Abstract
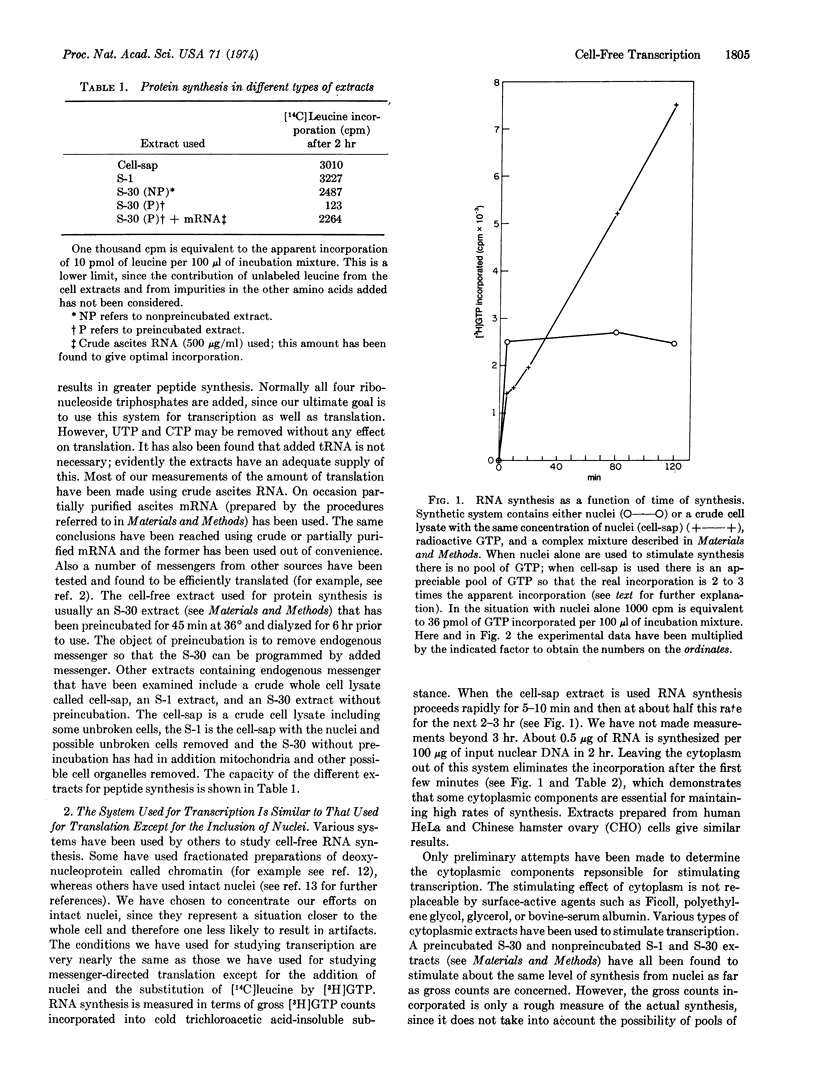
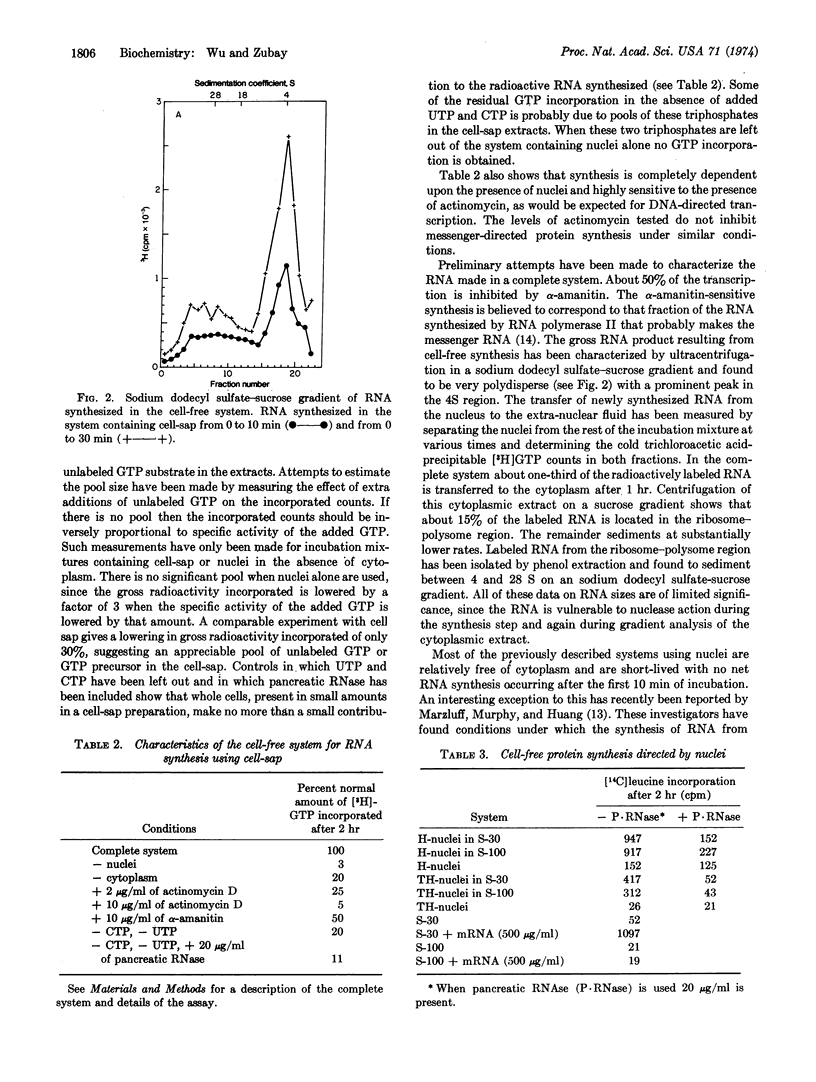
A cell-free system for nuclear-directed transcription has been developed that gives prolonged synthesis in the presence of cytoplasm. The nuclear and cytoplasmic components have been prepared from Krebs II ascites tumor cells for most experiments but further observations indicate that components prepared from other cell types may be used. After an initial 5- to 10-min period of relatively rapid RNA synthesis a linear rate ensues for 2-3 hr. In the absence of cytoplasm no net RNA synthesis occurs after the initial 10-min period. Experiments with α-amanitin suggest that about half of the cell-free synthesized RNA is made by RNA polymerase II, the enzyme believed to be responsible for messenger synthesis in vivo.
The conditions used for RNA synthesis were derived from conditions found to be optimal for protein synthesis that proceeds linearly for 2-3 hr. It has not yet been possible to demonstrate the synthesis of protein from cell-free synthesized RNA in this system. A major problem here is that isolated nuclei, even when carefully washed, contain a great deal of translatable RNA.
Keywords: transcription nuclei, RNA synthesis, protein synthesis
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aviv H., Boime I., Leder P. Protein synthesis directed by encephalomyocarditis virus RNA: properties of a transfer RNA-dependent system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Sep;68(9):2303–2307. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.9.2303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aviv H., Leder P. Purification of biologically active globin messenger RNA by chromatography on oligothymidylic acid-cellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1408–1412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Axel R., Cedar H., Felsenfeld G. Synthesis of globin ribonucleic acid from duck-reticulocyte chromatin in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Jul;70(7):2029–2032. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.7.2029. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bancroft F. C., Wu G. J., Zubay G. Cell-free synthesis of rat growth hormone. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Dec;70(12):3646–3649. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.12.3646. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLarco J., Guroff G. The binding of RNA to various celluloses. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Jan 23;50(2):486–492. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)90866-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindell T. J., Weinberg F., Morris P. W., Roeder R. G., Rutter W. J. Specific inhibition of nuclear RNA polymerase II by alpha-amanitin. Science. 1970 Oct 23;170(3956):447–449. doi: 10.1126/science.170.3956.447. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lockard R. E., Lingrel J. B. The synthesis of mouse hemoglobin beta-chains in a rabbit reticulocyte cell-free system programmed with mouse reticulocyte 9S RNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1969 Oct 8;37(2):204–212. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(69)90720-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marzluff W. F., Jr, Murphy E. C., Jr, Huang R. C. Transcription of ribonucleic acid in isolated mouse myeloma nuclei. Biochemistry. 1973 Aug 28;12(18):3440–3446. doi: 10.1021/bi00742a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schutz G., Beato M., Feigelson P. Isolation of eukaryotic messenger RNA on cellulose and its translation in vitro. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Nov 1;49(3):680–689. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90465-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zubay G. In vitro synthesis of protein in microbial systems. Annu Rev Genet. 1973;7:267–287. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.07.120173.001411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zylber E. A., Penman S. Products of RNA polymerases in HeLa cell nuclei. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Nov;68(11):2861–2865. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.11.2861. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


