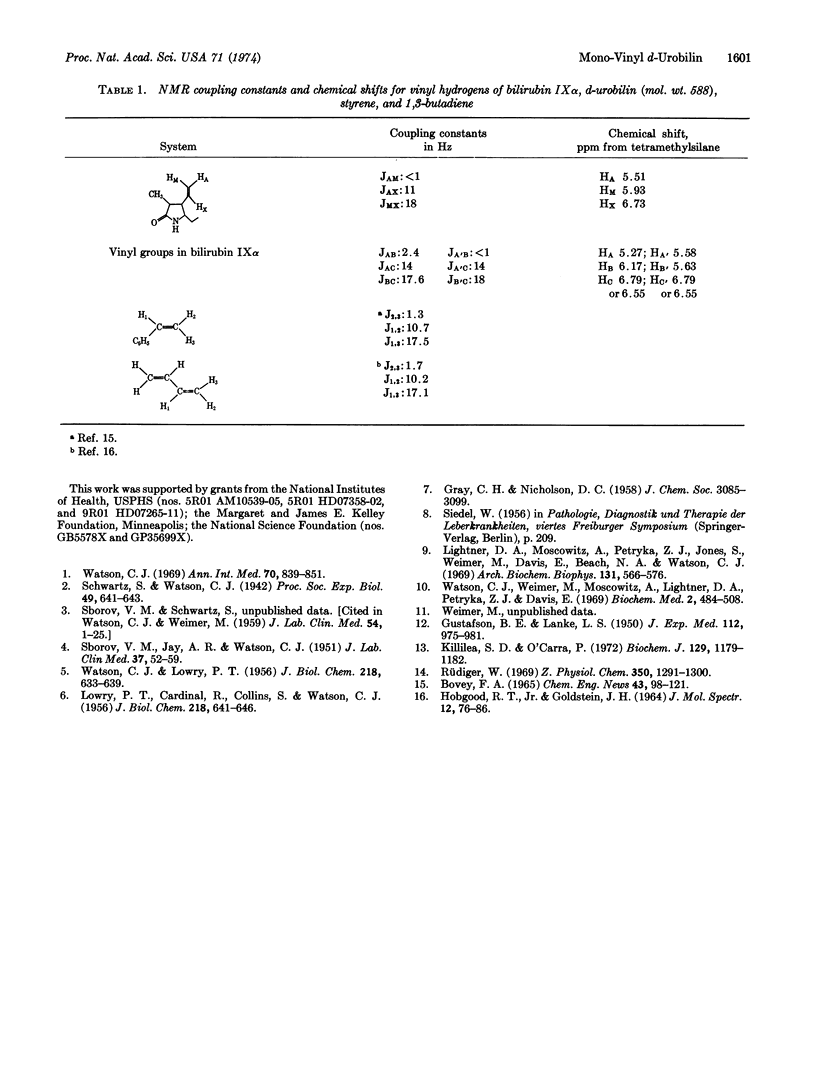
Chromic acid degradation of a d-urobilin, obtained after incubation of bilirubin in fecal bacterial cultures, gave methylvinylmaleimide and methylethylmaleimide. The d-urobilin, molecular weight 588, C33H40-N4O6, clearly showed the presence of both vinyl and ethyl resonances in the nuclear magnetic resonance spectrum. These results point unambiguously to a urobilin structure with one vinyl and one ethyl beta-substituent.
Keywords: d-urobilin 588, nuclear magnetic resonance, chromic acid oxidation
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- GUSTAFSSON B. E., LANKE L. S. Bilirubin and urobilins in germfree, ex-germfree, and conventional rats. J Exp Med. 1960 Dec 1;112:975–981. doi: 10.1084/jem.112.6.975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Killilea S. D., O'Carra P. Structure of d-urobilin. Biochem J. 1972 Oct;129(5):1179–1182. doi: 10.1042/bj1291179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY P. T., CARDINAL R., COLLINS S., WATSON C. J. The isolation of crystalline d-urobilinogen. J Biol Chem. 1956 Feb;218(2):641–646. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lightner D. A., Moscowitz A., Petryka Z. J., Jones S., Weimer M., Davis E., Beach N. A., Watson C. J. Mass spectrometry and ferric chloride oxidation applied to urobilinoid structures. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1969 May;131(2):566–576. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(69)90431-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rüdiger W. Chromsäure- und Chromatabbau con Gallengarbstoffen. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1969 Nov;350(11):1291–1300. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SBOROV V. M., JAY A. R., WATSON C. J. The effect of aureomycin on urobilinogen formation and the fecal flora. J Lab Clin Med. 1951 Jan;37(1):52–59. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WATSON C. J., LOWRY P. T. A further study of crystalline d-urobilin. J Biol Chem. 1956 Feb;218(2):633–639. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WATSON C. J., WEIMER M. Composition of the urobilin group in urine bile, and feces and the significance of variations in health and disease. J Lab Clin Med. 1959 Jul;54(1):1–25. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson C. J. Gold from dross: the first century of the urobilinoids. Ann Intern Med. 1969 Apr;70(4):839–851. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-70-4-839. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


